Qibin Ye
Low-Complexity Joint Azimuth-Range-Velocity Estimation for Integrated Sensing and Communication with OFDM Waveform
May 15, 2024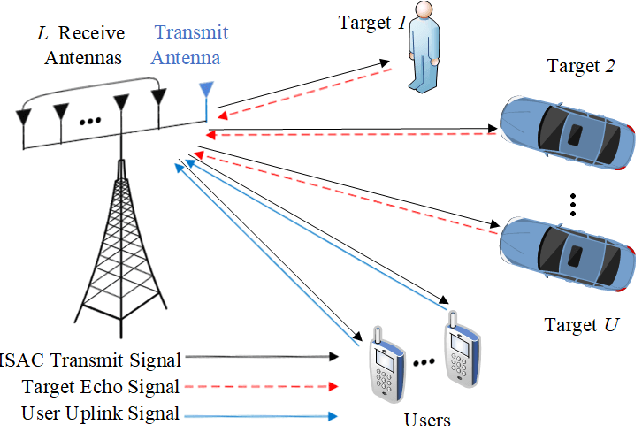
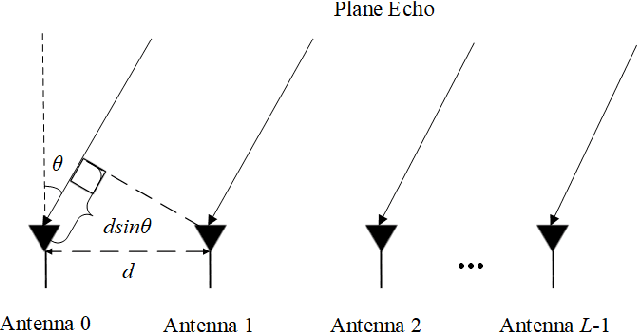
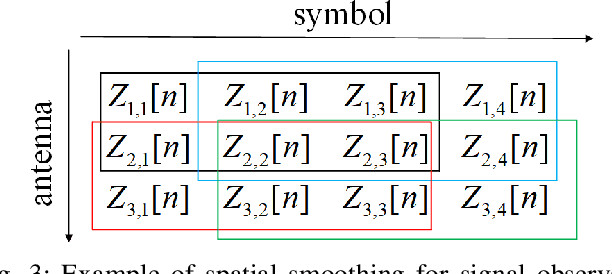
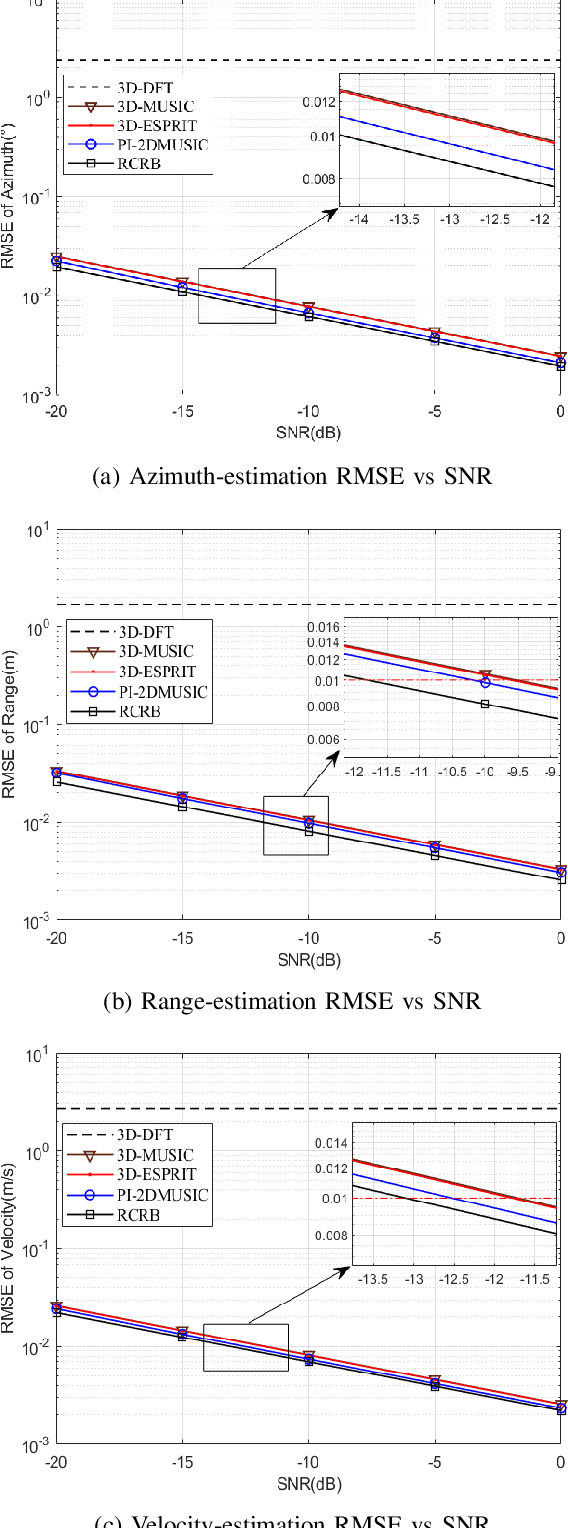
Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a main application scenario of the sixth-generation mobile communication systems. Due to the fast-growing number of antennas and subcarriers in cellular systems, the computational complexity of joint azimuth-range-velocity estimation (JARVE) in ISAC systems is extremely high. This paper studies the JARVE problem for a monostatic ISAC system with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) waveform, in which a base station receives the echos of its transmitted cellular OFDM signals to sense multiple targets. The Cramer-Rao bounds are first derived for JARVE. A low-complexity algorithm is further designed for super-resolution JARVE, which utilizes the proposed iterative subspace update scheme and Levenberg-Marquardt optimization method to replace the exhaustive search of spatial spectrum in multiple-signal-classification (MUSIC) algorithm. Finally, with the practical parameters of 5G New Radio, simulation results verify that the proposed algorithm can reduce the computational complexity by three orders of magnitude and two orders of magnitude compared to the existing three-dimensional MUSIC algorithm and estimation-of-signal-parameters-using-rotational-invariance-techniques (ESPRIT) algorithm, respectively, and also improve the estimation performance.
Joint Range-Velocity-Azimuth Estimation for OFDM-Based Integrated Sensing and Communication
Dec 20, 2023



Abstract:Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)-based integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is promising for future sixth-generation mobile communication systems. Existing works focus on the joint estimation of the targets' range and velocity for OFDM-based ISAC systems. In contrast, this paper studies the three-dimensional joint estimation (3DJE) of range, velocity, and azimuth for OFDM-based ISAC systems with multiple receive antennas. First, we establish the signal model and derive the Cramer-Rao bounds (CRBs) on the 3DJE. Furthermore, an auto-paired super-resolution 3DJE algorithm is proposed by exploiting the reconstructed observation sub-signal's translational invariance property in the time, frequency, and space domains. Finally, with the 5G New Radio parameter setup, simulation results show that the proposed algorithm achieves better estimation performance and its root mean square error is closer to the root of CRBs than existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge