Raksha Sharma
A Novel Lightweight Transformer with Edge-Aware Fusion for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Transformer-based models have achieved strong performance in remote sensing image captioning by capturing long-range dependencies and contextual information. However, their practical deployment is hindered by high computational costs, especially in multi-modal frameworks that employ separate transformer-based encoders and decoders. In addition, existing remote sensing image captioning models primarily focus on high-level semantic extraction while often overlooking fine-grained structural features such as edges, contours, and object boundaries. To address these challenges, a lightweight transformer architecture is proposed by reducing the dimensionality of the encoder layers and employing a distilled version of GPT-2 as the decoder. A knowledge distillation strategy is used to transfer knowledge from a more complex teacher model to improve the performance of the lightweight network. Furthermore, an edge-aware enhancement strategy is incorporated to enhance image representation and object boundary understanding, enabling the model to capture fine-grained spatial details in remote sensing images. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly improves caption quality compared to state-of-the-art methods.
Good Representation, Better Explanation: Role of Convolutional Neural Networks in Transformer-Based Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Feb 22, 2025Abstract:Remote Sensing Image Captioning (RSIC) is the process of generating meaningful descriptions from remote sensing images. Recently, it has gained significant attention, with encoder-decoder models serving as the backbone for generating meaningful captions. The encoder extracts essential visual features from the input image, transforming them into a compact representation, while the decoder utilizes this representation to generate coherent textual descriptions. Recently, transformer-based models have gained significant popularity due to their ability to capture long-range dependencies and contextual information. The decoder has been well explored for text generation, whereas the encoder remains relatively unexplored. However, optimizing the encoder is crucial as it directly influences the richness of extracted features, which in turn affects the quality of generated captions. To address this gap, we systematically evaluate twelve different convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures within a transformer-based encoder framework to assess their effectiveness in RSIC. The evaluation consists of two stages: first, a numerical analysis categorizes CNNs into different clusters, based on their performance. The best performing CNNs are then subjected to human evaluation from a human-centric perspective by a human annotator. Additionally, we analyze the impact of different search strategies, namely greedy search and beam search, to ensure the best caption. The results highlight the critical role of encoder selection in improving captioning performance, demonstrating that specific CNN architectures significantly enhance the quality of generated descriptions for remote sensing images. By providing a detailed comparison of multiple encoders, this study offers valuable insights to guide advances in transformer-based image captioning models.
FE-LWS: Refined Image-Text Representations via Decoder Stacking and Fused Encodings for Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Remote sensing image captioning aims to generate descriptive text from remote sensing images, typically employing an encoder-decoder framework. In this setup, a convolutional neural network (CNN) extracts feature representations from the input image, which then guide the decoder in a sequence-to-sequence caption generation process. Although much research has focused on refining the decoder, the quality of image representations from the encoder remains crucial for accurate captioning. This paper introduces a novel approach that integrates features from two distinct CNN based encoders, capturing complementary information to enhance caption generation. Additionally, we propose a weighted averaging technique to combine the outputs of all GRUs in the stacked decoder. Furthermore, a comparison-based beam search strategy is incorporated to refine caption selection. The results demonstrate that our fusion-based approach, along with the enhanced stacked decoder, significantly outperforms both the transformer-based state-of-the-art model and other LSTM-based baselines.
A TextGCN-Based Decoding Approach for Improving Remote Sensing Image Captioning
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:Remote sensing images are highly valued for their ability to address complex real-world issues such as risk management, security, and meteorology. However, manually captioning these images is challenging and requires specialized knowledge across various domains. This letter presents an approach for automatically describing (captioning) remote sensing images. We propose a novel encoder-decoder setup that deploys a Text Graph Convolutional Network (TextGCN) and multi-layer LSTMs. The embeddings generated by TextGCN enhance the decoder's understanding by capturing the semantic relationships among words at both the sentence and corpus levels. Furthermore, we advance our approach with a comparison-based beam search method to ensure fairness in the search strategy for generating the final caption. We present an extensive evaluation of our approach against various other state-of-the-art encoder-decoder frameworks. We evaluated our method across three datasets using seven metrics: BLEU-1 to BLEU-4, METEOR, ROUGE-L, and CIDEr. The results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art encoder-decoder methods.
Leveraging Dependency Grammar for Fine-Grained Offensive Language Detection using Graph Convolutional Networks
May 26, 2022
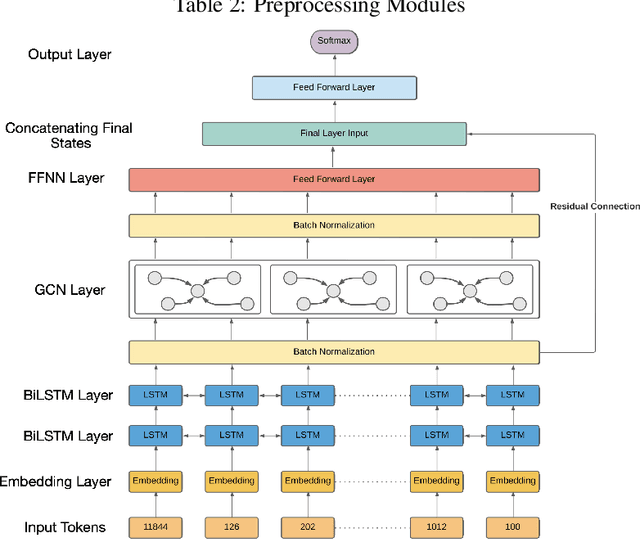
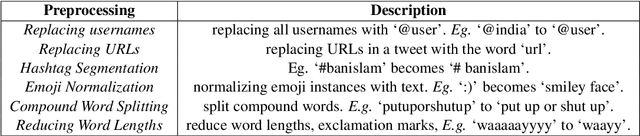
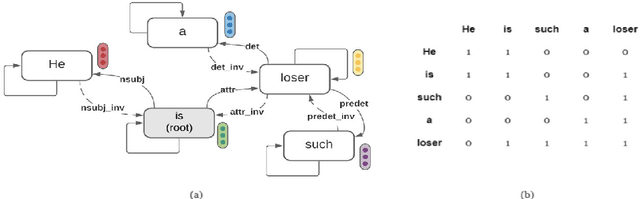
Abstract:The last few years have witnessed an exponential rise in the propagation of offensive text on social media. Identification of this text with high precision is crucial for the well-being of society. Most of the existing approaches tend to give high toxicity scores to innocuous statements (e.g., "I am a gay man"). These false positives result from over-generalization on the training data where specific terms in the statement may have been used in a pejorative sense (e.g., "gay"). Emphasis on such words alone can lead to discrimination against the classes these systems are designed to protect. In this paper, we address the problem of offensive language detection on Twitter, while also detecting the type and the target of the offence. We propose a novel approach called SyLSTM, which integrates syntactic features in the form of the dependency parse tree of a sentence and semantic features in the form of word embeddings into a deep learning architecture using a Graph Convolutional Network. Results show that the proposed approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art BERT model with orders of magnitude fewer number of parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge