Fabien Tencé
LISYC
Learning a Representation of a Believable Virtual Character's Environment with an Imitation Algorithm
Dec 29, 2010
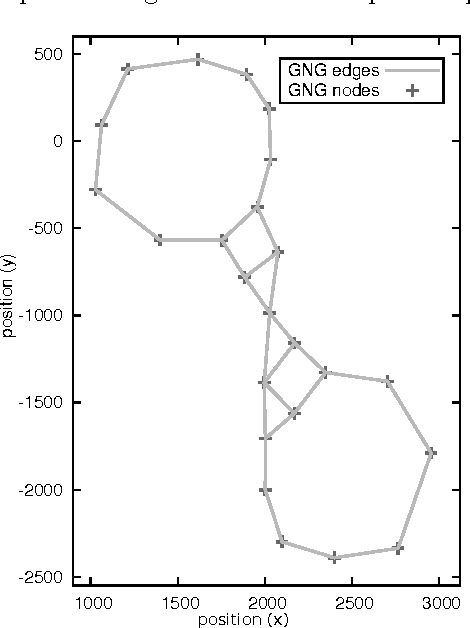
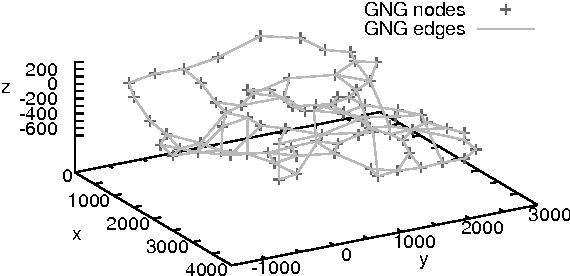
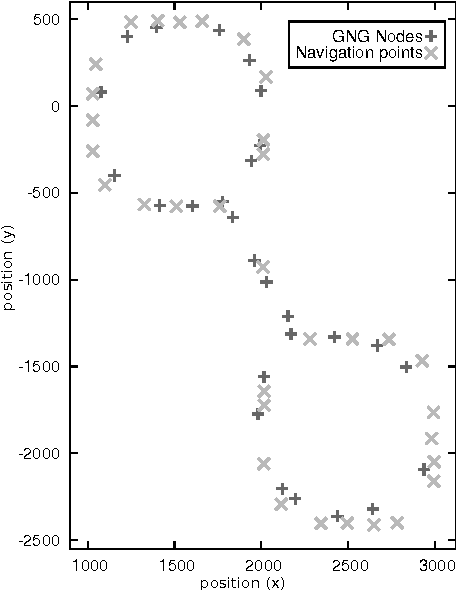
Abstract:In video games, virtual characters' decision systems often use a simplified representation of the world. To increase both their autonomy and believability we want those characters to be able to learn this representation from human players. We propose to use a model called growing neural gas to learn by imitation the topology of the environment. The implementation of the model, the modifications and the parameters we used are detailed. Then, the quality of the learned representations and their evolution during the learning are studied using different measures. Improvements for the growing neural gas to give more information to the character's model are given in the conclusion.
Automatable Evaluation Method Oriented toward Behaviour Believability for Video Games
Sep 02, 2010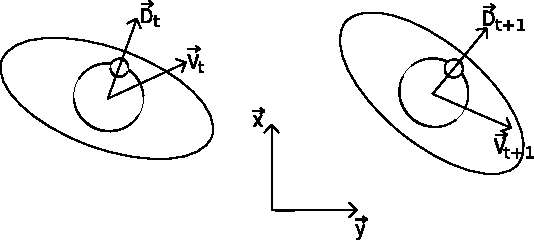
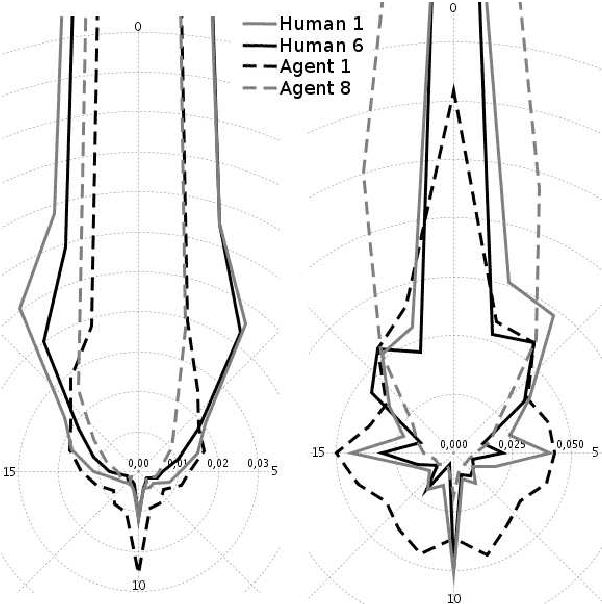
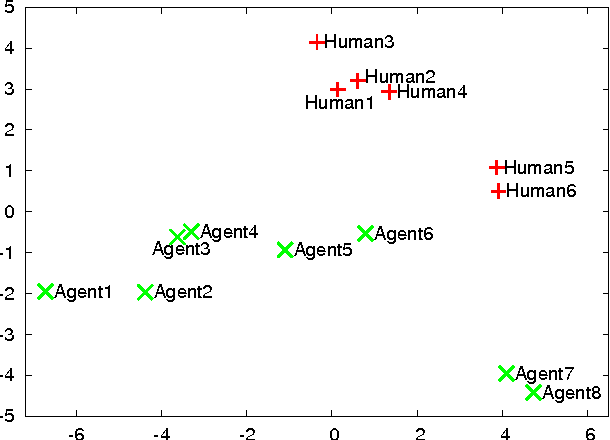
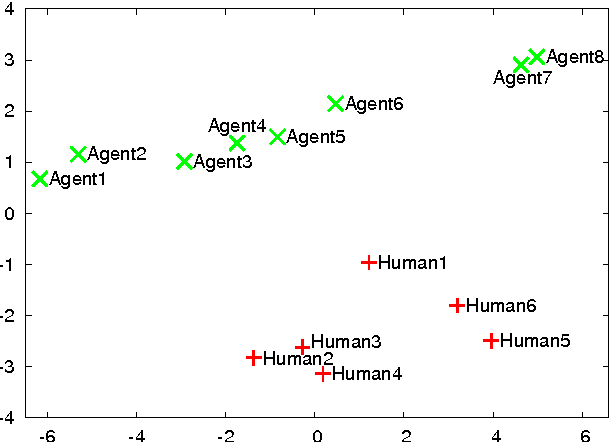
Abstract:Classic evaluation methods of believable agents are time-consuming because they involve many human to judge agents. They are well suited to validate work on new believable behaviours models. However, during the implementation, numerous experiments can help to improve agents' believability. We propose a method which aim at assessing how much an agent's behaviour looks like humans' behaviours. By representing behaviours with vectors, we can store data computed for humans and then evaluate as many agents as needed without further need of humans. We present a test experiment which shows that even a simple evaluation following our method can reveal differences between quite believable agents and humans. This method seems promising although, as shown in our experiment, results' analysis can be difficult.
The Challenge of Believability in Video Games: Definitions, Agents Models and Imitation Learning
Sep 02, 2010Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of creating believable agents (virtual characters) in video games. We consider only one meaning of believability, ``giving the feeling of being controlled by a player'', and outline the problem of its evaluation. We present several models for agents in games which can produce believable behaviours, both from industry and research. For high level of believability, learning and especially imitation learning seems to be the way to go. We make a quick overview of different approaches to make video games' agents learn from players. To conclude we propose a two-step method to develop new models for believable agents. First we must find the criteria for believability for our application and define an evaluation method. Then the model and the learning algorithm can be designed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge