Rose Catherine
Explainable Entity-based Recommendations with Knowledge Graphs
Jul 12, 2017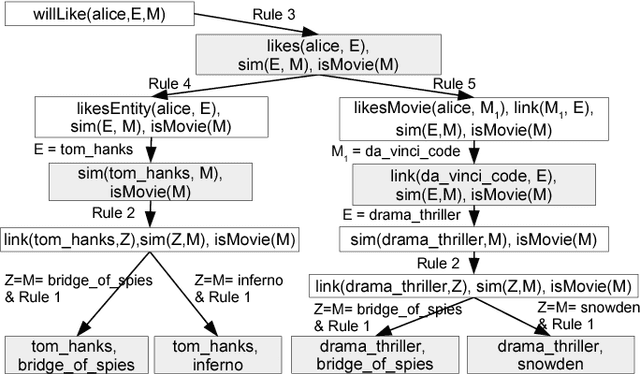
Abstract:Explainable recommendation is an important task. Many methods have been proposed which generate explanations from the content and reviews written for items. When review text is unavailable, generating explanations is still a hard problem. In this paper, we illustrate how explanations can be generated in such a scenario by leveraging external knowledge in the form of knowledge graphs. Our method jointly ranks items and knowledge graph entities using a Personalized PageRank procedure to produce recommendations together with their explanations.
TransNets: Learning to Transform for Recommendation
Jun 30, 2017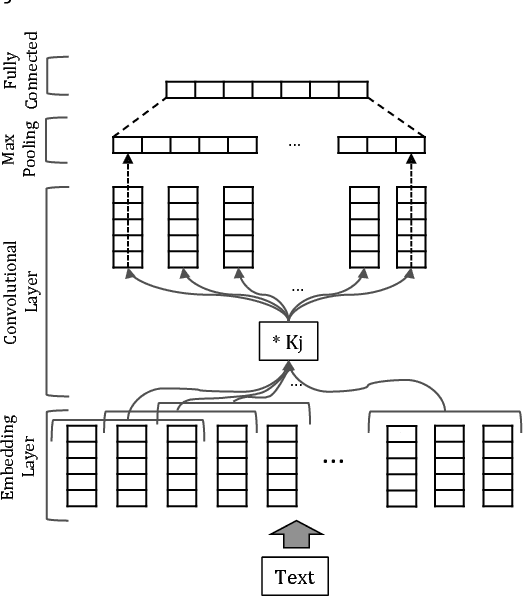
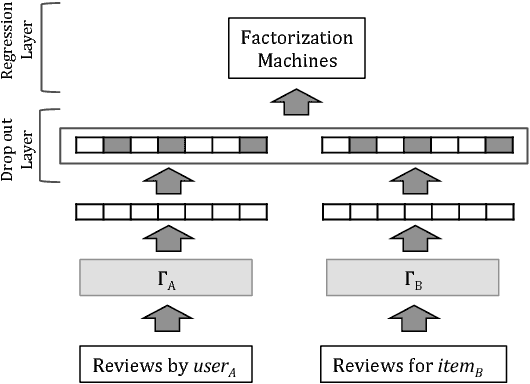
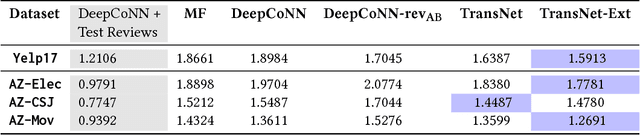
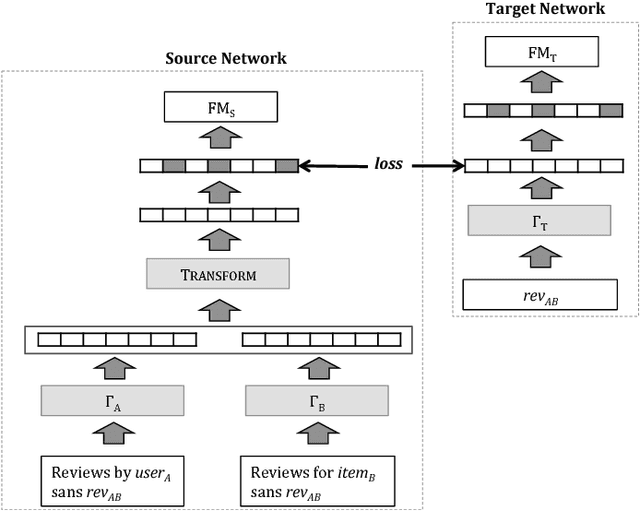
Abstract:Recently, deep learning methods have been shown to improve the performance of recommender systems over traditional methods, especially when review text is available. For example, a recent model, DeepCoNN, uses neural nets to learn one latent representation for the text of all reviews written by a target user, and a second latent representation for the text of all reviews for a target item, and then combines these latent representations to obtain state-of-the-art performance on recommendation tasks. We show that (unsurprisingly) much of the predictive value of review text comes from reviews of the target user for the target item. We then introduce a way in which this information can be used in recommendation, even when the target user's review for the target item is not available. Our model, called TransNets, extends the DeepCoNN model by introducing an additional latent layer representing the target user-target item pair. We then regularize this layer, at training time, to be similar to another latent representation of the target user's review of the target item. We show that TransNets and extensions of it improve substantially over the previous state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge