Qingchun Hou
T-SKM-Net: Trainable Neural Network Framework for Linear Constraint Satisfaction via Sampling Kaczmarz-Motzkin Method
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Neural network constraint satisfaction is crucial for safety-critical applications such as power system optimization, robotic path planning, and autonomous driving. However, existing constraint satisfaction methods face efficiency-applicability trade-offs, with hard constraint methods suffering from either high computational complexity or restrictive assumptions on constraint structures. The Sampling Kaczmarz-Motzkin (SKM) method is a randomized iterative algorithm for solving large-scale linear inequality systems with favorable convergence properties, but its argmax operations introduce non-differentiability, posing challenges for neural network applications. This work proposes the Trainable Sampling Kaczmarz-Motzkin Network (T-SKM-Net) framework and, for the first time, systematically integrates SKM-type methods into neural network constraint satisfaction. The framework transforms mixed constraint problems into pure inequality problems through null space transformation, employs SKM for iterative solving, and maps solutions back to the original constraint space, efficiently handling both equality and inequality constraints. We provide theoretical proof of post-processing effectiveness in expectation and end-to-end trainability guarantees based on unbiased gradient estimators, demonstrating that despite non-differentiable operations, the framework supports standard backpropagation. On the DCOPF case118 benchmark, our method achieves 4.27ms/item GPU serial forward inference with 0.0025% max optimality gap with post-processing mode and 5.25ms/item with 0.0008% max optimality gap with joint training mode, delivering over 25$\times$ speedup compared to the pandapower solver while maintaining zero constraint violations under given tolerance.
Sparse Oblique Decision Tree for Power System Security Rules Extraction and Embedding
Apr 20, 2020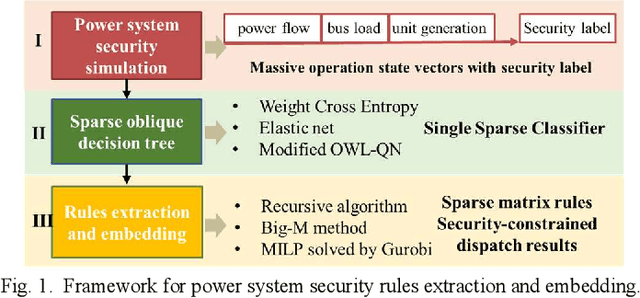
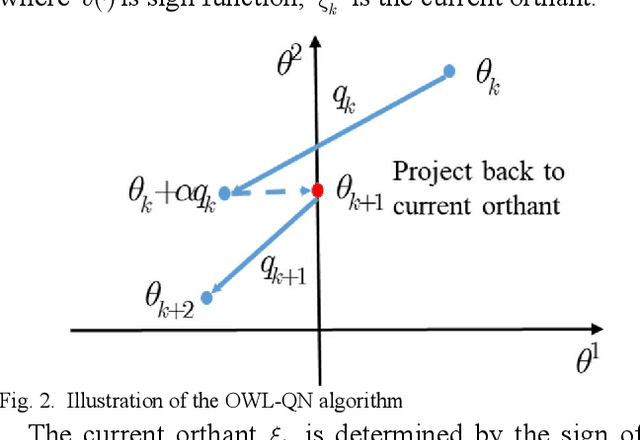
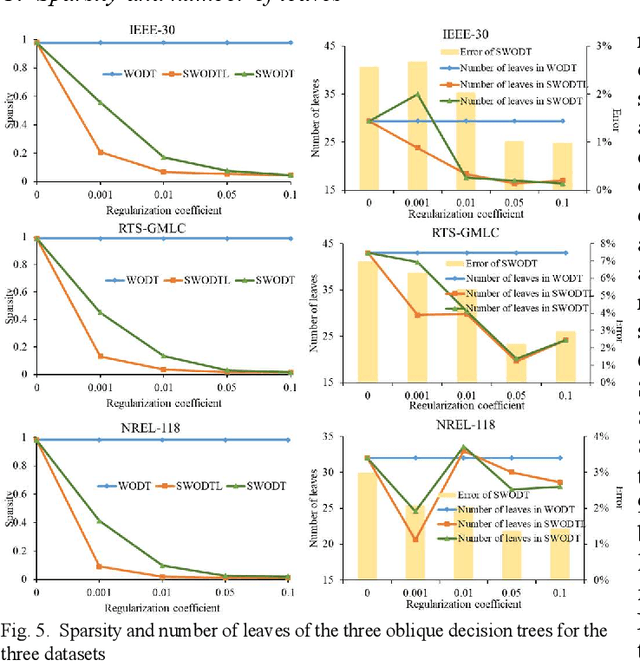
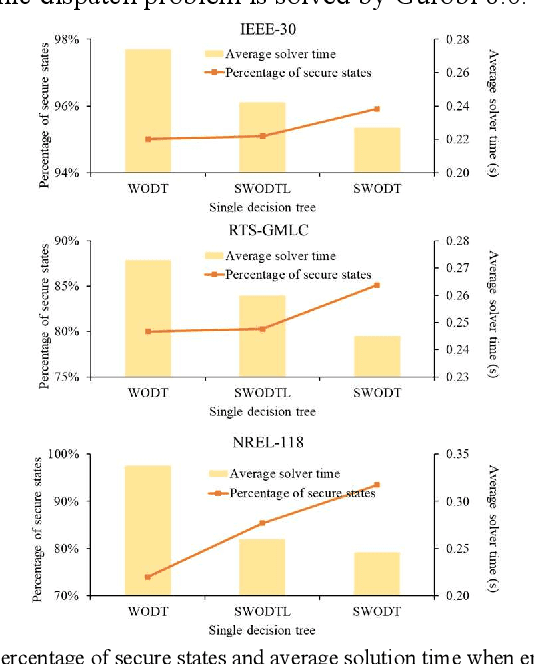
Abstract:Increasing the penetration of variable generation has a substantial effect on the operational reliability of power systems. The higher level of uncertainty that stems from this variability makes it more difficult to determine whether a given operating condition will be secure or insecure. Data-driven techniques provide a promising way to identify security rules that can be embedded in economic dispatch model to keep power system operating states secure. This paper proposes using a sparse weighted oblique decision tree to learn accurate, understandable, and embeddable security rules that are linear and can be extracted as sparse matrices using a recursive algorithm. These matrices can then be easily embedded as security constraints in power system economic dispatch calculations using the Big-M method. Tests on several large datasets with high renewable energy penetration demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. In particular, the sparse weighted oblique decision tree outperforms the state-of-art weighted oblique decision tree while keeping the security rules simple. When embedded in the economic dispatch, these rules significantly increase the percentage of secure states and reduce the average solution time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge