Reginald E. Bryant
An Empirical Study of Accuracy, Fairness, Explainability, Distributional Robustness, and Adversarial Robustness
Sep 29, 2021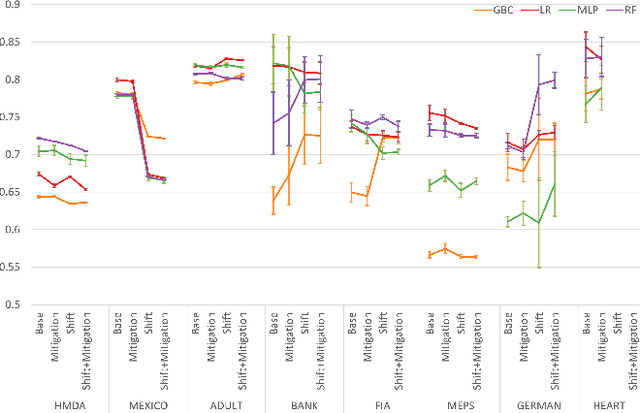
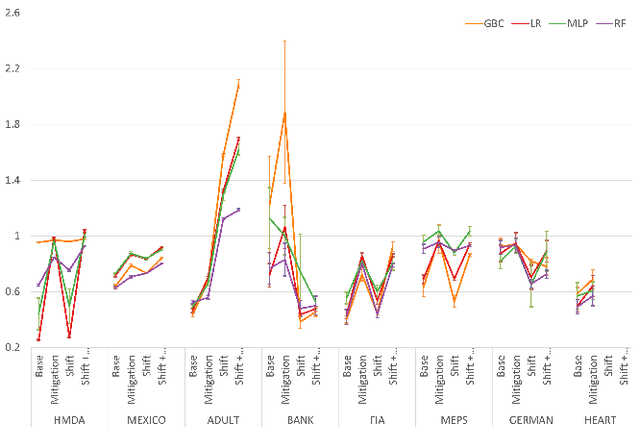
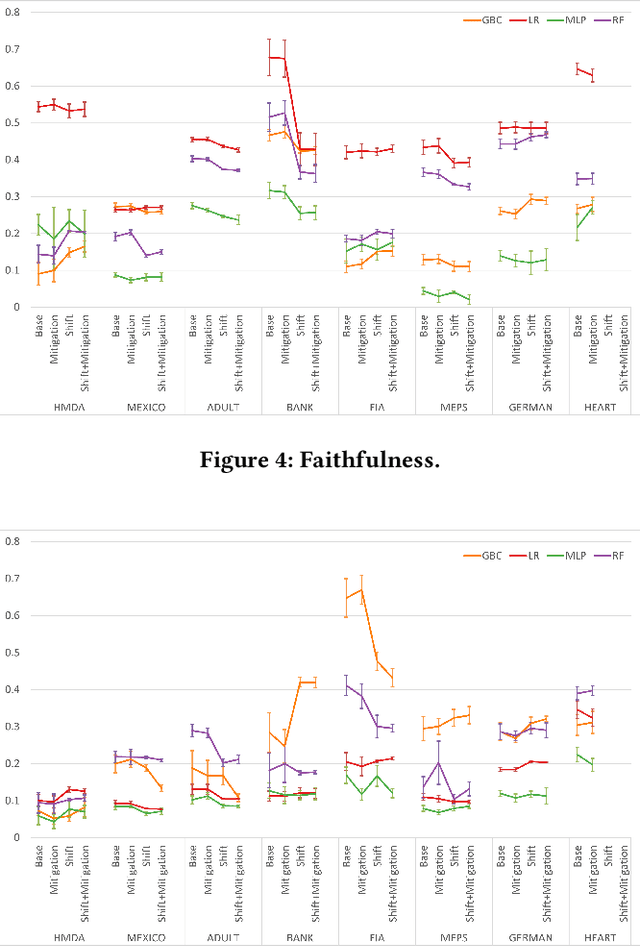
Abstract:To ensure trust in AI models, it is becoming increasingly apparent that evaluation of models must be extended beyond traditional performance metrics, like accuracy, to other dimensions, such as fairness, explainability, adversarial robustness, and distribution shift. We describe an empirical study to evaluate multiple model types on various metrics along these dimensions on several datasets. Our results show that no particular model type performs well on all dimensions, and demonstrate the kinds of trade-offs involved in selecting models evaluated along multiple dimensions.
Preservation of Anomalous Subgroups On Machine Learning Transformed Data
Nov 09, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the effect of machine learning based anonymization on anomalous subgroup preservation. In particular, we train a binary classifier to discover the most anomalous subgroup in a dataset by maximizing the bias between the group's predicted odds ratio from the model and observed odds ratio from the data. We then perform anonymization using a variational autoencoder (VAE) to synthesize an entirely new dataset that would ideally be drawn from the distribution of the original data. We repeat the anomalous subgroup discovery task on the new data and compare it to what was identified pre-anonymization. We evaluated our approach using publicly available datasets from the financial industry. Our evaluation confirmed that the approach was able to produce synthetic datasets that preserved a high level of subgroup differentiation as identified initially in the original dataset. Such a distinction was maintained while having distinctly different records between the synthetic and original dataset. Finally, we packed the above end to end process into what we call Utility Guaranteed Deep Privacy (UGDP) system. UGDP can be easily extended to onboard alternative generative approaches such as GANs to synthesize tabular data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge