Riccardo Campi
Visual-TCAV: Concept-based Attribution and Saliency Maps for Post-hoc Explainability in Image Classification
Nov 08, 2024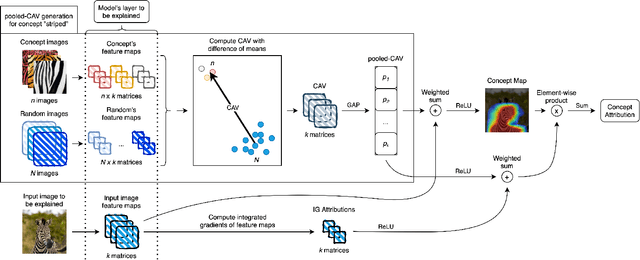

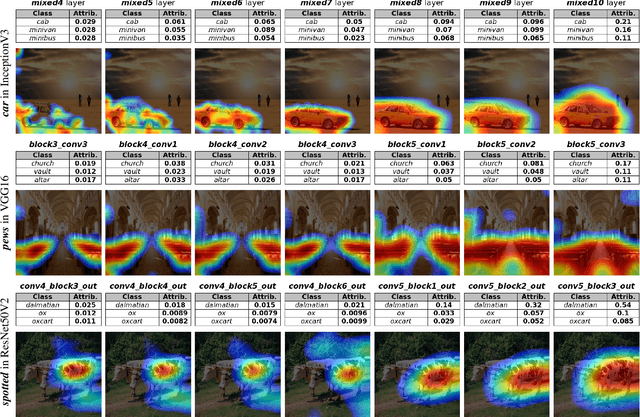
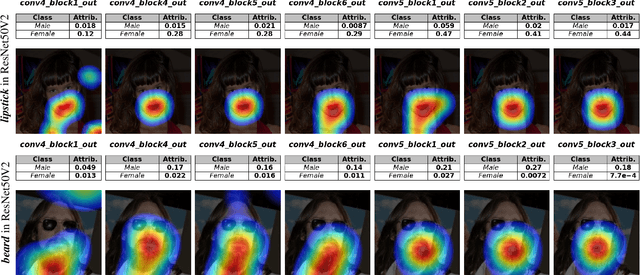
Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have seen significant performance improvements in recent years. However, due to their size and complexity, they function as black-boxes, leading to transparency concerns. State-of-the-art saliency methods generate local explanations that highlight the area in the input image where a class is identified but cannot explain how a concept of interest contributes to the prediction, which is essential for bias mitigation. On the other hand, concept-based methods, such as TCAV (Testing with Concept Activation Vectors), provide insights into how sensitive is the network to a concept, but cannot compute its attribution in a specific prediction nor show its location within the input image. This paper introduces a novel post-hoc explainability framework, Visual-TCAV, which aims to bridge the gap between these methods by providing both local and global explanations for CNN-based image classification. Visual-TCAV uses Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) to generate saliency maps that show where concepts are recognized by the network. Moreover, it can estimate the attribution of these concepts to the output of any class using a generalization of Integrated Gradients. This framework is evaluated on popular CNN architectures, with its validity further confirmed via experiments where ground truth for explanations is known, and a comparison with TCAV. Our code will be made available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge