Ruilin Tong
Model Inversion with Layer-Specific Modeling and Alignment for Data-Free Continual Learning
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Continual learning (CL) aims to incrementally train a model on a sequence of tasks while retaining performance on prior ones. However, storing and replaying data is often infeasible due to privacy or security constraints and impractical for arbitrary pre-trained models. Data-free CL seeks to update models without access to previous data. Beyond regularization, we employ model inversion to synthesize data from the trained model, enabling replay without storing samples. Yet, model inversion in predictive models faces two challenges: (1) generating inputs solely from compressed output labels causes drift between synthetic and real data, and replaying such data can erode prior knowledge; (2) inversion is computationally expensive since each step backpropagates through the full model. These issues are amplified in large pre-trained models such as CLIP. To improve efficiency, we propose Per-layer Model Inversion (PMI), inspired by faster convergence in single-layer optimization. PMI provides strong initialization for full-model inversion, substantially reducing iterations. To mitigate feature shift, we model class-wise features via Gaussian distributions and contrastive model, ensuring alignment between synthetic and real features. Combining PMI and feature modeling, our approach enables continual learning of new classes by generating pseudo-images from semantic-aware projected features, achieving strong effectiveness and compatibility across multiple CL settings.
Growing Neural Network with Shared Parameter
Jan 17, 2022Abstract:We propose a general method for growing neural network with shared parameter by matching trained network to new input. By leveraging Hoeffding's inequality, we provide a theoretical base for improving performance by adding subnetwork to existing network. With the theoretical base of adding new subnetwork, we implement a matching method to apply trained subnetwork of existing network to new input. Our method has shown the ability to improve performance with higher parameter efficiency. It can also be applied to trans-task case and realize transfer learning by changing the combination of subnetworks without training on new task.
The HUAWEI Speaker Diarisation System for the VoxCeleb Speaker Diarisation Challenge
Oct 23, 2020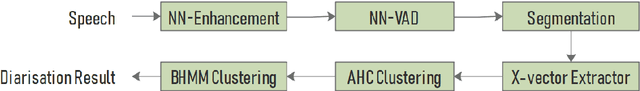
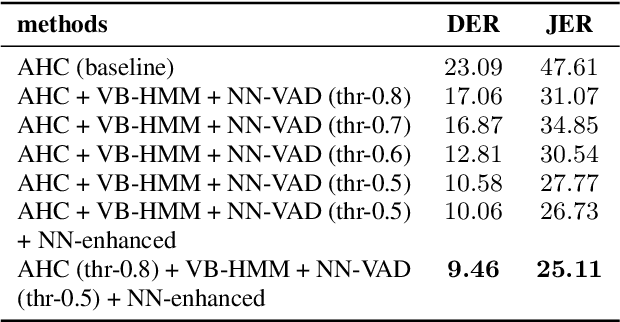


Abstract:This paper describes system setup of our submission to speaker diarisation track (Track 4) of VoxCeleb Speaker Recognition Challenge 2020. Our diarisation system consists of a well-trained neural network based speech enhancement model as pre-processing front-end of input speech signals. We replace conventional energy-based voice activity detection (VAD) with a neural network based VAD. The neural network based VAD provides more accurate annotation of speech segments containing only background music, noise, and other interference, which is crucial to diarisation performance. We apply agglomerative hierarchical clustering (AHC) of x-vectors and variational Bayesian hidden Markov model (VB-HMM) based iterative clustering for speaker clustering. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed system achieves substantial improvements over the baseline system, yielding diarisation error rate (DER) of 10.45%, and Jacard error rate (JER) of 22.46% on the evaluation set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge