Remo Pareschi
Can Semantic Methods Enhance Team Sports Tactics? A Methodology for Football with Broader Applications
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:This paper explores how semantic-space reasoning, traditionally used in computational linguistics, can be extended to tactical decision-making in team sports. Building on the analogy between texts and teams -- where players act as words and collective play conveys meaning -- the proposed methodology models tactical configurations as compositional semantic structures. Each player is represented as a multidimensional vector integrating technical, physical, and psychological attributes; team profiles are aggregated through contextual weighting into a higher-level semantic representation. Within this shared vector space, tactical templates such as high press, counterattack, or possession build-up are encoded analogously to linguistic concepts. Their alignment with team profiles is evaluated using vector-distance metrics, enabling the computation of tactical ``fit'' and opponent-exploitation potential. A Python-based prototype demonstrates how these methods can generate interpretable, dynamically adaptive strategy recommendations, accompanied by fine-grained diagnostic insights at the attribute level. Beyond football, the approach offers a generalizable framework for collective decision-making and performance optimization in team-based domains -- ranging from basketball and hockey to cooperative robotics and human-AI coordination systems. The paper concludes by outlining future directions toward real-world data integration, predictive simulation, and hybrid human-machine tactical intelligence.
Human-Artificial Interaction in the Age of Agentic AI: A System-Theoretical Approach
Feb 19, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents a novel perspective on human-computer interaction (HCI), framing it as a dynamic interplay between human and computational agents within a networked system. Going beyond traditional interface-based approaches, we emphasize the importance of coordination and communication among heterogeneous agents with different capabilities, roles, and goals. A key distinction is made between multi-agent systems (MAS) and Centaurian systems, which represent two different paradigms of human-AI collaboration. MAS maintain agent autonomy, with structured protocols enabling cooperation, while Centaurian systems deeply integrate human and AI capabilities, creating unified decision-making entities. To formalize these interactions, we introduce a framework for communication spaces, structured into surface, observation, and computation layers, ensuring seamless integration between MAS and Centaurian architectures, where colored Petri nets effectively represent structured Centaurian systems and high-level reconfigurable networks address the dynamic nature of MAS. Our research has practical applications in autonomous robotics, human-in-the-loop decision making, and AI-driven cognitive architectures, and provides a foundation for next-generation hybrid intelligence systems that balance structured coordination with emergent behavior.
Recommending Actionable Strategies: A Semantic Approach to Integrating Analytical Frameworks with Decision Heuristics
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:We present a novel approach for recommending actionable strategies by integrating strategic frameworks with decision heuristics through semantic analysis. While strategy frameworks provide systematic models for assessment and planning, and decision heuristics encode experiential knowledge,these traditions have historically remained separate. Our methodology bridges this gap using advanced natural language processing (NLP), demonstrated through integrating frameworks like the 6C model with the Thirty-Six Stratagems. The approach employs vector space representations and semantic similarity calculations to map framework parameters to heuristic patterns, supported by a computational architecture that combines deep semantic processing with constrained use of Large Language Models. By processing both primary content and secondary elements (diagrams, matrices) as complementary linguistic representations, we demonstrate effectiveness through corporate strategy case studies. The methodology generalizes to various analytical frameworks and heuristic sets, culminating in a plug-and-play architecture for generating recommender systems that enable cohesive integration of strategic frameworks and decision heuristics into actionable guidance.
Abductive Reasoning with the GPT-4 Language Model: Case studies from criminal investigation, medical practice, scientific research
Jul 17, 2023Abstract:This study evaluates the GPT-4 Large Language Model's abductive reasoning in complex fields like medical diagnostics, criminology, and cosmology. Using an interactive interview format, the AI assistant demonstrated reliability in generating and selecting hypotheses. It inferred plausible medical diagnoses based on patient data and provided potential causes and explanations in criminology and cosmology. The results highlight the potential of LLMs in complex problem-solving and the need for further research to maximize their practical applications.
A formal model for ledger management systems based on contracts and temporal logic
Sep 30, 2021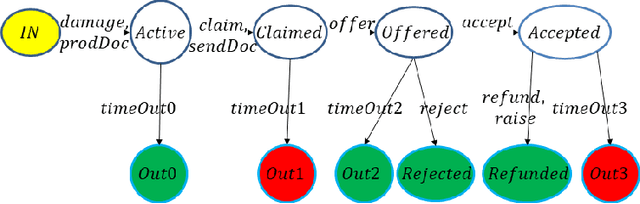
Abstract:A key component of blockchain technology is the ledger, viz., a database that, unlike standard databases, keeps in memory the complete history of past transactions as in a notarial archive for the benefit of any future test. In second-generation blockchains such as Ethereum the ledger is coupled with smart contracts, which enable the automation of transactions associated with agreements between the parties of a financial or commercial nature. The coupling of smart contracts and ledgers provides the technological background for very innovative application areas, such as Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi), which propelled blockchains beyond cryptocurrencies that were the only focus of first generation blockchains such as the Bitcoin. However, the currently used implementation of smart contracts as arbitrary programming constructs has made them susceptible to dangerous bugs that can be exploited maliciously and has moved their semantics away from that of legal contracts. We propose here to recompose the split and recover the reliability of databases by formalizing a notion of contract modelled as a finite-state automaton with well-defined computational characteristics derived from an encoding in terms of allocations of resources to actors, as an alternative to the approach based on programming. To complete the work, we use temporal logic as the basis for an abstract query language that is effectively suited to the historical nature of the information kept in the ledger.
Integrating Heuristics and Learning in a Computational Architecture for Cognitive Trading
Aug 27, 2021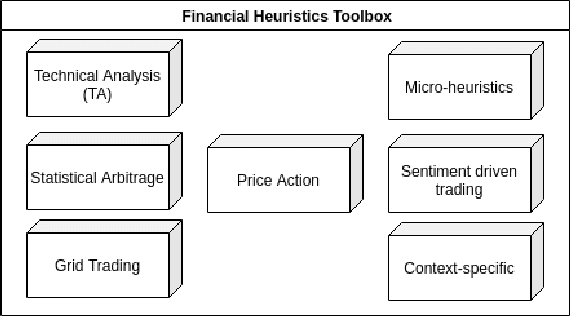

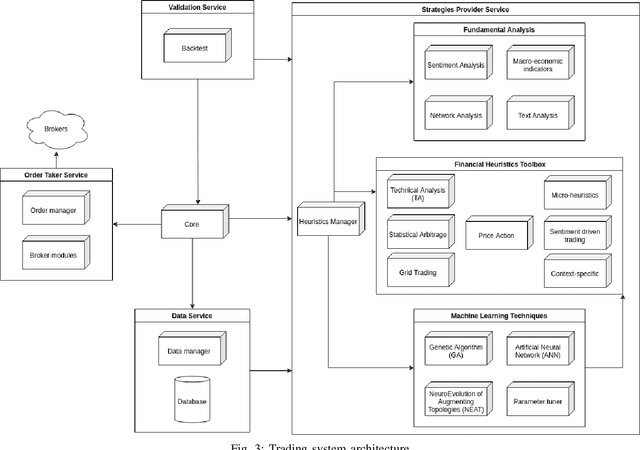
Abstract:The successes of Artificial Intelligence in recent years in areas such as image analysis, natural language understanding and strategy games have sparked interest from the world of finance. Specifically, there are high expectations, and ongoing engineering projects, regarding the creation of artificial agents, known as robotic traders, capable of juggling the financial markets with the skill of experienced human traders. Obvious economic implications aside, this is certainly an area of great scientific interest, due to the challenges that such a real context poses to the use of AI techniques. Precisely for this reason, we must be aware that artificial agents capable of operating at such levels are not just round the corner, and that there will be no simple answers, but rather a concurrence of various technologies and methods to the success of the effort. In the course of this article, we review the issues inherent in the design of effective robotic traders as well as the consequently applicable solutions, having in view the general objective of bringing the current state of the art of robo-trading up to the next level of intelligence, which we refer to as Cognitive Trading. Key to our approach is the joining of two methodological and technological directions which, although both deeply rooted in the disciplinary field of artificial intelligence, have so far gone their separate ways: heuristics and learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge