Qipin Chen
Homotopy Relaxation Training Algorithms for Infinite-Width Two-Layer ReLU Neural Networks
Sep 26, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we present a novel training approach called the Homotopy Relaxation Training Algorithm (HRTA), aimed at accelerating the training process in contrast to traditional methods. Our algorithm incorporates two key mechanisms: one involves building a homotopy activation function that seamlessly connects the linear activation function with the ReLU activation function; the other technique entails relaxing the homotopy parameter to enhance the training refinement process. We have conducted an in-depth analysis of this novel method within the context of the neural tangent kernel (NTK), revealing significantly improved convergence rates. Our experimental results, especially when considering networks with larger widths, validate the theoretical conclusions. This proposed HRTA exhibits the potential for other activation functions and deep neural networks.
A Weight Initialization Based on the Linear Product Structure for Neural Networks
Sep 01, 2021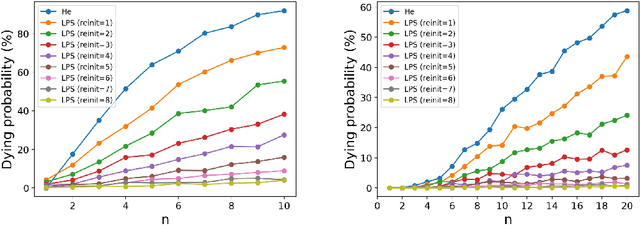
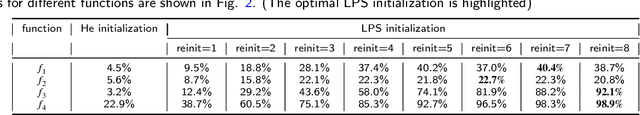
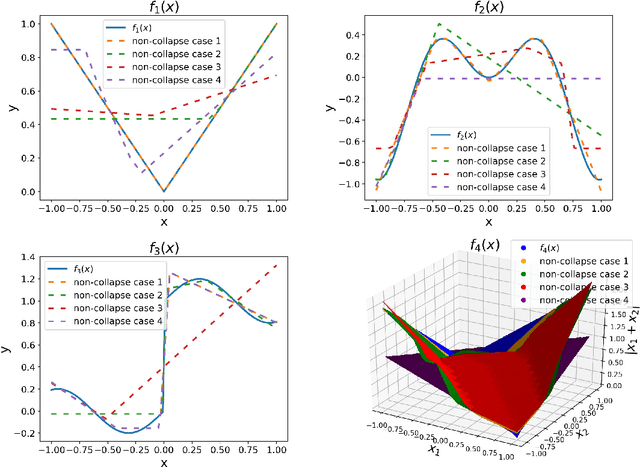
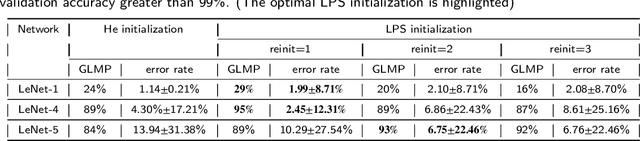
Abstract:Weight initialization plays an important role in training neural networks and also affects tremendous deep learning applications. Various weight initialization strategies have already been developed for different activation functions with different neural networks. These initialization algorithms are based on minimizing the variance of the parameters between layers and might still fail when neural networks are deep, e.g., dying ReLU. To address this challenge, we study neural networks from a nonlinear computation point of view and propose a novel weight initialization strategy that is based on the linear product structure (LPS) of neural networks. The proposed strategy is derived from the polynomial approximation of activation functions by using theories of numerical algebraic geometry to guarantee to find all the local minima. We also provide a theoretical analysis that the LPS initialization has a lower probability of dying ReLU comparing to other existing initialization strategies. Finally, we test the LPS initialization algorithm on both fully connected neural networks and convolutional neural networks to show its feasibility, efficiency, and robustness on public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge