Ruineng Li
TokenMotion: Decoupled Motion Control via Token Disentanglement for Human-centric Video Generation
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Human-centric motion control in video generation remains a critical challenge, particularly when jointly controlling camera movements and human poses in scenarios like the iconic Grammy Glambot moment. While recent video diffusion models have made significant progress, existing approaches struggle with limited motion representations and inadequate integration of camera and human motion controls. In this work, we present TokenMotion, the first DiT-based video diffusion framework that enables fine-grained control over camera motion, human motion, and their joint interaction. We represent camera trajectories and human poses as spatio-temporal tokens to enable local control granularity. Our approach introduces a unified modeling framework utilizing a decouple-and-fuse strategy, bridged by a human-aware dynamic mask that effectively handles the spatially-and-temporally varying nature of combined motion signals. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate TokenMotion's effectiveness across both text-to-video and image-to-video paradigms, consistently outperforming current state-of-the-art methods in human-centric motion control tasks. Our work represents a significant advancement in controllable video generation, with particular relevance for creative production applications.
Replacing Language Model for Style Transfer
Nov 14, 2022


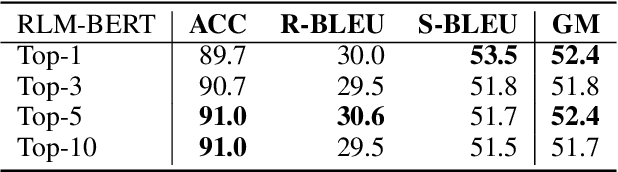
Abstract:We introduce replacing language model (RLM), a sequence-to-sequence language modeling framework for text style transfer. Our method autoregressively replaces each token in the original sentence with a text span in the target style. In contrast, the new span is generated via a non-autoregressive masked language model. The RLM generation scheme gathers the flexibility of autoregressive models and the accuracy of non-autoregressive models, which bridges the gap between sentence-level and word-level style transfer methods. To further control the style of generated sentences, we conduct a style-content disentanglement on the hidden representations of RLM. Empirical results on real-world text style transfer tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of RLM compared with other baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge