Pratyush Anand
Dynamic Inhomogeneous Quantum Resource Scheduling with Reinforcement Learning
May 25, 2024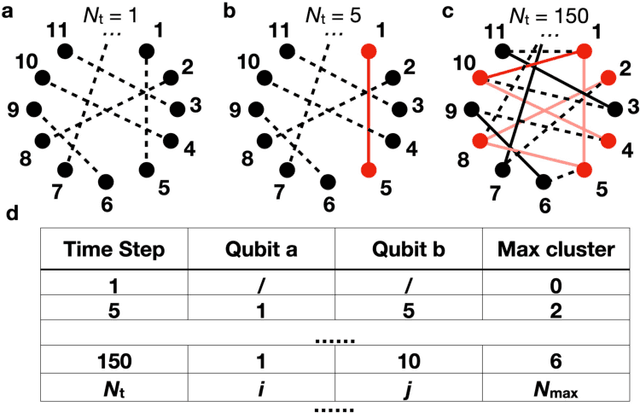
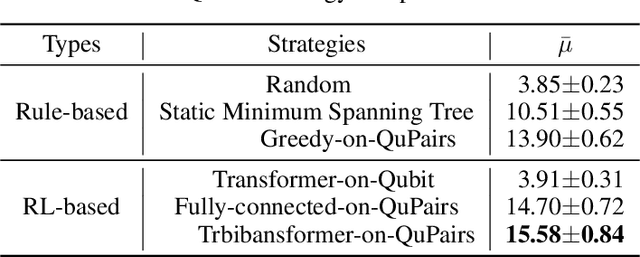
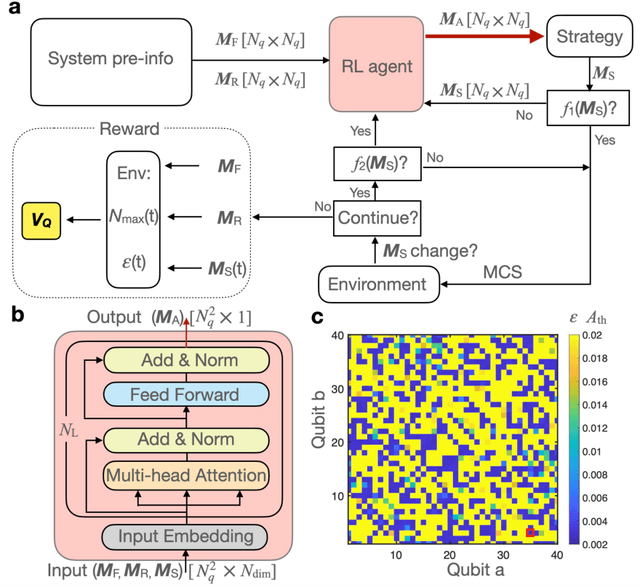
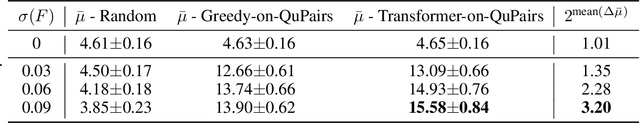
Abstract:A central challenge in quantum information science and technology is achieving real-time estimation and feedforward control of quantum systems. This challenge is compounded by the inherent inhomogeneity of quantum resources, such as qubit properties and controls, and their intrinsically probabilistic nature. This leads to stochastic challenges in error detection and probabilistic outcomes in processes such as heralded remote entanglement. Given these complexities, optimizing the construction of quantum resource states is an NP-hard problem. In this paper, we address the quantum resource scheduling issue by formulating the problem and simulating it within a digitized environment, allowing the exploration and development of agent-based optimization strategies. We employ reinforcement learning agents within this probabilistic setting and introduce a new framework utilizing a Transformer model that emphasizes self-attention mechanisms for pairs of qubits. This approach facilitates dynamic scheduling by providing real-time, next-step guidance. Our method significantly improves the performance of quantum systems, achieving more than a 3$\times$ improvement over rule-based agents, and establishes an innovative framework that improves the joint design of physical and control systems for quantum applications in communication, networking, and computing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge