Purvesh Khatri
Development of Machine Learning Classifiers for Blood-based Diagnosis and Prognosis of Suspected Acute Infections and Sepsis
Jul 03, 2024



Abstract:We applied machine learning to the unmet medical need of rapid and accurate diagnosis and prognosis of acute infections and sepsis in emergency departments. Our solution consists of a Myrna (TM) Instrument and embedded TriVerity (TM) classifiers. The instrument measures abundances of 29 messenger RNAs in patient's blood, subsequently used as features for machine learning. The classifiers convert the input features to an intuitive test report comprising the separate likelihoods of (1) a bacterial infection (2) a viral infection, and (3) severity (need for Intensive Care Unit-level care). In internal validation, the system achieved AUROC = 0.83 on the three-class disease diagnosis (bacterial, viral, or non-infected) and AUROC = 0.77 on binary prognosis of disease severity. The Myrna, TriVerity system was granted breakthrough device designation by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This engineering manuscript teaches the standard and novel machine learning methods used to translate an academic research concept to a clinical product aimed at improving patient care, and discusses lessons learned.
Use of a Structured Knowledge Base Enhances Metadata Curation by Large Language Models
Apr 08, 2024
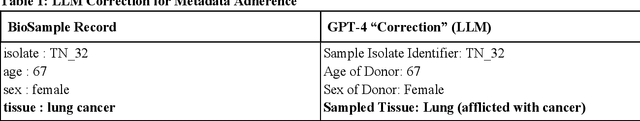
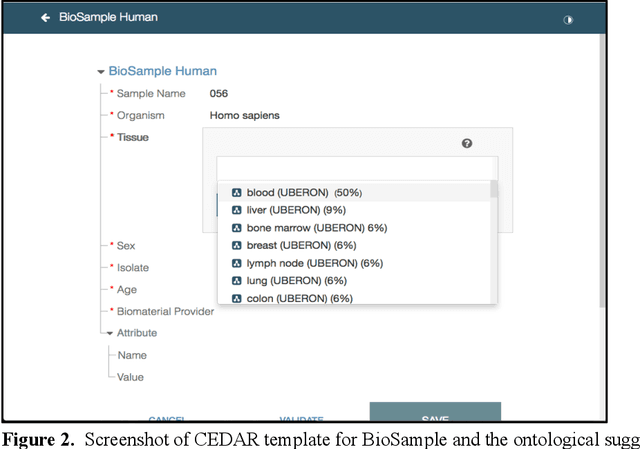

Abstract:Metadata play a crucial role in ensuring the findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability of datasets. This paper investigates the potential of large language models (LLMs), specifically GPT-4, to improve adherence to metadata standards. We conducted experiments on 200 random data records describing human samples relating to lung cancer from the NCBI BioSample repository, evaluating GPT-4's ability to suggest edits for adherence to metadata standards. We computed the adherence accuracy of field name-field value pairs through a peer review process, and we observed a marginal average improvement in adherence to the standard data dictionary from 79% to 80% (p<0.01). We then prompted GPT-4 with domain information in the form of the textual descriptions of CEDAR templates and recorded a significant improvement to 97% from 79% (p<0.01). These results indicate that, while LLMs may not be able to correct legacy metadata to ensure satisfactory adherence to standards when unaided, they do show promise for use in automated metadata curation when integrated with a structured knowledge base.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge