Ruchit Agrawal
A comprehensive survey of contemporary Arabic sentiment analysis: Methods, Challenges, and Future Directions
Feb 06, 2025



Abstract:Sentiment Analysis, a popular subtask of Natural Language Processing, employs computational methods to extract sentiment, opinions, and other subjective aspects from linguistic data. Given its crucial role in understanding human sentiment, research in sentiment analysis has witnessed significant growth in the recent years. However, the majority of approaches are aimed at the English language, and research towards Arabic sentiment analysis remains relatively unexplored. This paper presents a comprehensive and contemporary survey of Arabic Sentiment Analysis, identifies the challenges and limitations of existing literature in this field and presents avenues for future research. We present a systematic review of Arabic sentiment analysis methods, focusing specifically on research utilizing deep learning. We then situate Arabic Sentiment Analysis within the broader context, highlighting research gaps in Arabic sentiment analysis as compared to general sentiment analysis. Finally, we outline the main challenges and promising future directions for research in Arabic sentiment analysis.
MMSD-Net: Towards Multi-modal Stuttering Detection
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Stuttering is a common speech impediment that is caused by irregular disruptions in speech production, affecting over 70 million people across the world. Standard automatic speech processing tools do not take speech ailments into account and are thereby not able to generate meaningful results when presented with stuttered speech as input. The automatic detection of stuttering is an integral step towards building efficient, context-aware speech processing systems. While previous approaches explore both statistical and neural approaches for stuttering detection, all of these methods are uni-modal in nature. This paper presents MMSD-Net, the first multi-modal neural framework for stuttering detection. Experiments and results demonstrate that incorporating the visual signal significantly aids stuttering detection, and our model yields an improvement of 2-17% in the F1-score over existing state-of-the-art uni-modal approaches.
Towards Context-Aware Neural Performance-Score Synchronisation
May 31, 2022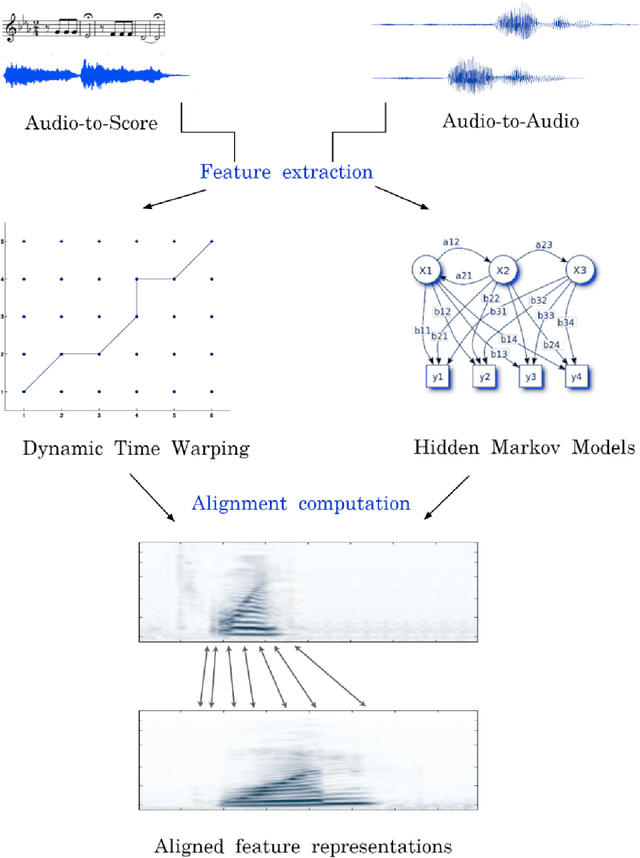
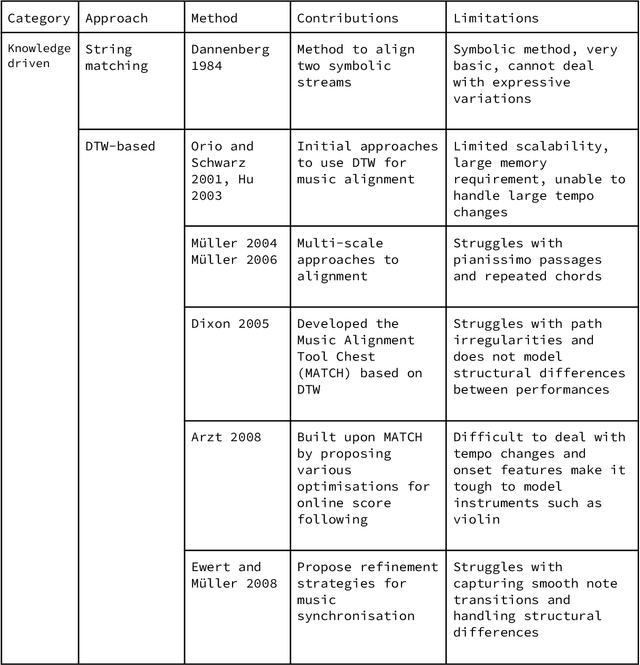
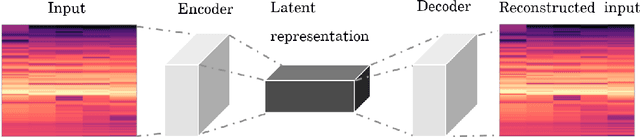

Abstract:Music can be represented in multiple forms, such as in the audio form as a recording of a performance, in the symbolic form as a computer readable score, or in the image form as a scan of the sheet music. Music synchronisation provides a way to navigate among multiple representations of music in a unified manner by generating an accurate mapping between them, lending itself applicable to a myriad of domains like music education, performance analysis, automatic accompaniment and music editing. Traditional synchronisation methods compute alignment using knowledge-driven and stochastic approaches, typically employing handcrafted features. These methods are often unable to generalise well to different instruments, acoustic environments and recording conditions, and normally assume complete structural agreement between the performances and the scores. This PhD furthers the development of performance-score synchronisation research by proposing data-driven, context-aware alignment approaches, on three fronts: Firstly, I replace the handcrafted features by employing a metric learning based approach that is adaptable to different acoustic settings and performs well in data-scarce conditions. Secondly, I address the handling of structural differences between the performances and scores, which is a common limitation of standard alignment methods. Finally, I eschew the reliance on both feature engineering and dynamic programming, and propose a completely data-driven synchronisation method that computes alignments using a neural framework, whilst also being robust to structural differences between the performances and scores.
A Convolutional-Attentional Neural Framework for Structure-Aware Performance-Score Synchronization
Apr 19, 2022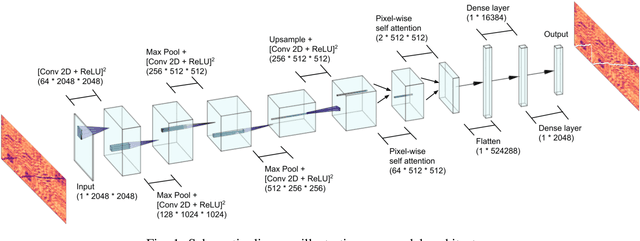

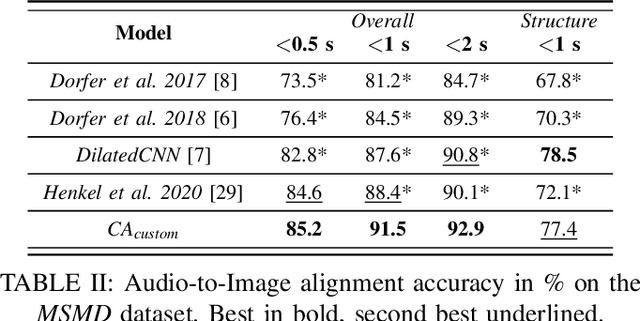
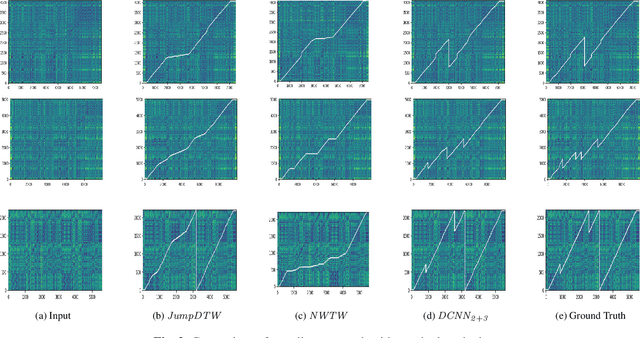
Abstract:Performance-score synchronization is an integral task in signal processing, which entails generating an accurate mapping between an audio recording of a performance and the corresponding musical score. Traditional synchronization methods compute alignment using knowledge-driven and stochastic approaches, and are typically unable to generalize well to different domains and modalities. We present a novel data-driven method for structure-aware performance-score synchronization. We propose a convolutional-attentional architecture trained with a custom loss based on time-series divergence. We conduct experiments for the audio-to-MIDI and audio-to-image alignment tasks pertained to different score modalities. We validate the effectiveness of our method via ablation studies and comparisons with state-of-the-art alignment approaches. We demonstrate that our approach outperforms previous synchronization methods for a variety of test settings across score modalities and acoustic conditions. Our method is also robust to structural differences between the performance and score sequences, which is a common limitation of standard alignment approaches.
Structure-Aware Audio-to-Score Alignment using Progressively Dilated Convolutional Neural Networks
Feb 14, 2021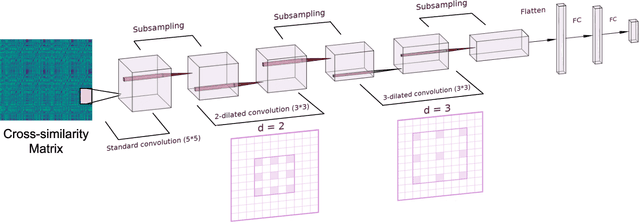
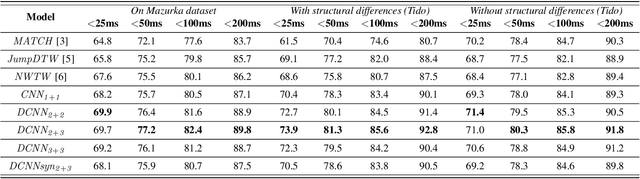
Abstract:The identification of structural differences between a music performance and the score is a challenging yet integral step of audio-to-score alignment, an important subtask of music information retrieval. We present a novel method to detect such differences between the score and performance for a given piece of music using progressively dilated convolutional neural networks. Our method incorporates varying dilation rates at different layers to capture both short-term and long-term context, and can be employed successfully in the presence of limited annotated data. We conduct experiments on audio recordings of real performances that differ structurally from the score, and our results demonstrate that our models outperform standard methods for structure-aware audio-to-score alignment.
Learning Frame Similarity using Siamese networks for Audio-to-Score Alignment
Nov 15, 2020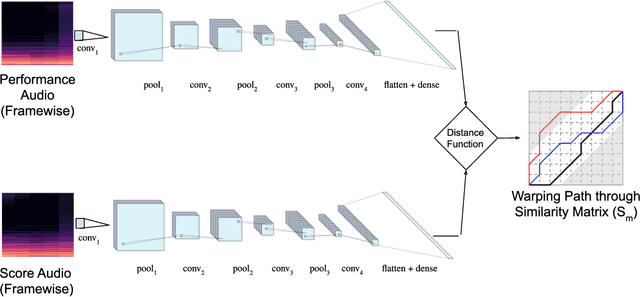
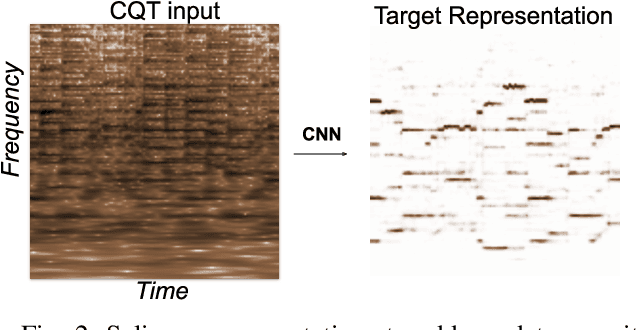
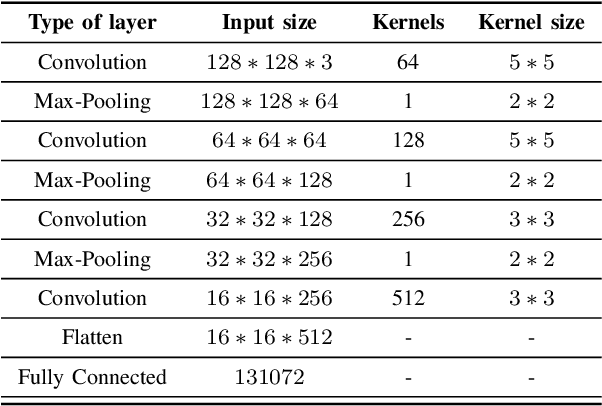
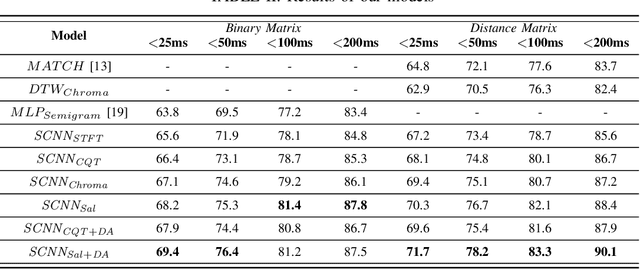
Abstract:Audio-to-score alignment aims at generating an accurate mapping between a performance audio and the score of a given piece. Standard alignment methods are based on Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) and employ handcrafted features, which cannot be adapted to different acoustic conditions. We propose a method to overcome this limitation using learned frame similarity for audio-to-score alignment. We focus on offline audio-to-score alignment of piano music. Experiments on music data from different acoustic conditions demonstrate that our method achieves higher alignment accuracy than a standard DTW-based method that uses handcrafted features, and generates robust alignments whilst being adaptable to different domains at the same time.
A Hybrid Approach to Audio-to-Score Alignment
Jul 28, 2020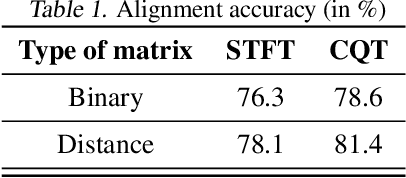
Abstract:Audio-to-score alignment aims at generating an accurate mapping between a performance audio and the score of a given piece. Standard alignment methods are based on Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) and employ handcrafted features. We explore the usage of neural networks as a preprocessing step for DTW-based automatic alignment methods. Experiments on music data from different acoustic conditions demonstrate that this method generates robust alignments whilst being adaptable at the same time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge