Renato Stoffalette João
On Informative Tweet Identification For Tracking Mass Events
Jan 14, 2021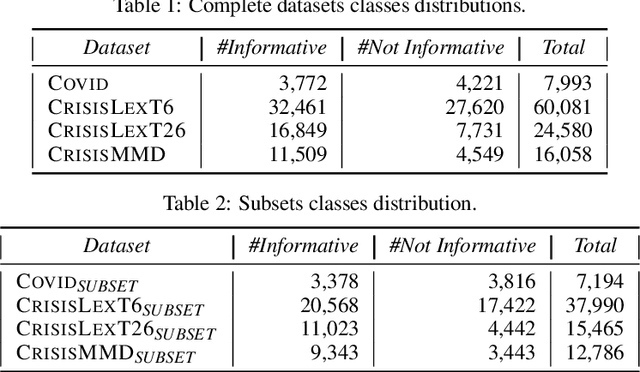
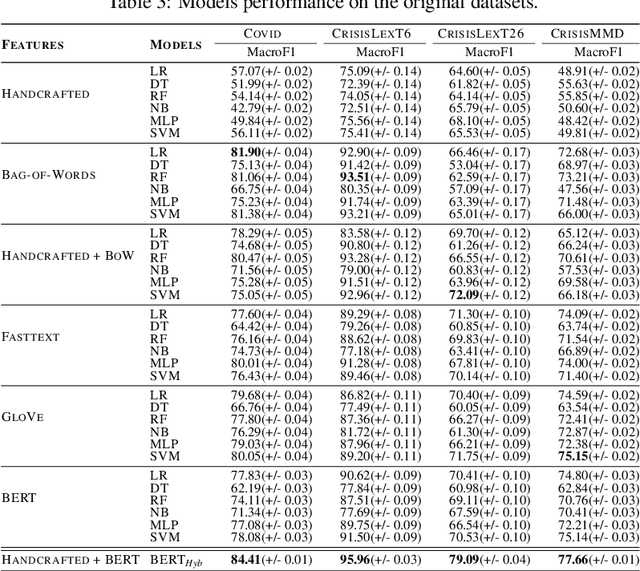
Abstract:Twitter has been heavily used as an important channel for communicating and discussing about events in real-time. In such major events, many uninformative tweets are also published rapidly by many users, making it hard to follow the events. In this paper, we address this problem by investigating machine learning methods for automatically identifying informative tweets among those that are relevant to a target event. We examine both traditional approaches with a rich set of handcrafted features and state of the art approaches with automatically learned features. We further propose a hybrid model that leverages both the handcrafted features and the automatically learned ones. Our experiments on several large datasets of real-world events show that the latter approaches significantly outperform the former and our proposed model performs the best, suggesting highly effective mechanisms for tracking mass events.
Better Together -- An Ensemble Learner for Combining the Results of Ready-made Entity Linking Systems
Jan 14, 2021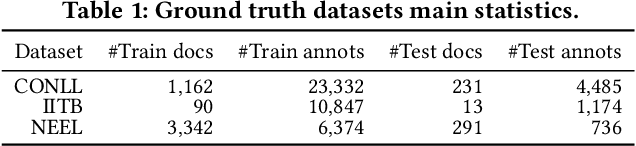
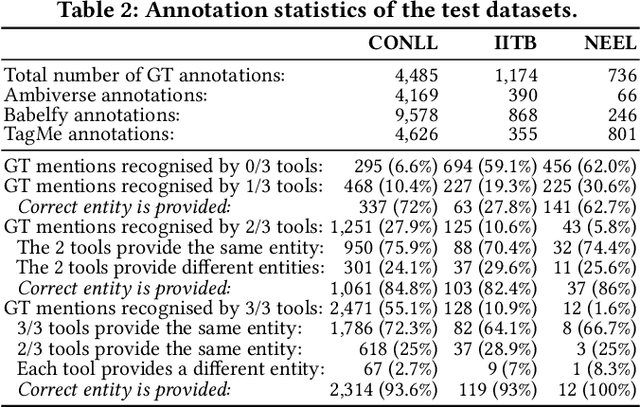
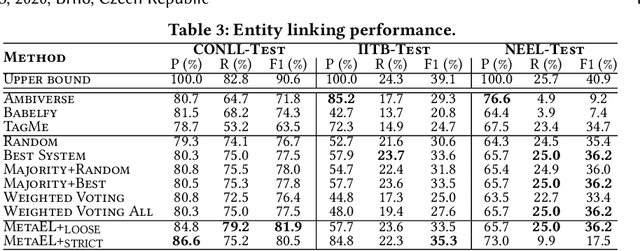
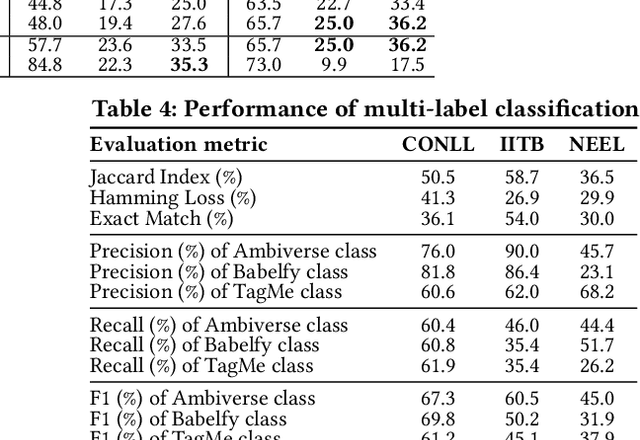
Abstract:Entity linking (EL) is the task of automatically identifying entity mentions in text and resolving them to a corresponding entity in a reference knowledge base like Wikipedia. Throughout the past decade, a plethora of EL systems and pipelines have become available, where performance of individual systems varies heavily across corpora, languages or domains. Linking performance varies even between different mentions in the same text corpus, where, for instance, some EL approaches are better able to deal with short surface forms while others may perform better when more context information is available. To this end, we argue that performance may be optimised by exploiting results from distinct EL systems on the same corpus, thereby leveraging their individual strengths on a per-mention basis. In this paper, we introduce a supervised approach which exploits the output of multiple ready-made EL systems by predicting the correct link on a per-mention basis. Experimental results obtained on existing ground truth datasets and exploiting three state-of-the-art EL systems show the effectiveness of our approach and its capacity to significantly outperform the individual EL systems as well as a set of baseline methods.
Same but Different: Distant Supervision for Predicting and Understanding Entity Linking Difficulty
Dec 13, 2018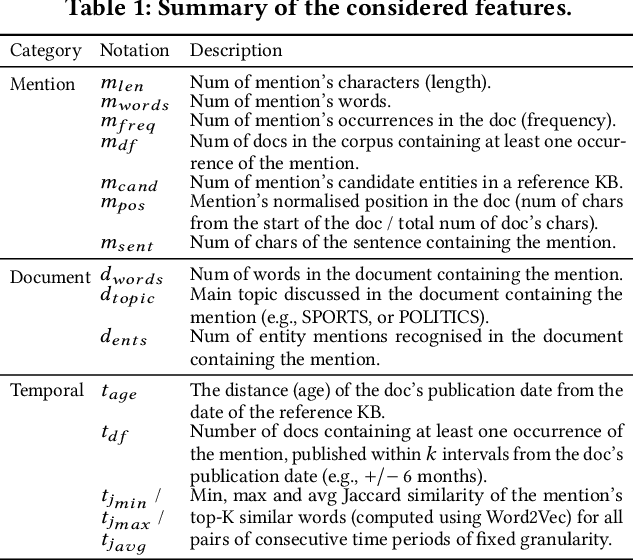
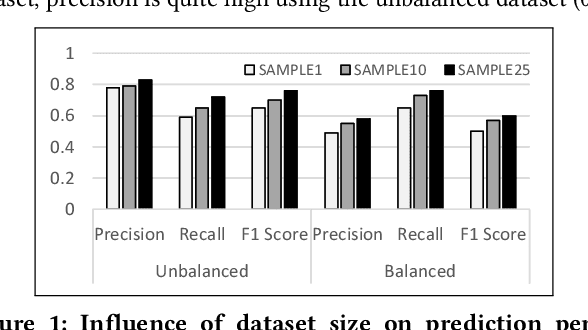
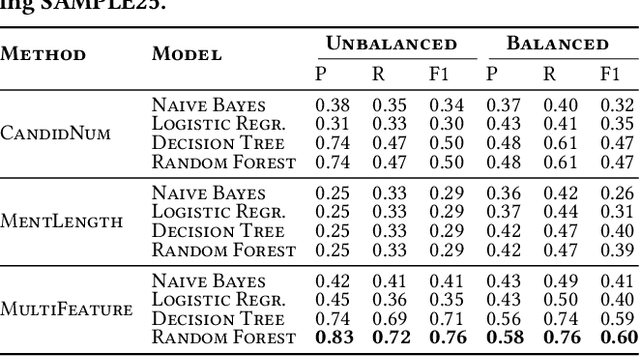

Abstract:Entity Linking (EL) is the task of automatically identifying entity mentions in a piece of text and resolving them to a corresponding entity in a reference knowledge base like Wikipedia. There is a large number of EL tools available for different types of documents and domains, yet EL remains a challenging task where the lack of precision on particularly ambiguous mentions often spoils the usefulness of automated disambiguation results in real applications. A priori approximations of the difficulty to link a particular entity mention can facilitate flagging of critical cases as part of semi-automated EL systems, while detecting latent factors that affect the EL performance, like corpus-specific features, can provide insights on how to improve a system based on the special characteristics of the underlying corpus. In this paper, we first introduce a consensus-based method to generate difficulty labels for entity mentions on arbitrary corpora. The difficulty labels are then exploited as training data for a supervised classification task able to predict the EL difficulty of entity mentions using a variety of features. Experiments over a corpus of news articles show that EL difficulty can be estimated with high accuracy, revealing also latent features that affect EL performance. Finally, evaluation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method to inform semi-automated EL pipelines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge