Roy F. Riascos
Leveraging Spatial Information in Radiology Reports for Ischemic Stroke Phenotyping
Oct 10, 2020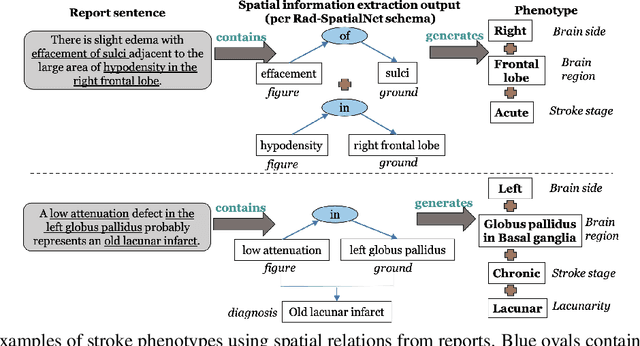
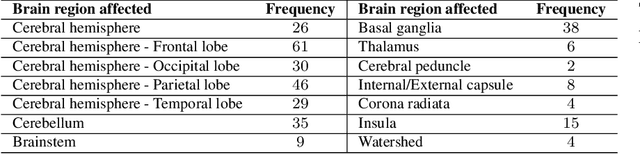
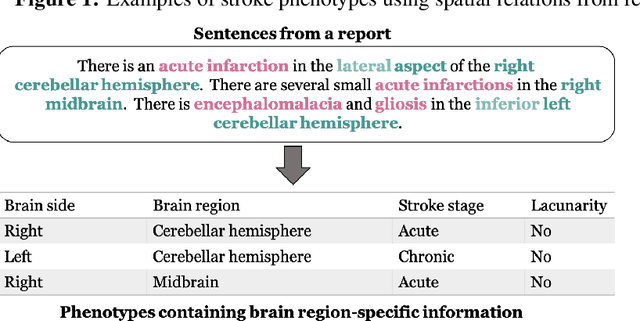
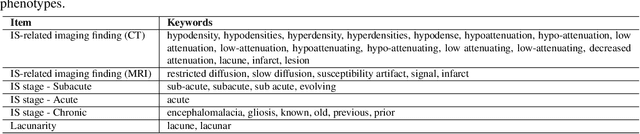
Abstract:Classifying fine-grained ischemic stroke phenotypes relies on identifying important clinical information. Radiology reports provide relevant information with context to determine such phenotype information. We focus on stroke phenotypes with location-specific information: brain region affected, laterality, stroke stage, and lacunarity. We use an existing fine-grained spatial information extraction system--Rad-SpatialNet--to identify clinically important information and apply simple domain rules on the extracted information to classify phenotypes. The performance of our proposed approach is promising (recall of 89.62% for classifying brain region and 74.11% for classifying brain region, side, and stroke stage together). Our work demonstrates that an information extraction system based on a fine-grained schema can be utilized to determine complex phenotypes with the inclusion of simple domain rules. These phenotypes have the potential to facilitate stroke research focusing on post-stroke outcome and treatment planning based on the stroke location.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge