Rikab Gambhir
Moments of Clarity: Streamlining Latent Spaces in Machine Learning using Moment Pooling
Mar 13, 2024Abstract:Many machine learning applications involve learning a latent representation of data, which is often high-dimensional and difficult to directly interpret. In this work, we propose "Moment Pooling", a natural extension of Deep Sets networks which drastically decrease latent space dimensionality of these networks while maintaining or even improving performance. Moment Pooling generalizes the summation in Deep Sets to arbitrary multivariate moments, which enables the model to achieve a much higher effective latent dimensionality for a fixed latent dimension. We demonstrate Moment Pooling on the collider physics task of quark/gluon jet classification by extending Energy Flow Networks (EFNs) to Moment EFNs. We find that Moment EFNs with latent dimensions as small as 1 perform similarly to ordinary EFNs with higher latent dimension. This small latent dimension allows for the internal representation to be directly visualized and interpreted, which in turn enables the learned internal jet representation to be extracted in closed form.
Bias and Priors in Machine Learning Calibrations for High Energy Physics
May 10, 2022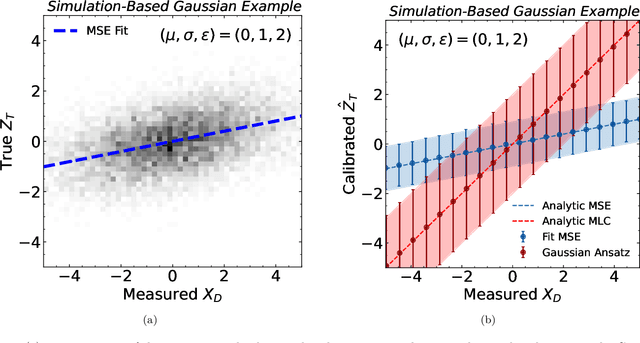
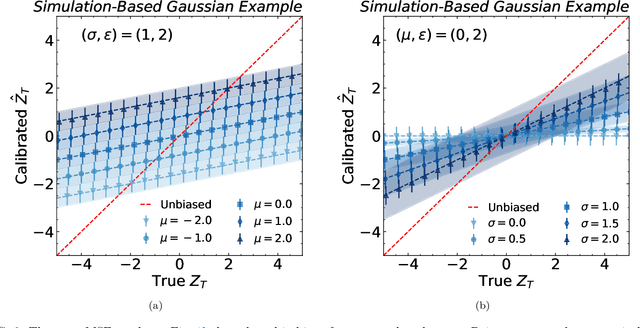
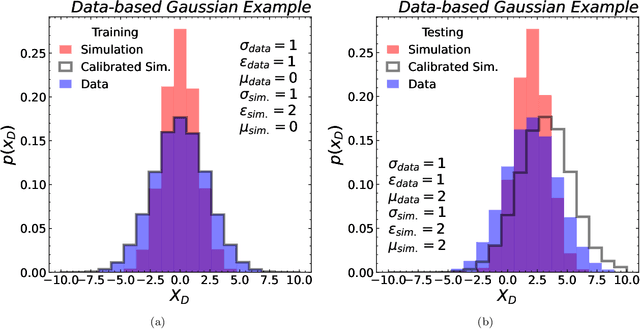
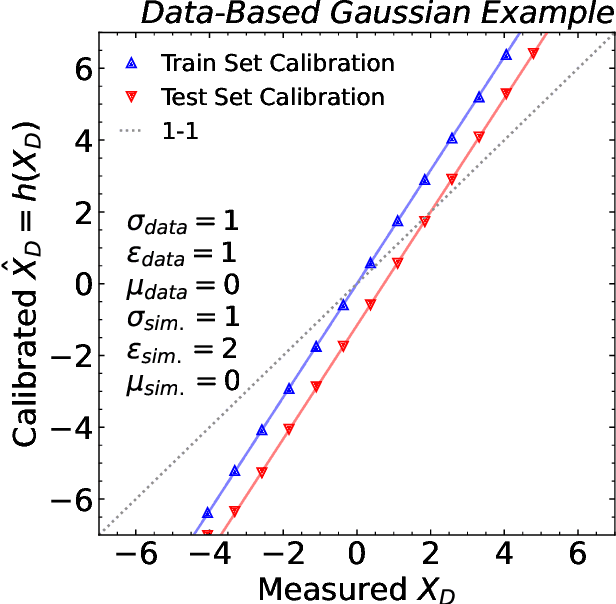
Abstract:Machine learning offers an exciting opportunity to improve the calibration of nearly all reconstructed objects in high-energy physics detectors. However, machine learning approaches often depend on the spectra of examples used during training, an issue known as prior dependence. This is an undesirable property of a calibration, which needs to be applicable in a variety of environments. The purpose of this paper is to explicitly highlight the prior dependence of some machine learning-based calibration strategies. We demonstrate how some recent proposals for both simulation-based and data-based calibrations inherit properties of the sample used for training, which can result in biases for downstream analyses. In the case of simulation-based calibration, we argue that our recently proposed Gaussian Ansatz approach can avoid some of the pitfalls of prior dependence, whereas prior-independent data-based calibration remains an open problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge