Richard Segal
Monte Carlo Tree Search for Recipe Generation using GPT-2
Jan 10, 2024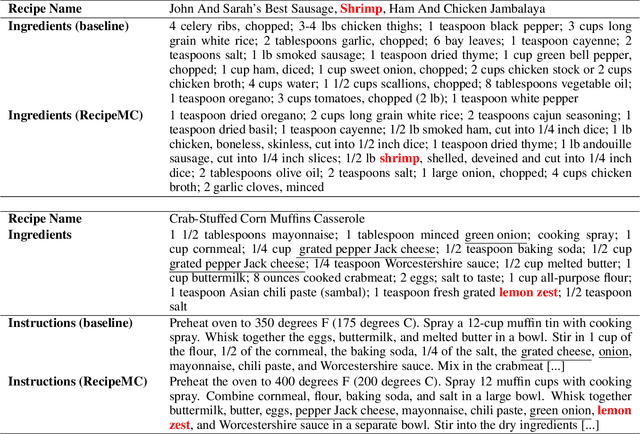
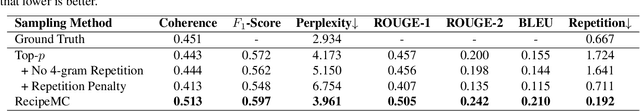


Abstract:Automatic food recipe generation methods provide a creative tool for chefs to explore and to create new, and interesting culinary delights. Given the recent success of large language models (LLMs), they have the potential to create new recipes that can meet individual preferences, dietary constraints, and adapt to what is in your refrigerator. Existing research on using LLMs to generate recipes has shown that LLMs can be finetuned to generate realistic-sounding recipes. However, on close examination, these generated recipes often fail to meet basic requirements like including chicken as an ingredient in chicken dishes. In this paper, we propose RecipeMC, a text generation method using GPT-2 that relies on Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS). RecipeMC allows us to define reward functions to put soft constraints on text generation and thus improve the credibility of the generated recipes. Our results show that human evaluators prefer recipes generated with RecipeMC more often than recipes generated with other baseline methods when compared with real recipes.
Bayesian Inference in Monte-Carlo Tree Search
Mar 15, 2012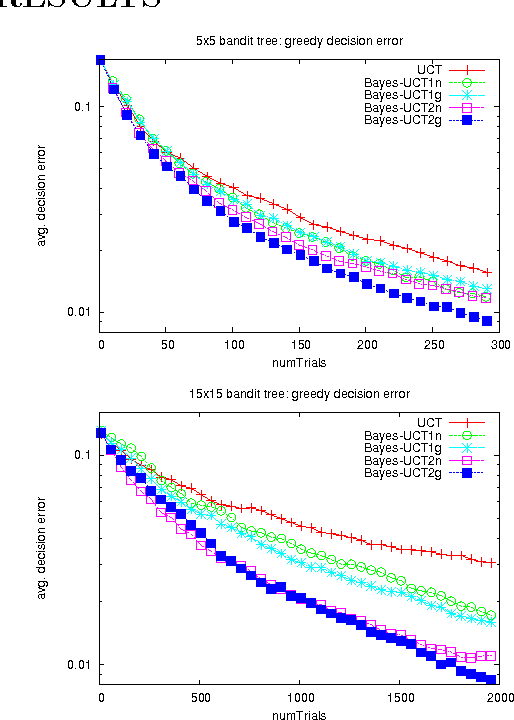
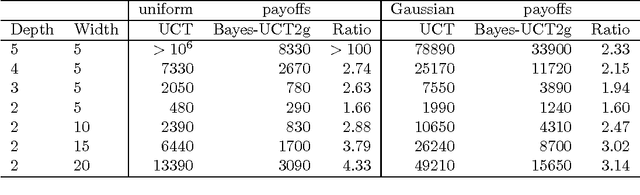
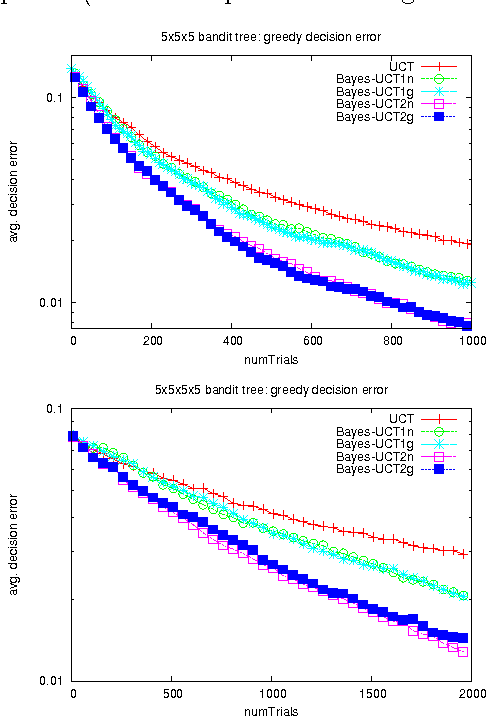
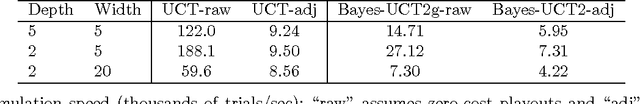
Abstract:Monte-Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) methods are drawing great interest after yielding breakthrough results in computer Go. This paper proposes a Bayesian approach to MCTS that is inspired by distributionfree approaches such as UCT [13], yet significantly differs in important respects. The Bayesian framework allows potentially much more accurate (Bayes-optimal) estimation of node values and node uncertainties from a limited number of simulation trials. We further propose propagating inference in the tree via fast analytic Gaussian approximation methods: this can make the overhead of Bayesian inference manageable in domains such as Go, while preserving high accuracy of expected-value estimates. We find substantial empirical outperformance of UCT in an idealized bandit-tree test environment, where we can obtain valuable insights by comparing with known ground truth. Additionally we rigorously prove on-policy and off-policy convergence of the proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge