Runqing Zhang
GEA: Generation-Enhanced Alignment for Text-to-Image Person Retrieval
Nov 13, 2025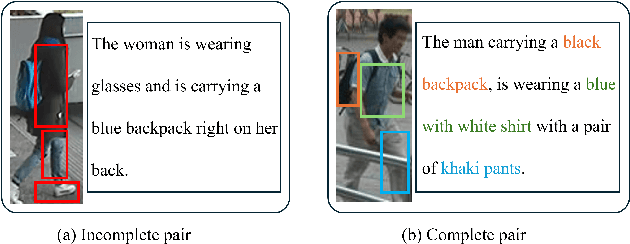
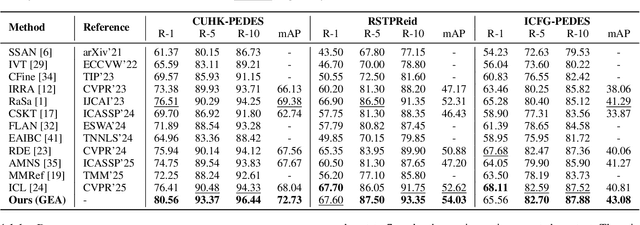
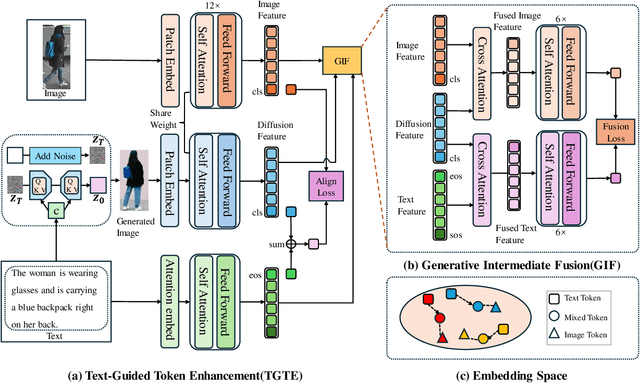
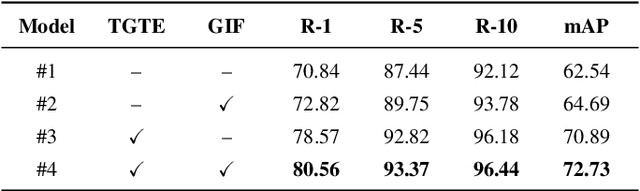
Abstract:Text-to-Image Person Retrieval (TIPR) aims to retrieve person images based on natural language descriptions. Although many TIPR methods have achieved promising results, sometimes textual queries cannot accurately and comprehensively reflect the content of the image, leading to poor cross-modal alignment and overfitting to limited datasets. Moreover, the inherent modality gap between text and image further amplifies these issues, making accurate cross-modal retrieval even more challenging. To address these limitations, we propose the Generation-Enhanced Alignment (GEA) from a generative perspective. GEA contains two parallel modules: (1) Text-Guided Token Enhancement (TGTE), which introduces diffusion-generated images as intermediate semantic representations to bridge the gap between text and visual patterns. These generated images enrich the semantic representation of text and facilitate cross-modal alignment. (2) Generative Intermediate Fusion (GIF), which combines cross-attention between generated images, original images, and text features to generate a unified representation optimized by triplet alignment loss. We conduct extensive experiments on three public TIPR datasets, CUHK-PEDES, RSTPReid, and ICFG-PEDES, to evaluate the performance of GEA. The results justify the effectiveness of our method. More implementation details and extended results are available at https://github.com/sugelamyd123/Sup-for-GEA.
AMNS: Attention-Weighted Selective Mask and Noise Label Suppression for Text-to-Image Person Retrieval
Sep 11, 2024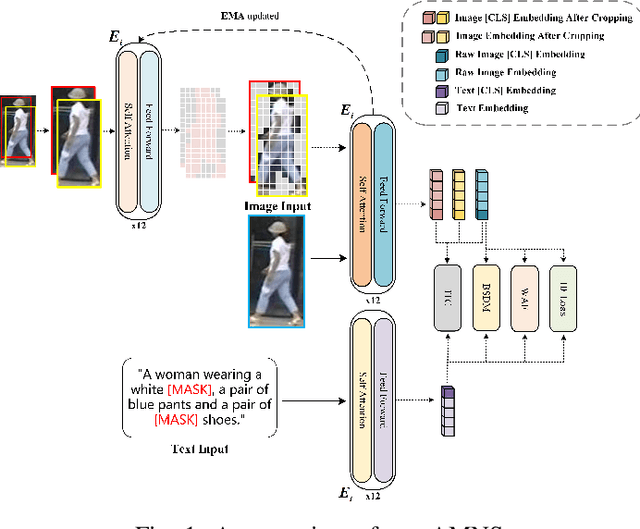
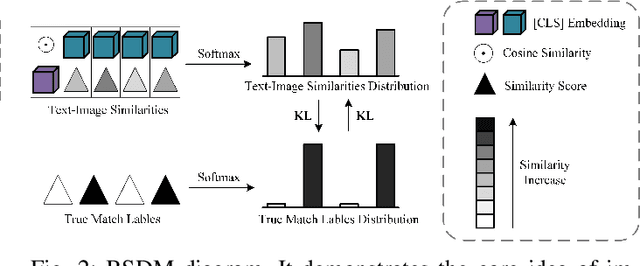
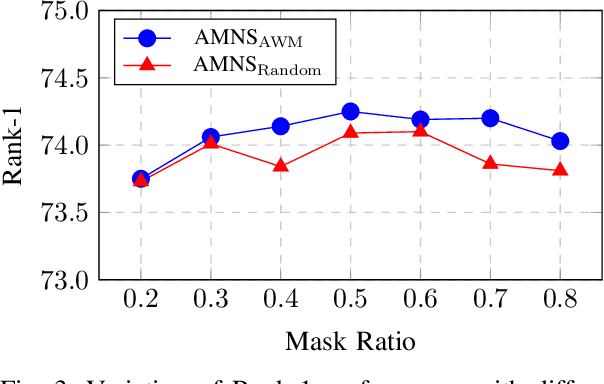
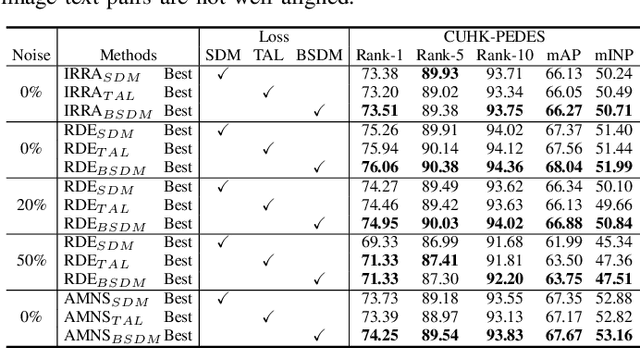
Abstract:Text-to-image person retrieval aims to retrieve images of person given textual descriptions, and most methods implicitly assume that the training image-text pairs are correctly aligned, but in practice, under-correlated and false-correlated problems arise for image-text pairs due to poor image quality and mislabeling. Meanwhile, the random masking augmentation strategy may incorrectly discard semantic content resulting in the problem of generating noisy pairings between image lexical elements and text descriptions. To solve these two problems, we propose a new noise label suppression method and alleviate the problem generated by random mask through an attention-weighted selective mask strategy. In the proposed noise label suppression method, the effect of noise labels is suppressed by preventing the model from being overconfident by considering the inverse KL scatter loss, which is combined with the weight adjustment focus loss to further improve the model's recognition ability on difficult samples. On the other hand, Attention-Weighted Selective Mask processes the raw image through the EMA version of the image encoder, retaining some of the tokens with strong semantic associations with the corresponding text descriptions in order to extract better features. Numerous experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach in terms of dealing with noisy problems. The code will be available soon at https://github.com/RunQing715/AMNS.git.
EAANet: Efficient Attention Augmented Convolutional Networks
Jun 03, 2022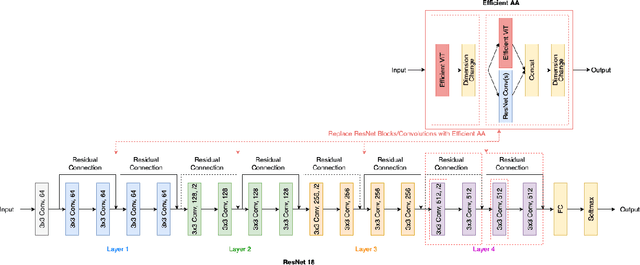
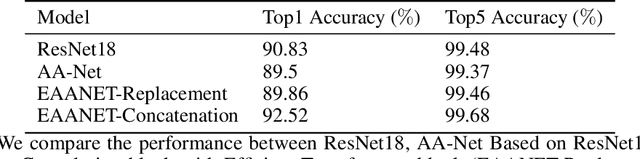
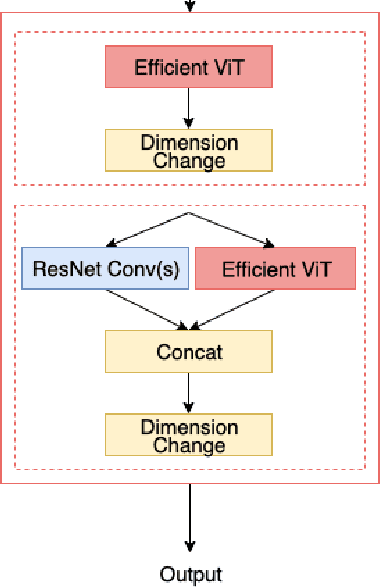
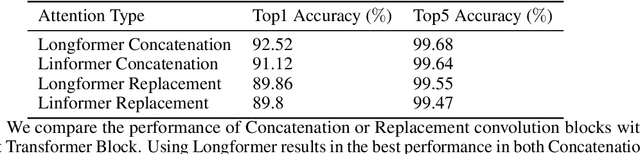
Abstract:Humans can effectively find salient regions in complex scenes. Self-attention mechanisms were introduced into Computer Vision (CV) to achieve this. Attention Augmented Convolutional Network (AANet) is a mixture of convolution and self-attention, which increases the accuracy of a typical ResNet. However, The complexity of self-attention is O(n2) in terms of computation and memory usage with respect to the number of input tokens. In this project, we propose EAANet: Efficient Attention Augmented Convolutional Networks, which incorporates efficient self-attention mechanisms in a convolution and self-attention hybrid architecture to reduce the model's memory footprint. Our best model show performance improvement over AA-Net and ResNet18. We also explore different methods to augment Convolutional Network with self-attention mechanisms and show the difficulty of training those methods compared to ResNet. Finally, we show that augmenting efficient self-attention mechanisms with ResNet scales better with input size than normal self-attention mechanisms. Therefore, our EAANet is more capable of working with high-resolution images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge