Po-Yu Liang
PepEDiff: Zero-Shot Peptide Binder Design via Protein Embedding Diffusion
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:We present PepEDiff, a novel peptide binder generator that designs binding sequences given a target receptor protein sequence and its pocket residues. Peptide binder generation is critical in therapeutic and biochemical applications, yet many existing methods rely heavily on intermediate structure prediction, adding complexity and limiting sequence diversity. Our approach departs from this paradigm by generating binder sequences directly in a continuous latent space derived from a pretrained protein embedding model, without relying on predicted structures, thereby improving structural and sequence diversity. To encourage the model to capture binding-relevant features rather than memorizing known sequences, we perform latent-space exploration and diffusion-based sampling, enabling the generation of peptides beyond the limited distribution of known binders. This zero-shot generative strategy leverages the global protein embedding manifold as a semantic prior, allowing the model to propose novel peptide sequences in previously unseen regions of the protein space. We evaluate PepEDiff on TIGIT, a challenging target with a large, flat protein-protein interaction interface that lacks a druggable pocket. Despite its simplicity, our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches across benchmark tests and in the TIGIT case study, demonstrating its potential as a general, structure-free framework for zero-shot peptide binder design. The code for this research is available at GitHub: https://github.com/LabJunBMI/PepEDiff-An-Peptide-binder-Embedding-Diffusion-Model
E(3)-invariant diffusion model for pocket-aware peptide generation
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Biologists frequently desire protein inhibitors for a variety of reasons, including use as research tools for understanding biological processes and application to societal problems in agriculture, healthcare, etc. Immunotherapy, for instance, relies on immune checkpoint inhibitors to block checkpoint proteins, preventing their binding with partner proteins and boosting immune cell function against abnormal cells. Inhibitor discovery has long been a tedious process, which in recent years has been accelerated by computational approaches. Advances in artificial intelligence now provide an opportunity to make inhibitor discovery smarter than ever before. While extensive research has been conducted on computer-aided inhibitor discovery, it has mainly focused on either sequence-to-structure mapping, reverse mapping, or bio-activity prediction, making it unrealistic for biologists to utilize such tools. Instead, our work proposes a new method of computer-assisted inhibitor discovery: de novo pocket-aware peptide structure and sequence generation network. Our approach consists of two sequential diffusion models for end-to-end structure generation and sequence prediction. By leveraging angle and dihedral relationships between backbone atoms, we ensure an E(3)-invariant representation of peptide structures. Our results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art models, highlighting its potential in pocket-aware peptide design. This work offers a new approach for precise drug discovery using receptor-specific peptide generation.
E(3)-invaraint diffusion model for pocket-aware peptide generation
Oct 27, 2024



Abstract:Biologists frequently desire protein inhibitors for a variety of reasons, including use as research tools for understanding biological processes and application to societal problems in agriculture, healthcare, etc. Immunotherapy, for instance, relies on immune checkpoint inhibitors to block checkpoint proteins, preventing their binding with partner proteins and boosting immune cell function against abnormal cells. Inhibitor discovery has long been a tedious process, which in recent years has been accelerated by computational approaches. Advances in artificial intelligence now provide an opportunity to make inhibitor discovery smarter than ever before. While extensive research has been conducted on computer-aided inhibitor discovery, it has mainly focused on either sequence-to-structure mapping, reverse mapping, or bio-activity prediction, making it unrealistic for biologists to utilize such tools. Instead, our work proposes a new method of computer-assisted inhibitor discovery: de novo pocket-aware peptide structure and sequence generation network. Our approach consists of two sequential diffusion models for end-to-end structure generation and sequence prediction. By leveraging angle and dihedral relationships between backbone atoms, we ensure an E(3)-invariant representation of peptide structures. Our results demonstrate that our method achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art models, highlighting its potential in pocket-aware peptide design. This work offers a new approach for precise drug discovery using receptor-specific peptide generation.
Exploring Latent Space for Generating Peptide Analogs Using Protein Language Models
Aug 15, 2024
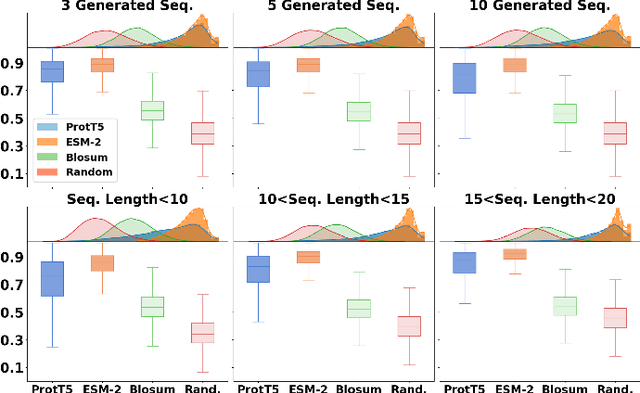


Abstract:Generating peptides with desired properties is crucial for drug discovery and biotechnology. Traditional sequence-based and structure-based methods often require extensive datasets, which limits their effectiveness. In this study, we proposed a novel method that utilized autoencoder shaped models to explore the protein embedding space, and generate novel peptide analogs by leveraging protein language models. The proposed method requires only a single sequence of interest, avoiding the need for large datasets. Our results show significant improvements over baseline models in similarity indicators of peptide structures, descriptors and bioactivities. The proposed method validated through Molecular Dynamics simulations on TIGIT inhibitors, demonstrates that our method produces peptide analogs with similar yet distinct properties, highlighting its potential to enhance peptide screening processes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge