Phillip Wozny
AI4GCC - Team: Below Sea Level: Critiques and Improvements
Aug 04, 2023

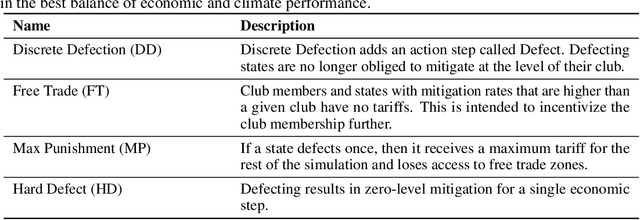
Abstract:We present a critical analysis of the simulation framework RICE-N, an integrated assessment model (IAM) for evaluating the impacts of climate change on the economy. We identify key issues with RICE-N, including action masking and irrelevant actions, and suggest improvements such as utilizing tariff revenue and penalizing overproduction. We also critically engage with features of IAMs in general, namely overly optimistic damage functions and unrealistic abatement cost functions. Our findings contribute to the ongoing efforts to further develop the RICE-N framework in an effort to improve the simulation, making it more useful as an inspiration for policymakers.
AI4GCC-Team -- Below Sea Level: Score and Real World Relevance
Aug 04, 2023

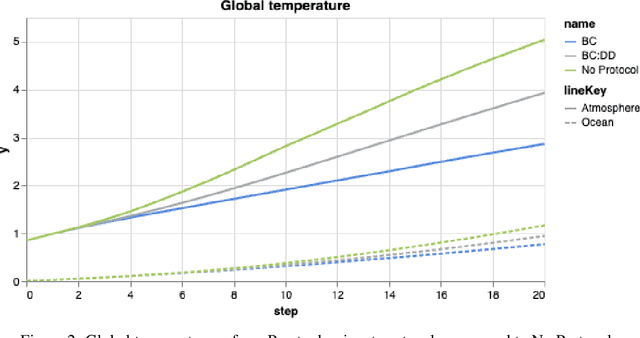
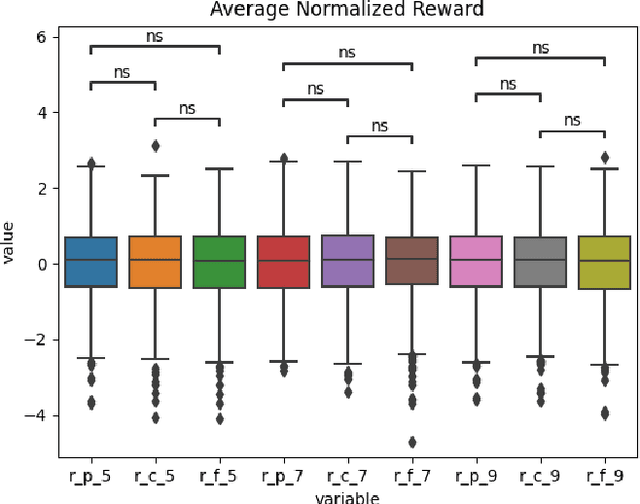
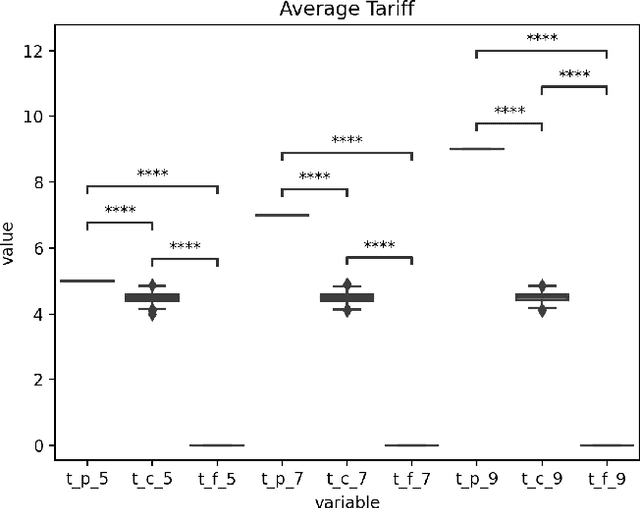
Abstract:As our submission for track three of the AI for Global Climate Cooperation (AI4GCC) competition, we propose a negotiation protocol for use in the RICE-N climate-economic simulation. Our proposal seeks to address the challenges of carbon leakage through methods inspired by the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and Climate Clubs (CC). We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach by comparing simulated outcomes to representative concentration pathways (RCP) and shared socioeconomic pathways (SSP). Our protocol results in a temperature rise comparable to RCP 3.4/4.5 and SSP 2. Furthermore, we provide an analysis of our protocol's World Trade Organization compliance, administrative and political feasibility, and ethical concerns. We recognize that our proposal risks hurting the least developing countries, and we suggest specific corrective measures to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities, such as technology sharing and wealth redistribution. Future research should improve the RICE-N tariff mechanism and implement actions allowing for the aforementioned corrective measures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge