Rubel Biswas
State of the Art: Face Recognition
Aug 26, 2021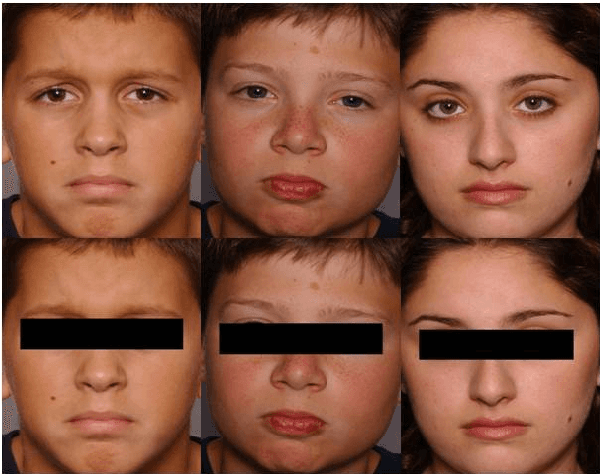
Abstract:Working with Child Sexual Exploitation Material (CSEM) in forensic applications might be benefited from the progress in automatic face recognition. However, discriminative parts of a face in CSEM, i.e., mostly the eyes, could be often occluded to difficult the victim's identification. Most of the face recognition approaches cannot deal with such kind of occlusions, resulting in inaccurate face recognition results. This document presents a short review face recognition methods for images with natural and eye occlude faces. The purpose is to select the best baseline approach for solving automatic face recognition of occluded faces.
State of the Art: Image Hashing
Aug 26, 2021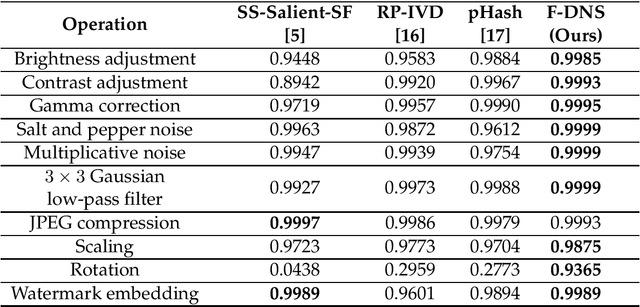
Abstract:Perceptual image hashing methods are often applied in various objectives, such as image retrieval, finding duplicate or near-duplicate images, and finding similar images from large-scale image content. The main challenge in image hashing techniques is robust feature extraction, which generates the same or similar hashes in images that are visually identical. In this article, we present a short review of the state-of-the-art traditional perceptual hashing and deep learning-based perceptual hashing methods, identifying the best approaches.
Perceptual Hashing applied to Tor domains recognition
May 21, 2020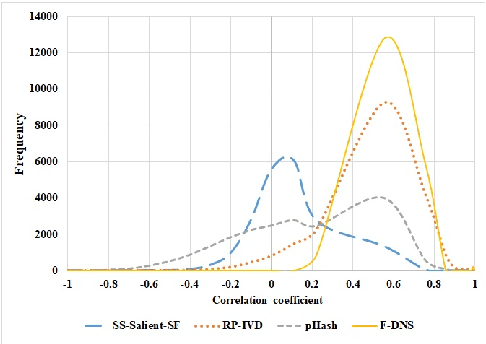
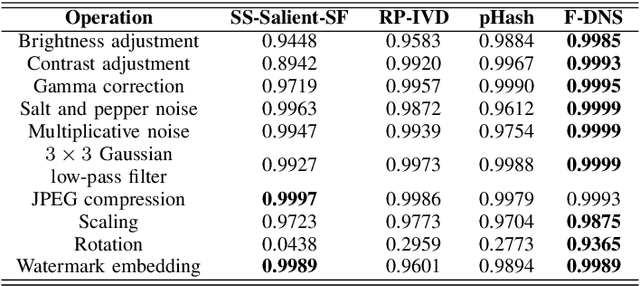
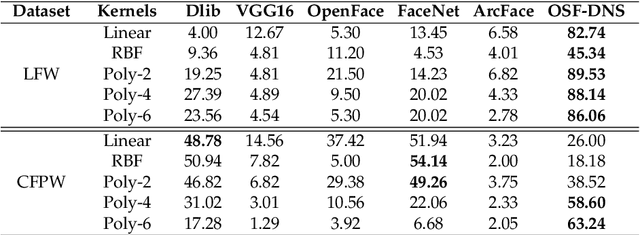
Abstract:The Tor darknet hosts different types of illegal content, which are monitored by cybersecurity agencies. However, manually classifying Tor content can be slow and error-prone. To support this task, we introduce Frequency-Dominant Neighborhood Structure (F-DNS), a new perceptual hashing method for automatically classifying domains by their screenshots. First, we evaluated F-DNS using images subject to various content preserving operations. We compared them with their original images, achieving better correlation coefficients than other state-of-the-art methods, especially in the case of rotation. Then, we applied F-DNS to categorize Tor domains using the Darknet Usage Service Images-2K (DUSI-2K), a dataset with screenshots of active Tor service domains. Finally, we measured the performance of F-DNS against an image classification approach and a state-of-the-art hashing method. Our proposal obtained 98.75% accuracy in Tor images, surpassing all other methods compared.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge