Pierre De Loor
CERV, Lab-STICC
Resource for Error Analysis in Text Simplification: New Taxonomy and Test Collection
May 22, 2025Abstract:The general public often encounters complex texts but does not have the time or expertise to fully understand them, leading to the spread of misinformation. Automatic Text Simplification (ATS) helps make information more accessible, but its evaluation methods have not kept up with advances in text generation, especially with Large Language Models (LLMs). In particular, recent studies have shown that current ATS metrics do not correlate with the presence of errors. Manual inspections have further revealed a variety of errors, underscoring the need for a more nuanced evaluation framework, which is currently lacking. This resource paper addresses this gap by introducing a test collection for detecting and classifying errors in simplified texts. First, we propose a taxonomy of errors, with a formal focus on information distortion. Next, we introduce a parallel dataset of automatically simplified scientific texts. This dataset has been human-annotated with labels based on our proposed taxonomy. Finally, we analyze the quality of the dataset, and we study the performance of existing models to detect and classify errors from that taxonomy. These contributions give researchers the tools to better evaluate errors in ATS, develop more reliable models, and ultimately improve the quality of automatically simplified texts.
Effects of Coupling in Human-Virtual Agent Body Interaction
Sep 19, 2014



Abstract:This paper presents a study of the dynamic coupling between a user and a virtual character during body interaction. Coupling is directly linked with other dimensions, such as co-presence, engagement, and believability, and was measured in an experiment that allowed users to describe their subjective feelings about those dimensions of interest. The experiment was based on a theatrical game involving the imitation of slow upper-body movements and the proposal of new movements by the user and virtual agent. The agent's behaviour varied in autonomy: the agent could limit itself to imitating the user's movements only, initiate new movements, or combine both behaviours. After the game, each participant completed a questionnaire regarding their engagement in the interaction, their subjective feeling about the co-presence of the agent, etc. Based on four main dimensions of interest, we tested several hypotheses against our experimental results, which are discussed here.
Enaction-Based Artificial Intelligence: Toward Coevolution with Humans in the Loop
Feb 26, 2014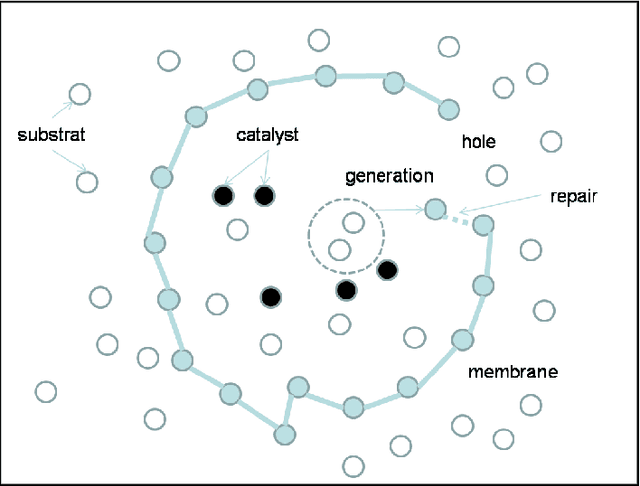
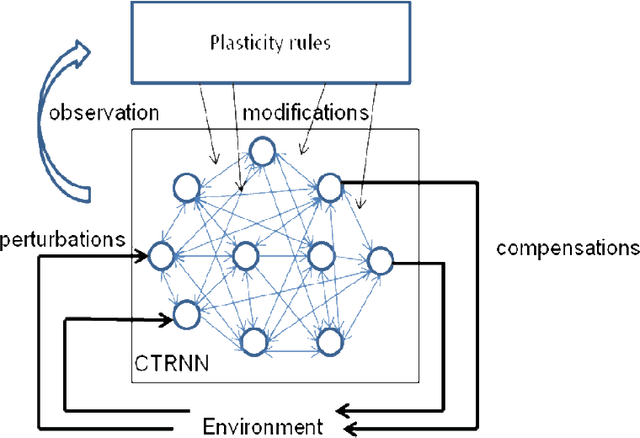
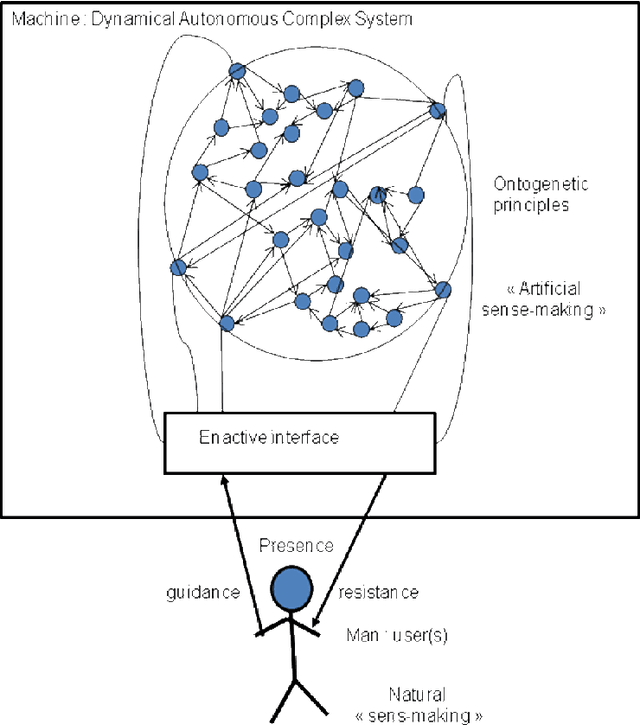
Abstract:This article deals with the links between the enaction paradigm and artificial intelligence. Enaction is considered a metaphor for artificial intelligence, as a number of the notions which it deals with are deemed incompatible with the phenomenal field of the virtual. After explaining this stance, we shall review previous works regarding this issue in terms of artifical life and robotics. We shall focus on the lack of recognition of co-evolution at the heart of these approaches. We propose to explicitly integrate the evolution of the environment into our approach in order to refine the ontogenesis of the artificial system, and to compare it with the enaction paradigm. The growing complexity of the ontogenetic mechanisms to be activated can therefore be compensated by an interactive guidance system emanating from the environment. This proposition does not however resolve that of the relevance of the meaning created by the machine (sense-making). Such reflections lead us to integrate human interaction into this environment in order to construct relevant meaning in terms of participative artificial intelligence. This raises a number of questions with regards to setting up an enactive interaction. The article concludes by exploring a number of issues, thereby enabling us to associate current approaches with the principles of morphogenesis, guidance, the phenomenology of interactions and the use of minimal enactive interfaces in setting up experiments which will deal with the problem of artificial intelligence in a variety of enaction-based ways.
Real-time retrieval for case-based reasoning in interactive multiagent-based simulations
Jul 17, 2011



Abstract:The aim of this paper is to present the principles and results about case-based reasoning adapted to real- time interactive simulations, more precisely concerning retrieval mechanisms. The article begins by introducing the constraints involved in interactive multiagent-based simulations. The second section pre- sents a framework stemming from case-based reasoning by autonomous agents. Each agent uses a case base of local situations and, from this base, it can choose an action in order to interact with other auton- omous agents or users' avatars. We illustrate this framework with an example dedicated to the study of dynamic situations in football. We then go on to address the difficulties of conducting such simulations in real-time and propose a model for case and for case base. Using generic agents and adequate case base structure associated with a dedicated recall algorithm, we improve retrieval performance under time pressure compared to classic CBR techniques. We present some results relating to the performance of this solution. The article concludes by outlining future development of our project.
From decision to action : intentionality, a guide for the specification of intelligent agents' behaviour
Jul 17, 2011



Abstract:This article introduces a reflexion about behavioural specification for interactive and participative agent-based simulation in virtual reality. Within this context, it is neces sary to reach a high level of expressivness in order to enforce interactions between the designer and the behavioural model during the in-line prototyping. This requires to consider the need of semantic very early in the design process. The Intentional agent model is here exposed as a possible answer. It relies on a mixed imperative and declarative approach which focuses on the link between decision and action. The design of a tool able to simulate virtual environment implying agents based on this model is discuss
Learning a Representation of a Believable Virtual Character's Environment with an Imitation Algorithm
Dec 29, 2010
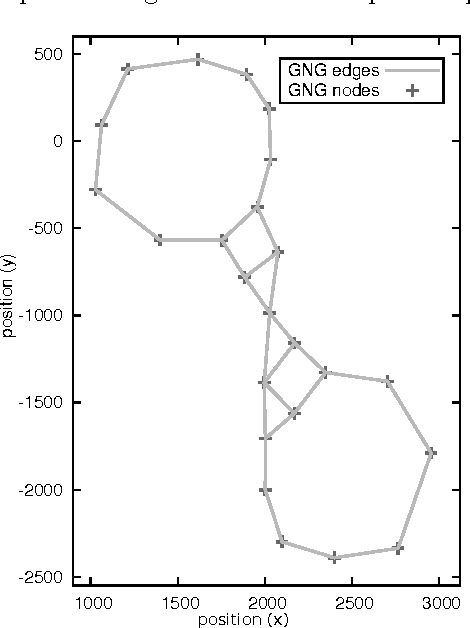
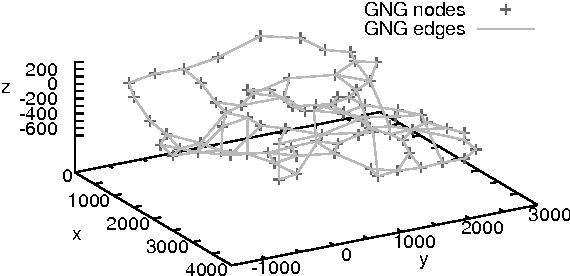
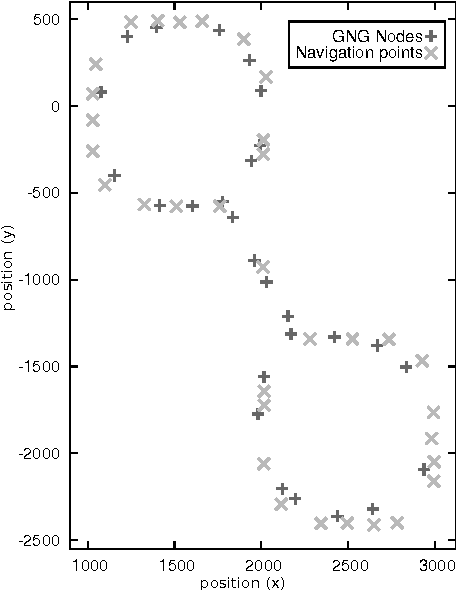
Abstract:In video games, virtual characters' decision systems often use a simplified representation of the world. To increase both their autonomy and believability we want those characters to be able to learn this representation from human players. We propose to use a model called growing neural gas to learn by imitation the topology of the environment. The implementation of the model, the modifications and the parameters we used are detailed. Then, the quality of the learned representations and their evolution during the learning are studied using different measures. Improvements for the growing neural gas to give more information to the character's model are given in the conclusion.
The Challenge of Believability in Video Games: Definitions, Agents Models and Imitation Learning
Sep 02, 2010Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of creating believable agents (virtual characters) in video games. We consider only one meaning of believability, ``giving the feeling of being controlled by a player'', and outline the problem of its evaluation. We present several models for agents in games which can produce believable behaviours, both from industry and research. For high level of believability, learning and especially imitation learning seems to be the way to go. We make a quick overview of different approaches to make video games' agents learn from players. To conclude we propose a two-step method to develop new models for believable agents. First we must find the criteria for believability for our application and define an evaluation method. Then the model and the learning algorithm can be designed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge