Pranav Garimidi
PROPm Allocations of Indivisible Goods to Multiple Agents
May 24, 2021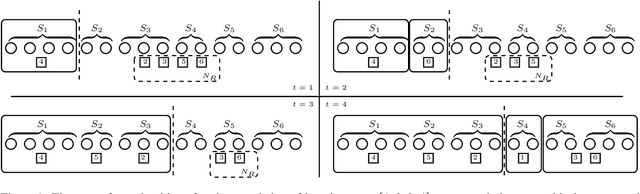
Abstract:We study the classic problem of fairly allocating a set of indivisible goods among a group of agents, and focus on the notion of approximate proportionality known as PROPm. Prior work showed that there exists an allocation that satisfies this notion of fairness for instances involving up to five agents, but fell short of proving that this is true in general. We extend this result to show that a PROPm allocation is guaranteed to exist for all instances, independent of the number of agents or goods. Our proof is constructive, providing an algorithm that computes such an allocation and, unlike prior work, the running time of this algorithm is polynomial in both the number of agents and the number of goods.
Achieving Proportionality up to the Maximin Item with Indivisible Goods
Sep 22, 2020Abstract:We study the problem of fairly allocating indivisible goods and focus on the classic fairness notion of proportionality. The indivisibility of the goods is long known to pose highly non-trivial obstacles to achieving fairness, and a very vibrant line of research has aimed to circumvent them using appropriate notions of approximate fairness. Recent work has established that even approximate versions of proportionality (PROPx) may be impossible to achieve even for small instances, while the best known achievable approximations (PROP1) are much weaker. We introduce the notion of proportionality up to the maximin item (PROPm) and show how to reach an allocation satisfying this notion for any instance involving up to five agents with additive valuations. PROPm provides a well motivated middle-ground between PROP1 and PROPx, while also capturing some elements of the well-studied maximin share (MMS) benchmark: another relaxation of proportionality that has attracted a lot of attention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge