Ritwik Kulkarni
Taming the Tail: Leveraging Asymmetric Loss and Pade Approximation to Overcome Medical Image Long-Tailed Class Imbalance
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Long-tailed problems in healthcare emerge from data imbalance due to variability in the prevalence and representation of different medical conditions, warranting the requirement of precise and dependable classification methods. Traditional loss functions such as cross-entropy and binary cross-entropy are often inadequate due to their inability to address the imbalances between the classes with high representation and the classes with low representation found in medical image datasets. We introduce a novel polynomial loss function based on Pade approximation, designed specifically to overcome the challenges associated with long-tailed classification. This approach incorporates asymmetric sampling techniques to better classify under-represented classes. We conducted extensive evaluations on three publicly available medical datasets and a proprietary medical dataset. Our implementation of the proposed loss function is open-sourced in the public repository:https://github.com/ipankhi/ALPA.
Towards automatic detection of wildlife trade using machine vision models
May 23, 2022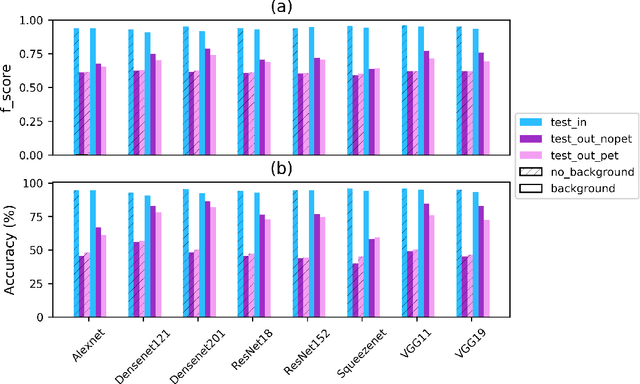
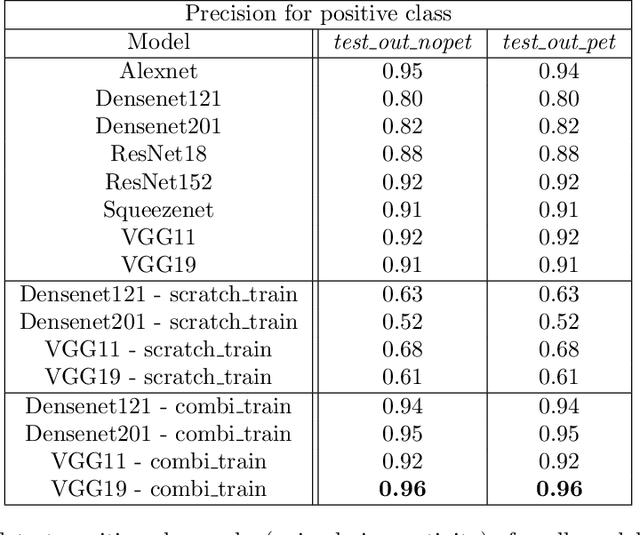
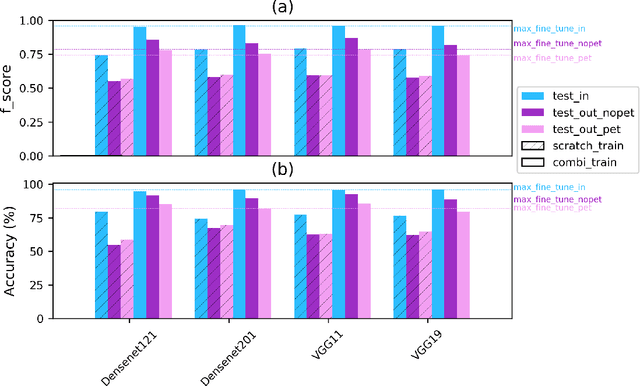
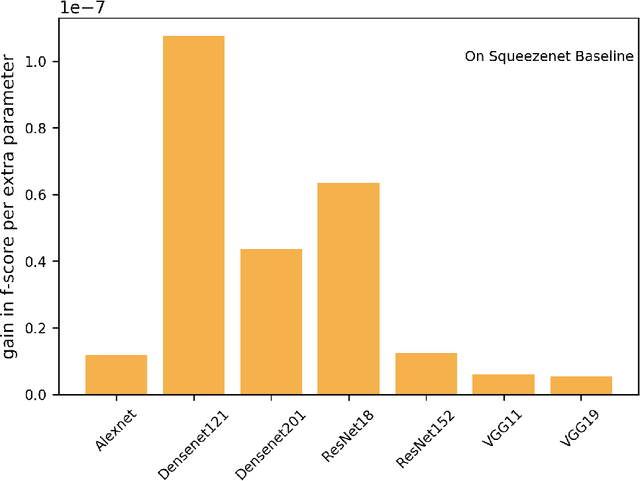
Abstract:Unsustainable trade in wildlife is one of the major threats affecting the global biodiversity crisis. An important part of the trade now occurs on the internet, especially on digital marketplaces and social media. Automated methods to identify trade posts are needed as resources for conservation are limited. Here, we developed machine vision models based on Deep Neural Networks with the aim to automatically identify images of exotic pet animals for sale. A new training dataset representing exotic pet animals advertised for sale on the web was generated for this purpose. We trained 24 neural-net models spanning a combination of five different architectures, three methods of training and two types of datasets. Specifically, model generalisation improved after setting a portion of the training images to represent negative features. Models were evaluated on both within and out of distribution data to test wider model applicability. The top performing models achieved an f-score of over 0.95 on within distribution evaluation and between 0.75 to 0.87 on the two out of distribution datasets. Notably, feature visualisation indicated that models performed well in detecting the surrounding context (e.g. a cage) in which an animal was located, therefore helping to automatically detect images of animals in non-natural environments. The proposed methods can help investigate the online wildlife trade, but can also be adapted to study other types of people-nature interactions from digital platforms. Future studies can use these findings to build robust machine learning models and new data collection pipelines for more taxonomic groups.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge