Razvan L. Miclea
for the Alzheimers Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Counterfactuals and Uncertainty-Based Explainable Paradigm for the Automated Detection and Segmentation of Renal Cysts in Computed Tomography Images: A Multi-Center Study
Aug 07, 2024Abstract:Routine computed tomography (CT) scans often detect a wide range of renal cysts, some of which may be malignant. Early and precise localization of these cysts can significantly aid quantitative image analysis. Current segmentation methods, however, do not offer sufficient interpretability at the feature and pixel levels, emphasizing the necessity for an explainable framework that can detect and rectify model inaccuracies. We developed an interpretable segmentation framework and validated it on a multi-centric dataset. A Variational Autoencoder Generative Adversarial Network (VAE-GAN) was employed to learn the latent representation of 3D input patches and reconstruct input images. Modifications in the latent representation using the gradient of the segmentation model generated counterfactual explanations for varying dice similarity coefficients (DSC). Radiomics features extracted from these counterfactual images, using a ground truth cyst mask, were analyzed to determine their correlation with segmentation performance. The DSCs for the original and VAE-GAN reconstructed images for counterfactual image generation showed no significant differences. Counterfactual explanations highlighted how variations in cyst image features influence segmentation outcomes and showed model discrepancies. Radiomics features correlating positively and negatively with dice scores were identified. The uncertainty of the predicted segmentation masks was estimated using posterior sampling of the weight space. The combination of counterfactual explanations and uncertainty maps provided a deeper understanding of the image features within the segmented renal cysts that lead to high uncertainty. The proposed segmentation framework not only achieved high segmentation accuracy but also increased interpretability regarding how image features impact segmentation performance.
Reproducible radiomics through automated machine learning validated on twelve clinical applications
Aug 19, 2021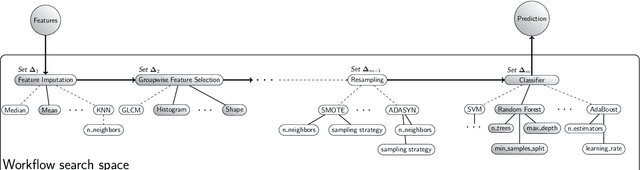
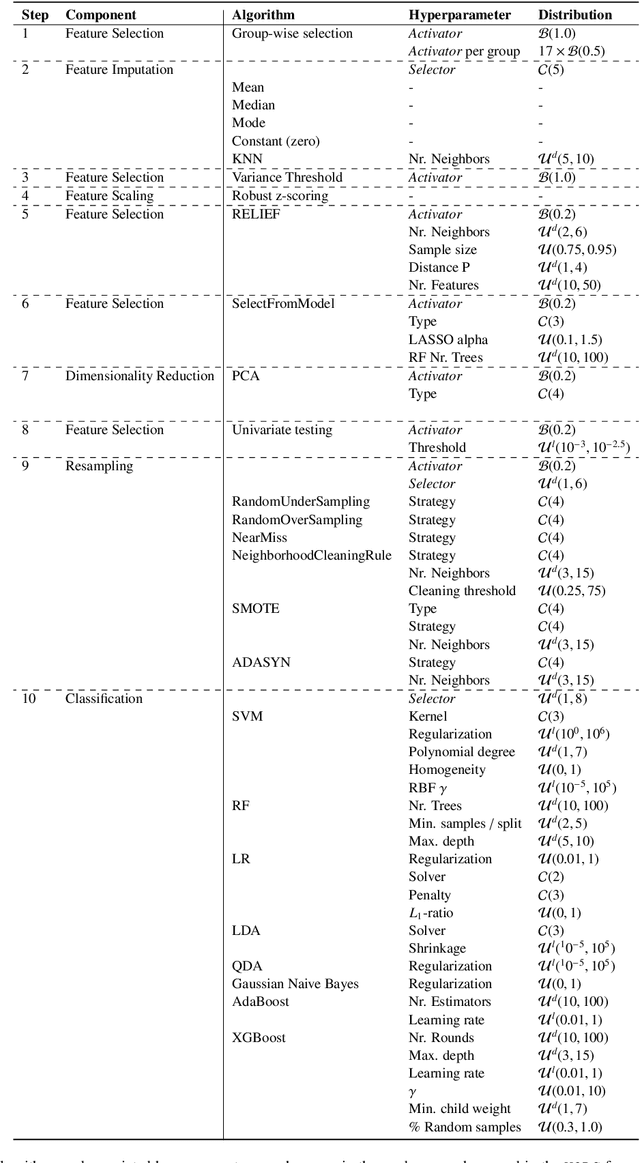
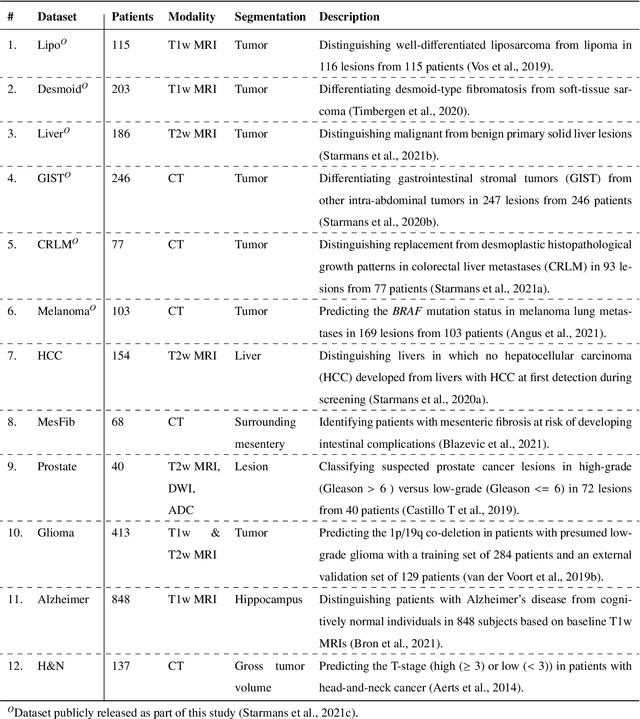
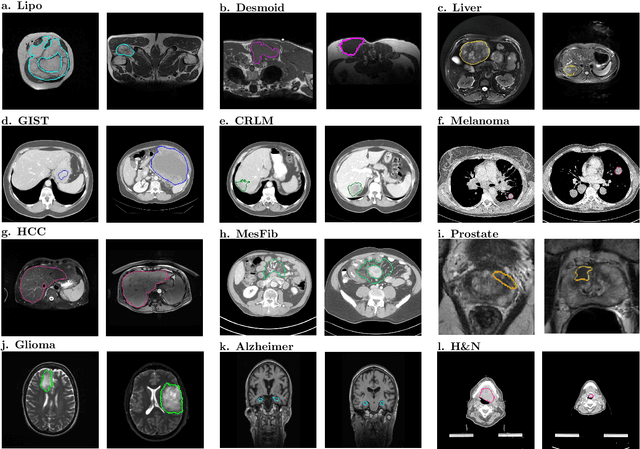
Abstract:Radiomics uses quantitative medical imaging features to predict clinical outcomes. While many radiomics methods have been described in the literature, these are generally designed for a single application. The aim of this study is to generalize radiomics across applications by proposing a framework to automatically construct and optimize the radiomics workflow per application. To this end, we formulate radiomics as a modular workflow, consisting of several components: image and segmentation preprocessing, feature extraction, feature and sample preprocessing, and machine learning. For each component, a collection of common algorithms is included. To optimize the workflow per application, we employ automated machine learning using a random search and ensembling. We evaluate our method in twelve different clinical applications, resulting in the following area under the curves: 1) liposarcoma (0.83); 2) desmoid-type fibromatosis (0.82); 3) primary liver tumors (0.81); 4) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (0.77); 5) colorectal liver metastases (0.68); 6) melanoma metastases (0.51); 7) hepatocellular carcinoma (0.75); 8) mesenteric fibrosis (0.81); 9) prostate cancer (0.72); 10) glioma (0.70); 11) Alzheimer's disease (0.87); and 12) head and neck cancer (0.84). Concluding, our method fully automatically constructs and optimizes the radiomics workflow, thereby streamlining the search for radiomics biomarkers in new applications. To facilitate reproducibility and future research, we publicly release six datasets, the software implementation of our framework (open-source), and the code to reproduce this study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge