Philipp Hanslovsky
HHMI Janelia Research Campus
Image-Based Correction of Continuous and Discontinuous Non-Planar Axial Distortion in Serial Section Microscopy
Jun 17, 2016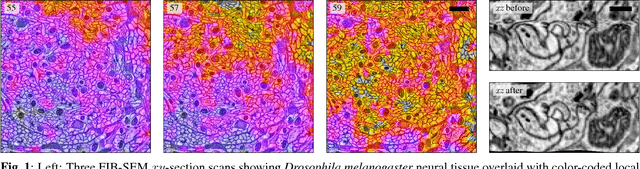
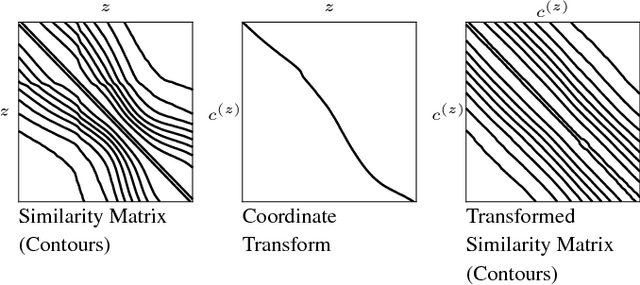
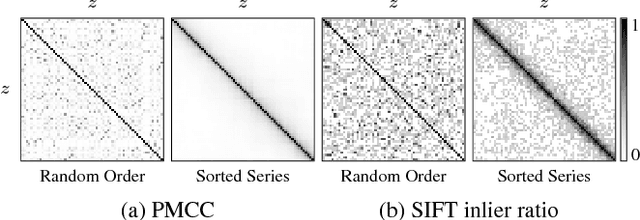
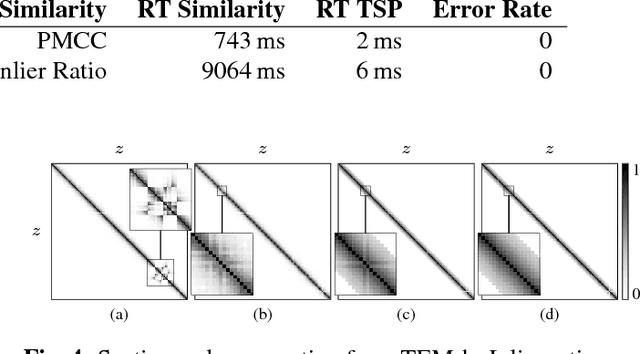
Abstract:Motivation: Serial section microscopy is an established method for detailed anatomy reconstruction of biological specimen. During the last decade, high resolution electron microscopy (EM) of serial sections has become the de-facto standard for reconstruction of neural connectivity at ever increasing scales (EM connectomics). In serial section microscopy, the axial dimension of the volume is sampled by physically removing thin sections from the embedded specimen and subsequently imaging either the block-face or the section series. This process has limited precision leading to inhomogeneous non-planar sampling of the axial dimension of the volume which, in turn, results in distorted image volumes. This includes that section series may be collected and imaged in unknown order. Results: We developed methods to identify and correct these distortions through image-based signal analysis without any additional physical apparatus or measurements. We demonstrate the efficacy of our methods in proof of principle experiments and application to real world problems. Availability and Implementation: We made our work available as libraries for the ImageJ distribution Fiji and for deployment in a high performance parallel computing environment. Our sources are open and available at http://github.com/saalfeldla/section-sort, http://github.com/saalfeldlab/em-thickness-estimation, and http://github.com/saalfeldlab/z-spacing-spark. Contact: saalfelds@janelia.hhmi.org
Robust Registration of Calcium Images by Learned Contrast Synthesis
Nov 03, 2015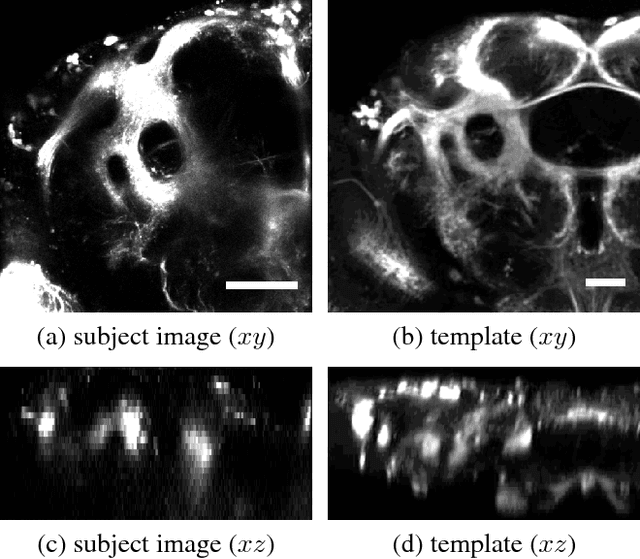
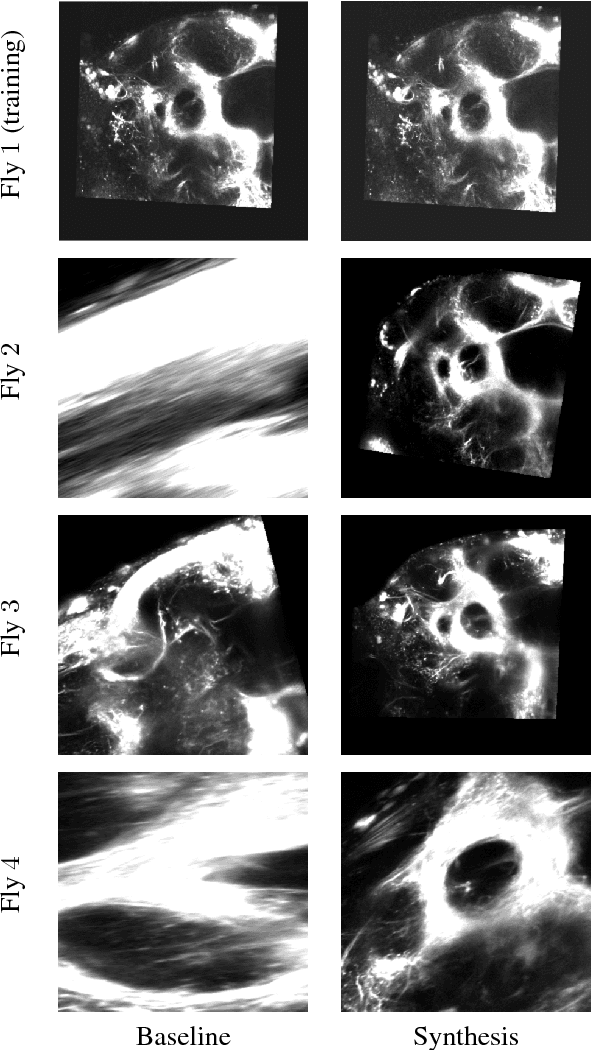
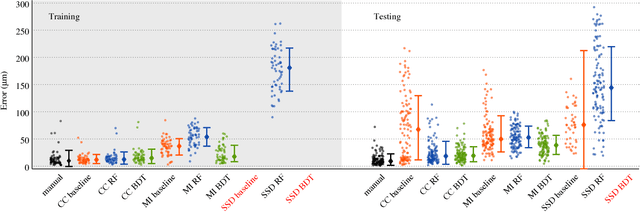
Abstract:Multi-modal image registration is a challenging task that is vital to fuse complementary signals for subsequent analyses. Despite much research into cost functions addressing this challenge, there exist cases in which these are ineffective. In this work, we show that (1) this is true for the registration of in-vivo Drosophila brain volumes visualizing genetically encoded calcium indicators to an nc82 atlas and (2) that machine learning based contrast synthesis can yield improvements. More specifically, the number of subjects for which the registration outright failed was greatly reduced (from 40% to 15%) by using a synthesized image.
Post-acquisition image based compensation for thickness variation in microscopy section series
May 27, 2015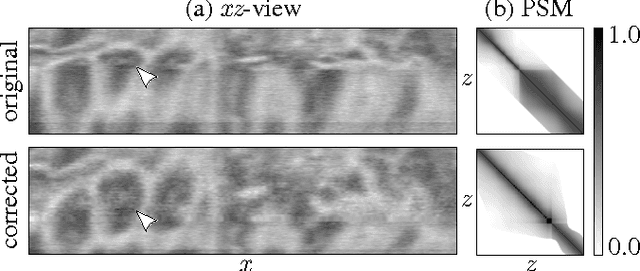

Abstract:Serial section Microscopy is an established method for volumetric anatomy reconstruction. Section series imaged with Electron Microscopy are currently vital for the reconstruction of the synaptic connectivity of entire animal brains such as that of Drosophila melanogaster. The process of removing ultrathin layers from a solid block containing the specimen, however, is a fragile procedure and has limited precision with respect to section thickness. We have developed a method to estimate the relative z-position of each individual section as a function of signal change across the section series. First experiments show promising results on both serial section Transmission Electron Microscopy (ssTEM) data and Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscopy (FIB-SEM) series. We made our solution available as Open Source plugins for the TrakEM2 software and the ImageJ distribution Fiji.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge