Pierluigi Pisu
A Multi-Scale Isolation Forest Approach for Real-Time Detection and Filtering of FGSM Adversarial Attacks in Video Streams of Autonomous Vehicles
Feb 22, 2025



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have demonstrated remarkable success across a wide range of tasks, particularly in fields such as image classification. However, DNNs are highly susceptible to adversarial attacks, where subtle perturbations are introduced to input images, leading to erroneous model outputs. In today's digital era, ensuring the security and integrity of images processed by DNNs is of critical importance. One of the most prominent adversarial attack methods is the Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM), which perturbs images in the direction of the loss gradient to deceive the model. This paper presents a novel approach for detecting and filtering FGSM adversarial attacks in image processing tasks. Our proposed method evaluates 10,000 images, each subjected to five different levels of perturbation, characterized by $\epsilon$ values of 0.01, 0.02, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2. These perturbations are applied in the direction of the loss gradient. We demonstrate that our approach effectively filters adversarially perturbed images, mitigating the impact of FGSM attacks. The method is implemented in Python, and the source code is publicly available on GitHub for reproducibility and further research.
A Robust Adversarial Ensemble with Causal (Feature Interaction) Interpretations for Image Classification
Dec 28, 2024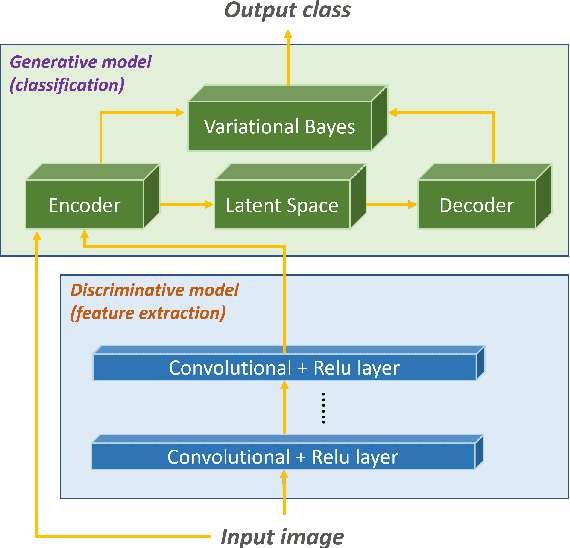
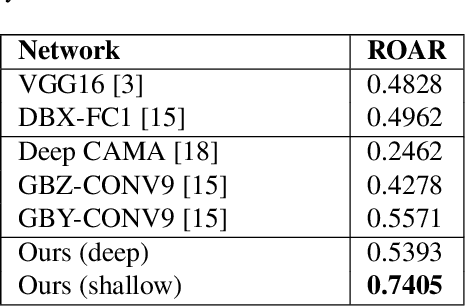
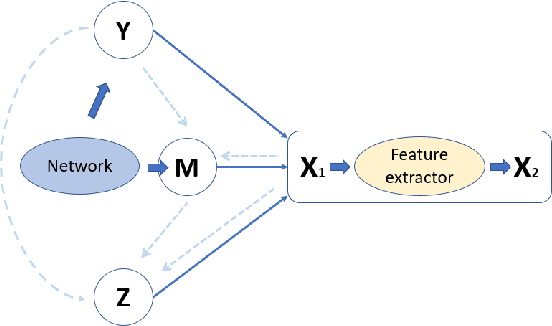
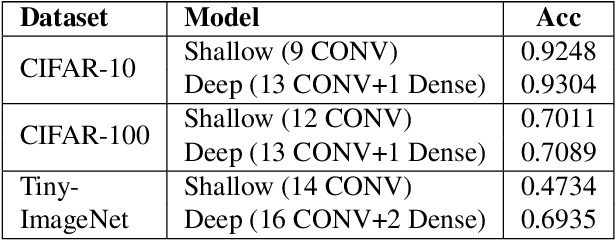
Abstract:Deep learning-based discriminative classifiers, despite their remarkable success, remain vulnerable to adversarial examples that can mislead model predictions. While adversarial training can enhance robustness, it fails to address the intrinsic vulnerability stemming from the opaque nature of these black-box models. We present a deep ensemble model that combines discriminative features with generative models to achieve both high accuracy and adversarial robustness. Our approach integrates a bottom-level pre-trained discriminative network for feature extraction with a top-level generative classification network that models adversarial input distributions through a deep latent variable model. Using variational Bayes, our model achieves superior robustness against white-box adversarial attacks without adversarial training. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 demonstrate our model's superior adversarial robustness. Through evaluations using counterfactual metrics and feature interaction-based metrics, we establish correlations between model interpretability and adversarial robustness. Additionally, preliminary results on Tiny-ImageNet validate our approach's scalability to more complex datasets, offering a practical solution for developing robust image classification models.
An Anomaly Detection System Based on Generative Classifiers for Controller Area Network
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:As electronic systems become increasingly complex and prevalent in modern vehicles, securing onboard networks is crucial, particularly as many of these systems are safety-critical. Researchers have demonstrated that modern vehicles are susceptible to various types of attacks, enabling attackers to gain control and compromise safety-critical electronic systems. Consequently, several Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) have been proposed in the literature to detect such cyber-attacks on vehicles. This paper introduces a novel generative classifier-based Intrusion Detection System (IDS) designed for anomaly detection in automotive networks, specifically focusing on the Controller Area Network (CAN). Leveraging variational Bayes, our proposed IDS utilizes a deep latent variable model to construct a causal graph for conditional probabilities. An auto-encoder architecture is utilized to build the classifier to estimate conditional probabilities, which contribute to the final prediction probabilities through Bayesian inference. Comparative evaluations against state-of-the-art IDSs on a public Car-hacking dataset highlight our proposed classifier's superior performance in improving detection accuracy and F1-score. The proposed IDS demonstrates its efficacy by outperforming existing models with limited training data, providing enhanced security assurance for automotive systems.
LSTM-based Load Forecasting Robustness Against Noise Injection Attack in Microgrid
Apr 25, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the robustness of an LSTM neural network against noise injection attacks for electric load forecasting in an ideal microgrid. The performance of the LSTM model is investigated under a black-box Gaussian noise attack with different SNRs. It is assumed that attackers have just access to the input data of the LSTM model. The results show that the noise attack affects the performance of the LSTM model. The load prediction means absolute error (MAE) is 0.047 MW for a healthy prediction, while this value increases up to 0.097 MW for a Gaussian noise insertion with SNR= 6 dB. To robustify the LSTM model against noise attack, a low-pass filter with optimal cut-off frequency is applied at the model's input to remove the noise attack. The filter performs better in case of noise with lower SNR and is less promising for small noises.
The Effect of Dust and Sand on the 5G Terrestrial Links
Aug 20, 2021



Abstract:Wireless connections are a communication channel used to support different applications in our life such as microwave connections, mobile cellular networks, and intelligent transportation systems. The wireless communication channels are affected by different weather factors such as rain, snow, fog, dust, and sand. This effect is more evident in the high frequencies of the millimeter-wave (mm-wave) band. Recently, the 5G opened the door to support different applications with high speed and good quality. A recent study investigates the effect of rain and snow on the 5G communication channel to reduce the challenge of using high millimeter-wave frequencies. This research investigates the impact of dust and sand on the communication channel of 5G mini links using Mie scattering model to estimate the propagating wave's attenuation by computing the free space loss of a dusty region. Also, the cross-polarization of the propagating wave with dust and sand is taken into account at different distances of the propagating length. Two kinds of mini links, ML-6363, and ML-6352, are considered to demonstrate the effect of dust and sand in these specific operating frequency bands. The 73.5 GHz (V-band) and (21.5GHz (K-band) are the ML-6352 and ML-6363 radio frequency, respectively. Also, signal depolarization is another important radio frequency transmission parameter that is considered heroin. The numerical and simulation results show that the 5G ML-6352 is more effect by dust and sand than ML6363. The 5G toolbox is used to build the communication system and simulate the effect of the dust and sand on the different frequency bands.
Behavior Identification and Prediction for a Probabilistic Risk Framework
May 20, 2019



Abstract:Operation in a real world traffic requires autonomous vehicles to be able to plan their motion in complex environments (multiple moving participants). Planning through such environment requires the right search space to be provided for the trajectory or maneuver planners so that the safest motion for the ego vehicle can be identified. Given the current states of the environment and its participants, analyzing the risks based on the predicted trajectories of all the traffic participants provides the necessary search space for the planning of motion. This paper provides a fresh taxonomy of safety / risks that an autonomous vehicle should be able to handle while navigating through traffic. It provides a reference system architecture that needs to be implemented as well as describes a novel way of identifying and predicting the behaviors of the traffic participants using classic Multi Model Adaptive Estimation (MMAE). Preliminary simulation results of the implemented model are included.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge