Ricardo Martins
Explainable Anomaly Detection for Industrial IoT Data Streams
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Industrial maintenance is being transformed by the Internet of Things and edge computing, generating continuous data streams that demand real-time, adaptive decision-making under limited computational resources. While data stream mining (DSM) addresses this challenge, most methods assume fully supervised settings, yet in practice, ground-truth labels are often delayed or unavailable. This paper presents a collaborative DSM framework that integrates unsupervised anomaly detection with interactive, human-in-the-loop learning to support maintenance decisions. We employ an online Isolation Forest and enhance interpretability using incremental Partial Dependence Plots and a feature importance score, derived from deviations of Individual Conditional Expectation curves from a fading average, enabling users to dynamically reassess feature relevance and adjust anomaly thresholds. We describe the real-time implementation and provide initial results for fault detection in a Jacquard loom unit. Ongoing work targets continuous monitoring to predict and explain imminent bearing failures.
Tension Estimation and Localization for a Tethered Micro Aerial Robot
Feb 07, 2023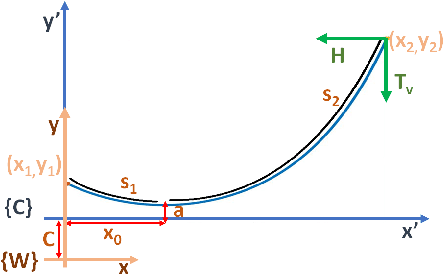
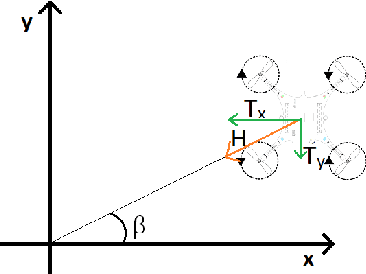
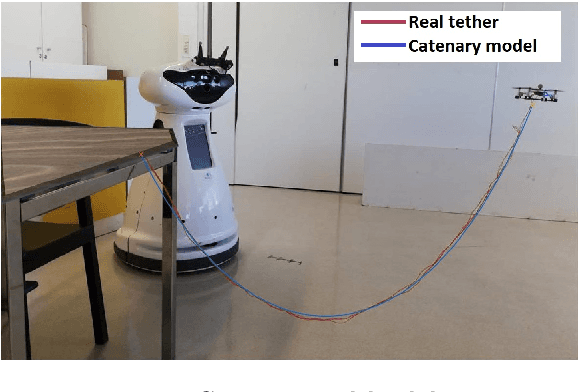
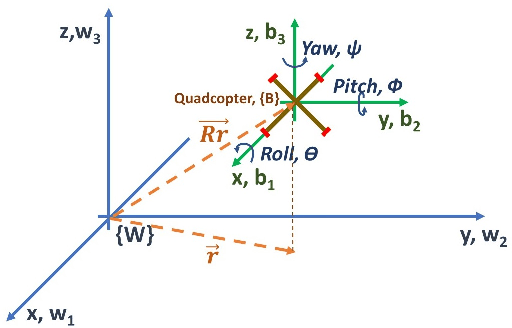
Abstract:This work focuses on the study of tethered fights of a micro quadcopter, with the aim of supplying continuous power to a small-sized aerial robot. Multiple features for facilitating the interaction between a tethered micro quadcopter and a ground base are described in this paper. Firstly, a tether model based on the catenary curve is presented that describes a quadcopter tethered to a point in space. Furthermore, a method capable of estimating the tension applied to the quadcopter, based only on the inertial information from the IMU sensors and the motor thrusts, is presented. Finally, a novel method for localizing the quadcopter by exploiting the tension imposed by the tether and the shape of the tether is described. The proposed methods are evaluated both in simulation and in real world prototype.
Touch attention Bayesian models for robotic active haptic exploration of heterogeneous surfaces
Sep 22, 2014



Abstract:This work contributes to the development of active haptic exploration strategies of surfaces using robotic hands in environments with an unknown structure. The architecture of the proposed approach consists two main Bayesian models, implementing the touch attention mechanisms of the system. The model pi_per perceives and discriminates different categories of materials (haptic stimulus) integrating compliance and texture features extracted from haptic sensory data. The model pi_tar actively infers the next region of the workspace that should be explored by the robotic system, integrating the task information, the permanently updated saliency and uncertainty maps extracted from the perceived haptic stimulus map, as well as, inhibition-of-return mechanisms. The experimental results demonstrate that the Bayesian model pi_per can be used to discriminate 10 different classes of materials with an average recognition rate higher than 90% . The generalization capability of the proposed models was demonstrated experimentally. The ATLAS robot, in the simulation, was able to perform the following of a discontinuity between two regions made of different materials with a divergence smaller than 1cm (30 trials). The tests were performed in scenarios with 3 different configurations of the discontinuity. The Bayesian models have demonstrated the capability to manage the uncertainty about the structure of the surfaces and sensory noise to make correct motor decisions from haptic percepts.
* 8 pages, presented in IROS 2014, Chicago
BW - Eye Ophthalmologic decision support system based on clinical workflow and data mining techniques-image registration algorithm
Dec 17, 2013

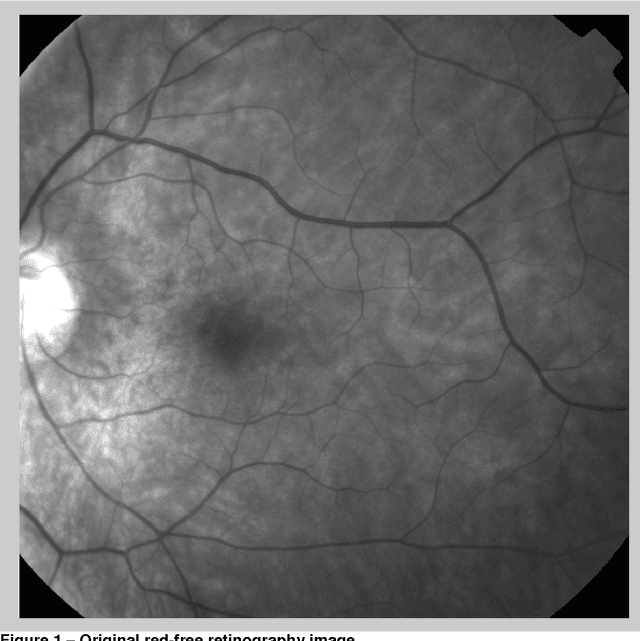
Abstract:Blueworks - Medical Expert Diagnosis is developing an application, BWEye, to be used as an ophthalmology consultation decision support system. The implementation of this application involves several different tasks and one of them is the implementation of an ophthalmology images registration algorithm. The work reported in this document is related with the implementation of an algorithm to register images of angiography, colour retinography and redfree retinography. The implementations described were developed in the software MATLAB. The implemented algorithm is based in the detection of the bifurcation points (y-features) of the vascular structures of the retina that usually are visible in the referred type of images. There are proposed two approaches to establish an initial set of features correspondences. The first approach is based in the maximization of the mutual information of the bifurcation regions of the features of images. The second approach is based in the characterization of each bifurcation point and in the minimization of the Euclidean distance between the descriptions of the features of the images in the descriptors space. The final set of the matching features for a pair of images is defined through the application of the RANSAC algorithm. Although, it was not achieved the implementation of a full functional algorithm, there were made several analysis that can be important to future improvement of the current implementation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge