Quentin Raymondaud
Probing the Information Encoded in Neural-based Acoustic Models of Automatic Speech Recognition Systems
Feb 29, 2024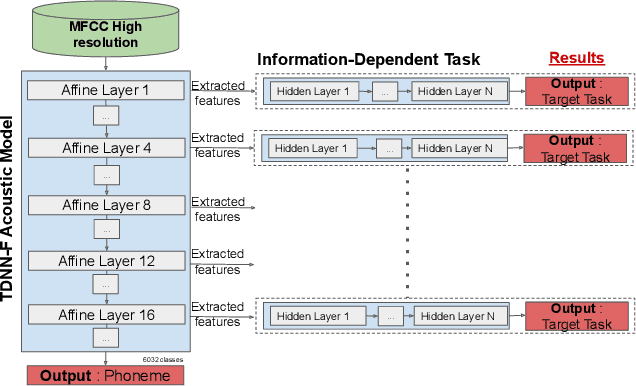
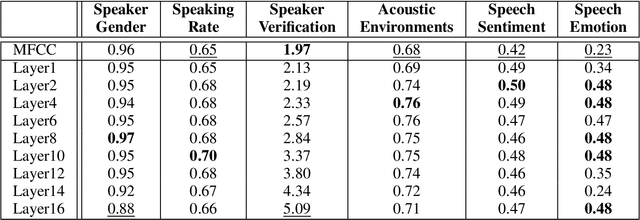
Abstract:Deep learning architectures have made significant progress in terms of performance in many research areas. The automatic speech recognition (ASR) field has thus benefited from these scientific and technological advances, particularly for acoustic modeling, now integrating deep neural network architectures. However, these performance gains have translated into increased complexity regarding the information learned and conveyed through these black-box architectures. Following many researches in neural networks interpretability, we propose in this article a protocol that aims to determine which and where information is located in an ASR acoustic model (AM). To do so, we propose to evaluate AM performance on a determined set of tasks using intermediate representations (here, at different layer levels). Regarding the performance variation and targeted tasks, we can emit hypothesis about which information is enhanced or perturbed at different architecture steps. Experiments are performed on both speaker verification, acoustic environment classification, gender classification, tempo-distortion detection systems and speech sentiment/emotion identification. Analysis showed that neural-based AMs hold heterogeneous information that seems surprisingly uncorrelated with phoneme recognition, such as emotion, sentiment or speaker identity. The low-level hidden layers globally appears useful for the structuring of information while the upper ones would tend to delete useless information for phoneme recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge