Rami Cohen
A Black-Box Attack Model for Visually-Aware Recommender Systems
Nov 05, 2020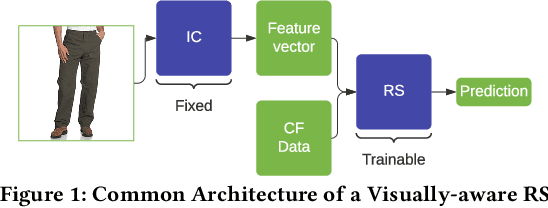

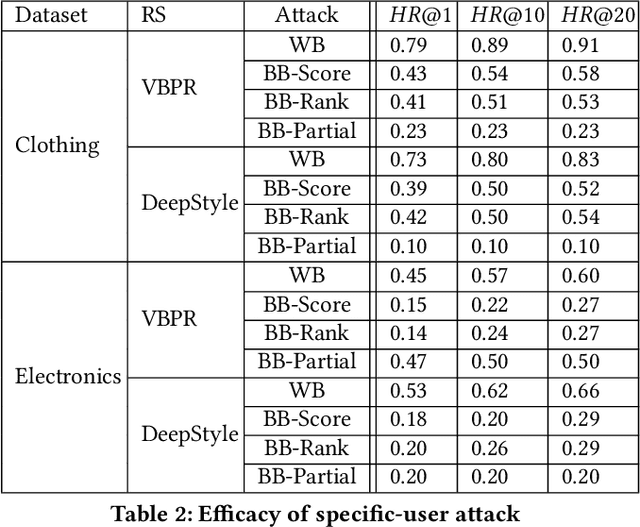
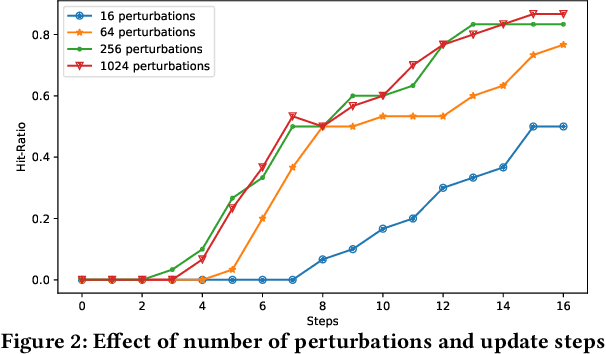
Abstract:Due to the advances in deep learning, visually-aware recommender systems (RS) have recently attracted increased research interest. Such systems combine collaborative signals with images, usually represented as feature vectors outputted by pre-trained image models. Since item catalogs can be huge, recommendation service providers often rely on images that are supplied by the item providers. In this work, we show that relying on such external sources can make an RS vulnerable to attacks, where the goal of the attacker is to unfairly promote certain pushed items. Specifically, we demonstrate how a new visual attack model can effectively influence the item scores and rankings in a black-box approach, i.e., without knowing the parameters of the model. The main underlying idea is to systematically create small human-imperceptible perturbations of the pushed item image and to devise appropriate gradient approximation methods to incrementally raise the pushed item's score. Experimental evaluations on two datasets show that the novel attack model is effective even when the contribution of the visual features to the overall performance of the recommender system is modest.
The Chan-Vese Algorithm
Jul 15, 2011



Abstract:Segmentation is the process of partitioning a digital image into multiple segments (sets of pixels). Such common segmentation tasks including segmenting written text or segmenting tumors from healthy brain tissue in an MRI image, etc. Chan-Vese model for active contours is a powerful and flexible method which is able to segment many types of images, including some that would be quite difficult to segment in means of "classical" segmentation - i.e., using thresholding or gradient based methods. This model is based on the Mumford-Shah functional for segmentation, and is used widely in the medical imaging field, especially for the segmentation of the brain, heart and trachea. The model is based on an energy minimization problem, which can be reformulated in the level set formulation, leading to an easier way to solve the problem. In this project, the model will be presented (there is an extension to color (vector-valued) images, but it will not be considered here), and Matlab code that implements it will be introduced.
Face Recognition using Curvelet Transform
Jul 14, 2011



Abstract:Face recognition has been studied extensively for more than 20 years now. Since the beginning of 90s the subject has became a major issue. This technology is used in many important real-world applications, such as video surveillance, smart cards, database security, internet and intranet access. This report reviews recent two algorithms for face recognition which take advantage of a relatively new multiscale geometric analysis tool - Curvelet transform, for facial processing and feature extraction. This transform proves to be efficient especially due to its good ability to detect curves and lines, which characterize the human's face. An algorithm which is based on the two algorithms mentioned above is proposed, and its performance is evaluated on three data bases of faces: AT&T (ORL), Essex Grimace and Georgia-Tech. k-nearest neighbour (k-NN) and Support vector machine (SVM) classifiers are used, along with Principal Component Analysis (PCA) for dimensionality reduction. This algorithm shows good results, and it even outperforms other algorithms in some cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge