Romain Xu-Darme
LSL
CaBRNet, an open-source library for developing and evaluating Case-Based Reasoning Models
Sep 25, 2024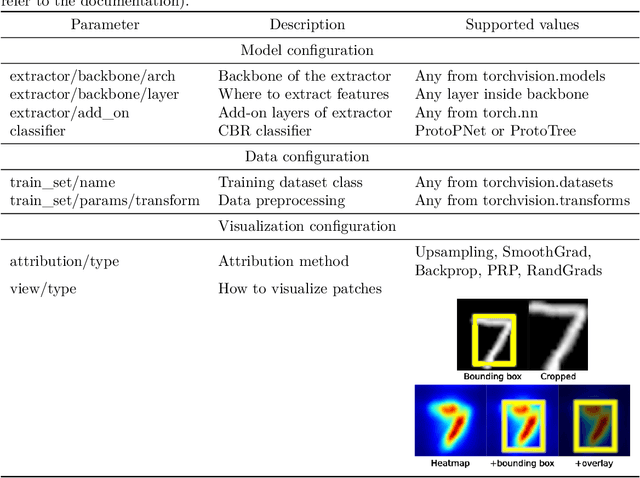
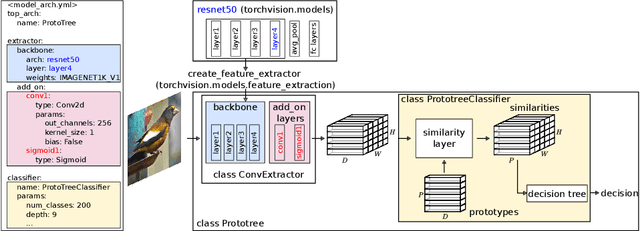
Abstract:In the field of explainable AI, a vibrant effort is dedicated to the design of self-explainable models, as a more principled alternative to post-hoc methods that attempt to explain the decisions after a model opaquely makes them. However, this productive line of research suffers from common downsides: lack of reproducibility, unfeasible comparison, diverging standards. In this paper, we propose CaBRNet, an open-source, modular, backward-compatible framework for Case-Based Reasoning Networks: https://github.com/aiser-team/cabrnet.
PARTICUL: Part Identification with Confidence measure using Unsupervised Learning
Jun 27, 2022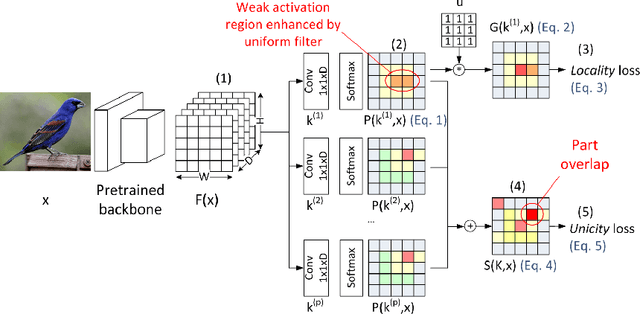



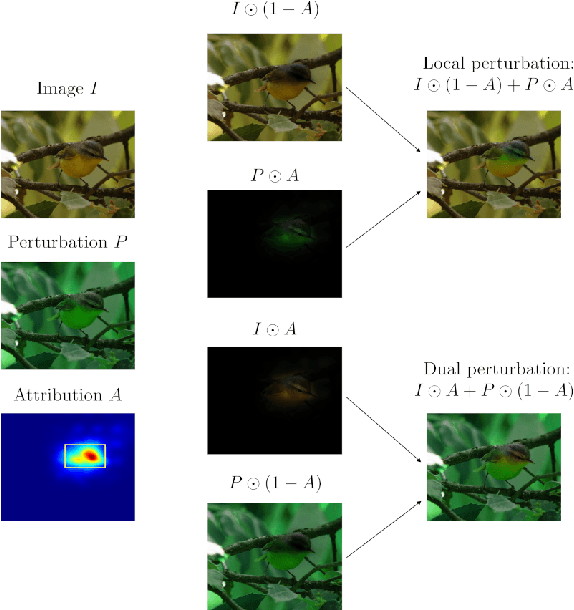
Abstract:In this paper, we present PARTICUL, a novel algorithm for unsupervised learning of part detectors from datasets used in fine-grained recognition. It exploits the macro-similarities of all images in the training set in order to mine for recurring patterns in the feature space of a pre-trained convolutional neural network. We propose new objective functions enforcing the locality and unicity of the detected parts. Additionally, we embed our detectors with a confidence measure based on correlation scores, allowing the system to estimate the visibility of each part. We apply our method on two public fine-grained datasets (Caltech-UCSD Bird 200 and Stanford Cars) and show that our detectors can consistently highlight parts of the object while providing a good measure of the confidence in their prediction. We also demonstrate that these detectors can be directly used to build part-based fine-grained classifiers that provide a good compromise between the transparency of prototype-based approaches and the performance of non-interpretable methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge