Rong Song
Dual-track Music Generation using Deep Learning
May 09, 2020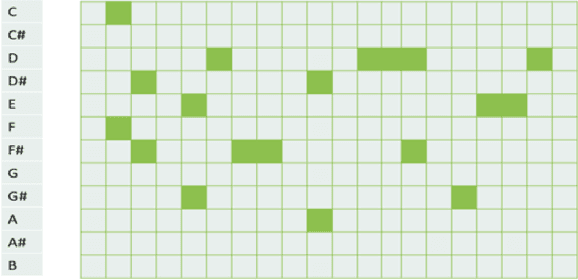
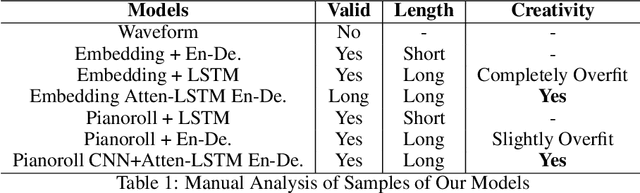

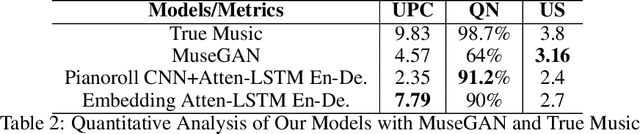
Abstract:Music generation is always interesting in a sense that there is no formalized recipe. In this work, we propose a novel dual-track architecture for generating classical piano music, which is able to model the inter-dependency of left-hand and right-hand piano music. Particularly, we experimented with a lot of different models of neural network as well as different representations of music, and the results show that our proposed model outperforms all other tested methods. Besides, we deployed some special policies for model training and generation, which contributed to the model performance remarkably. Finally, under two evaluation methods, we compared our models with the MuseGAN project and true music.
Efficient Multivariate Bandit Algorithm with Path Planning
Sep 06, 2019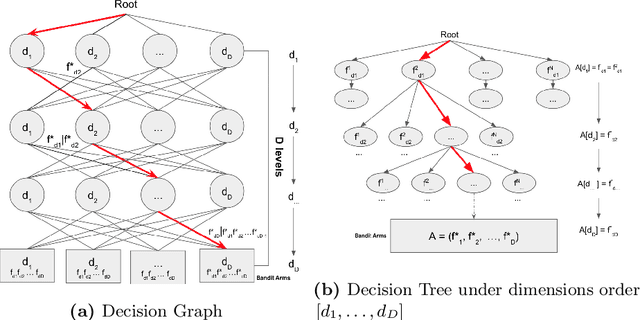
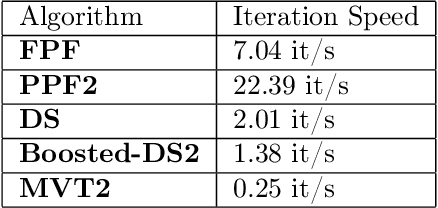
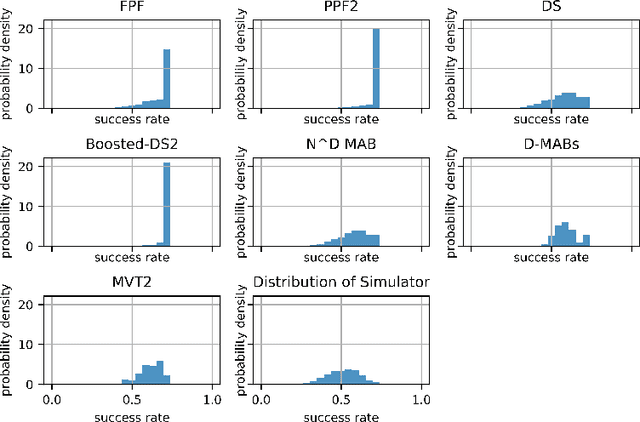
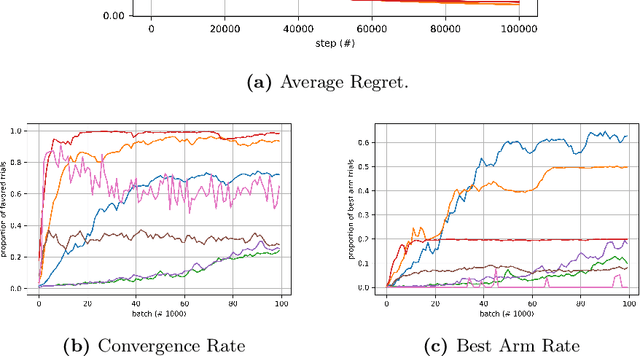
Abstract:In this paper, we solve the arms exponential exploding issue in multivariate Multi-Armed Bandit (Multivariate-MAB) problem when the arm dimension hierarchy is considered. We propose a framework called path planning (TS-PP) which utilizes decision graph/trees to model arm reward success rate with m-way dimension interaction, and adopts Thompson sampling (TS) for heuristic search of arm selection. Naturally, it is quite straightforward to combat the curse of dimensionality using a serial processes that operates sequentially by focusing on one dimension per each process. For our best acknowledge, we are the first to solve Multivariate-MAB problem using graph path planning strategy and deploying alike Monte-Carlo tree search ideas. Our proposed method utilizing tree models has advantages comparing with traditional models such as general linear regression. Simulation studies validate our claim by achieving faster convergence speed, better efficient optimal arm allocation and lower cumulative regret.
Improved Super-Resolution Convolution Neural Network for Large Images
Jul 26, 2019
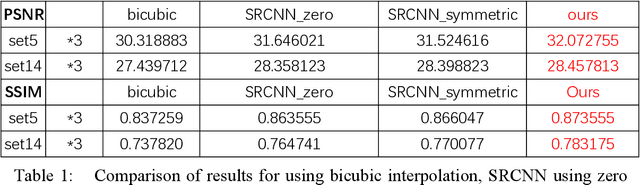
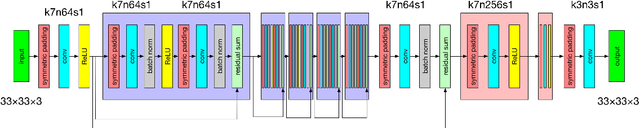
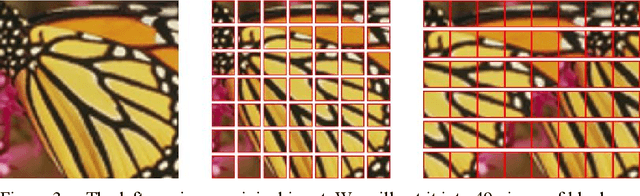
Abstract:Single image super-resolution (SISR) is a very popular topic nowadays, which has both research value and practical value. In daily life, we crop a large image into sub-images to do super-resolution and then merge them together. Although convolution neural network performs very well in the research field, if we use it to do super-resolution, we can easily observe cutting lines from merged pictures. To address these problems, in this paper, we propose a refined architecture of SRCNN with 'Symmetric padding', 'Random learning' and 'Residual learning'. Moreover, we have done a lot of experiments to prove our model performs best among a lot of the state-of-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge