Rajesh C. Panicker
Classification of ECG based on Hybrid Features using CNNs for Wearable Applications
Jun 14, 2022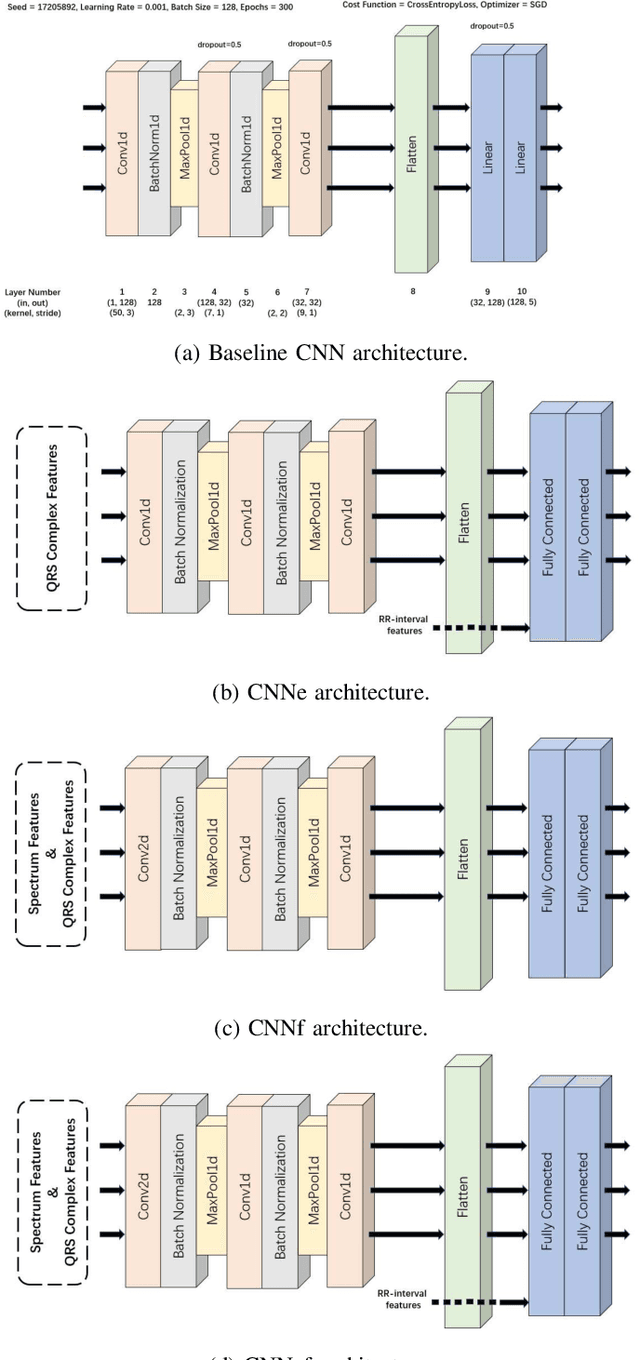
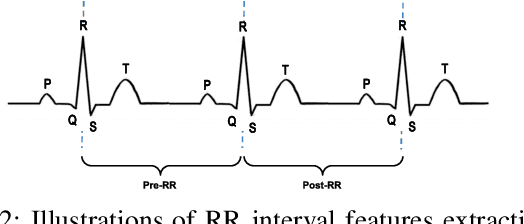
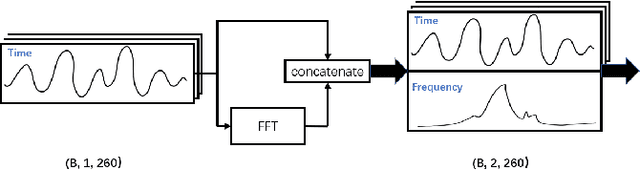
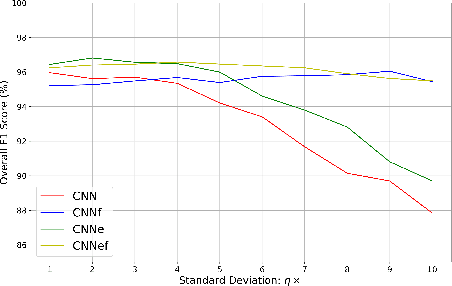
Abstract:Sudden cardiac death and arrhythmia account for a large percentage of all deaths worldwide. Electrocardiography (ECG) is the most widely used screening tool for cardiovascular diseases. Traditionally, ECG signals are classified manually, requiring experience and great skill, while being time-consuming and prone to error. Thus machine learning algorithms have been widely adopted because of their ability to perform complex data analysis. Features derived from the points of interest in ECG - mainly Q, R, and S, are widely used for arrhythmia detection. In this work, we demonstrate improved performance for ECG classification using hybrid features and three different models, building on a 1-D convolutional neural network (CNN) model that we had proposed in the past. An RR interval features based model proposed in this work achieved an accuracy of 98.98%, which is an improvement over the baseline model. To make the model immune to noise, we updated the model using frequency features and achieved good sustained performance in presence of noise with a slightly lower accuracy of 98.69%. Further, another model combining the frequency features and the RR interval features was developed, which achieved a high accuracy of 99% with good sustained performance in noisy environments. Due to its high accuracy and noise immunity, the proposed model which combines multiple hybrid features, is well suited for ambulatory wearable sensing applications.
Atrial Fibrillation Detection Using Weight-Pruned, Log-Quantised Convolutional Neural Networks
Jun 14, 2022


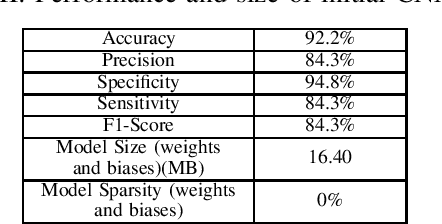
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNN) are a promising tool in medical applications. However, the implementation of complex DNNs on battery-powered devices is challenging due to high energy costs for communication. In this work, a convolutional neural network model is developed for detecting atrial fibrillation from electrocardiogram (ECG) signals. The model demonstrates high performance despite being trained on limited, variable-length input data. Weight pruning and logarithmic quantisation are combined to introduce sparsity and reduce model size, which can be exploited for reduced data movement and lower computational complexity. The final model achieved a 91.1% model compression ratio while maintaining high model accuracy of 91.7% and less than 1% loss.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge