Rakesh Kumar Sanodiya
EMGTTL: Transformers-Based Transfer Learning for Classification of ADL using Raw Surface EMG Signals
Oct 01, 2024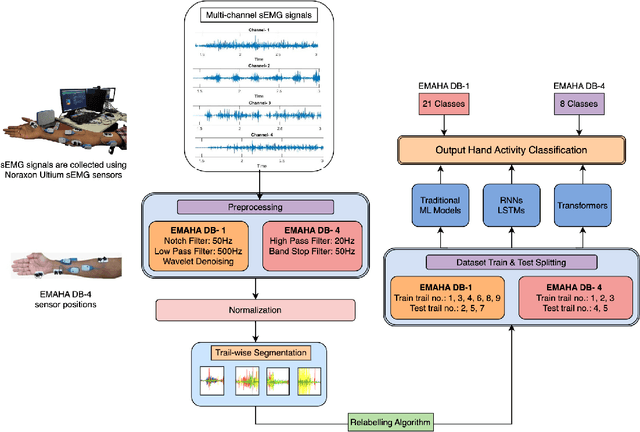
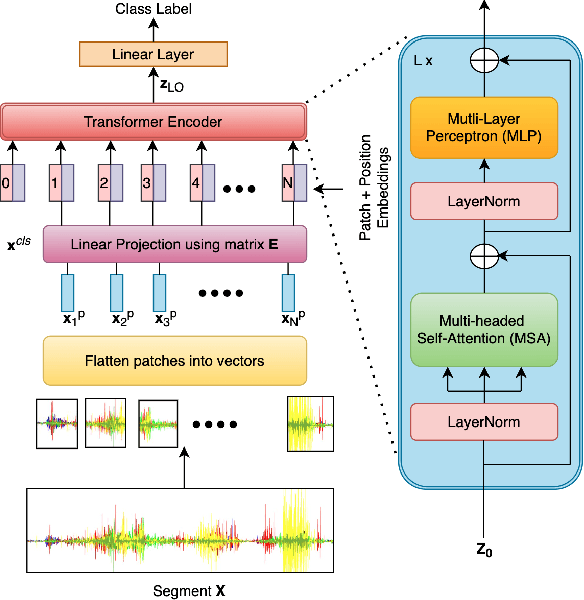
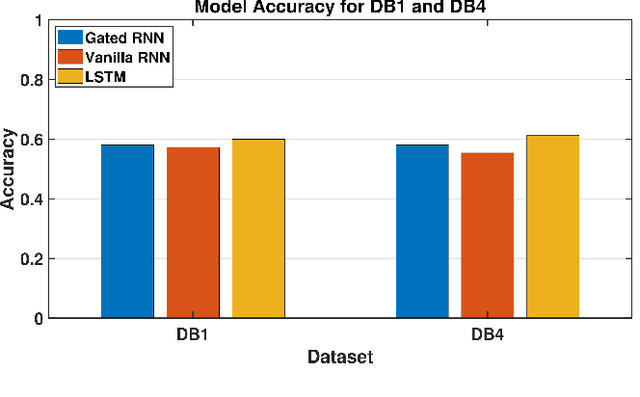
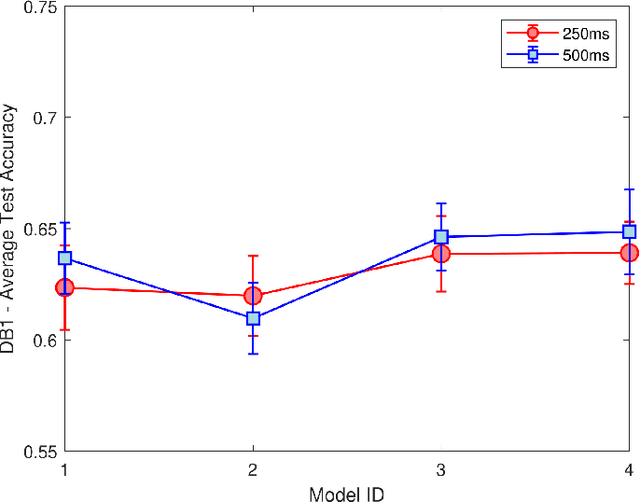
Abstract:Surface Electromyography (sEMG) is widely studied for its applications in rehabilitation, prosthetics, robotic arm control, and human-machine interaction. However, classifying Activities of Daily Living (ADL) using sEMG signals often requires extensive feature extraction, which can be time-consuming and energy-intensive. The objective of this study is stated as follows. Given sEMG datasets, such as electromyography analysis of human activity databases (DB1 and DB4), with multi-channel signals corresponding to ADL, is it possible to determine the ADL categories without explicit feature extraction from sEMG signals. Further is it possible to learn across the datasets to improve the classification performances. A classification framework, named EMGTTL, is developed that uses transformers for classification of ADL and the performance is enhanced by cross-data transfer learning. The methodology is implemented on EMAHA-DB1 and EMAHA-DB4. Experiments have shown that the transformer architecture achieved 64.47% accuracy for DB1 and 68.82% for DB4. Further, using transfer learning, the accuracy improved to 66.75% for DB1 (pre-trained on DB4) and 71.04% for DB4 (pre-trained on DB1).
Context Unaware Knowledge Distillation for Image Retrieval
Jul 19, 2022



Abstract:Existing data-dependent hashing methods use large backbone networks with millions of parameters and are computationally complex. Existing knowledge distillation methods use logits and other features of the deep (teacher) model and as knowledge for the compact (student) model, which requires the teacher's network to be fine-tuned on the context in parallel with the student model on the context. Training teacher on the target context requires more time and computational resources. In this paper, we propose context unaware knowledge distillation that uses the knowledge of the teacher model without fine-tuning it on the target context. We also propose a new efficient student model architecture for knowledge distillation. The proposed approach follows a two-step process. The first step involves pre-training the student model with the help of context unaware knowledge distillation from the teacher model. The second step involves fine-tuning the student model on the context of image retrieval. In order to show the efficacy of the proposed approach, we compare the retrieval results, no. of parameters and no. of operations of the student models with the teacher models under different retrieval frameworks, including deep cauchy hashing (DCH) and central similarity quantization (CSQ). The experimental results confirm that the proposed approach provides a promising trade-off between the retrieval results and efficiency. The code used in this paper is released publicly at \url{https://github.com/satoru2001/CUKDFIR}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge