Philip Potter
Gender Detection on Social Networks using Ensemble Deep Learning
Apr 13, 2020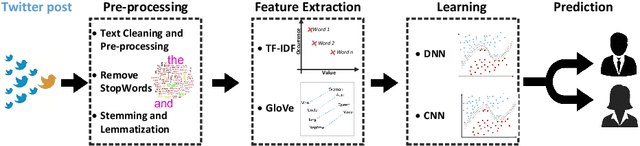
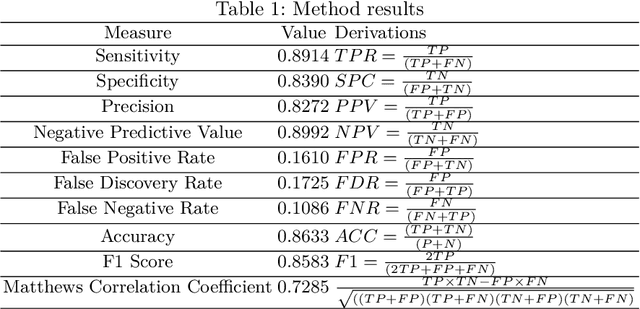


Abstract:Analyzing the ever-increasing volume of posts on social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter requires improved information processing methods for profiling authorship. Document classification is central to this task, but the performance of traditional supervised classifiers has degraded as the volume of social media has increased. This paper addresses this problem in the context of gender detection through ensemble classification that employs multi-model deep learning architectures to generate specialized understanding from different feature spaces.
Women in ISIS Propaganda: A Natural Language Processing Analysis of Topics and Emotions in a Comparison with Mainstream Religious Group
Dec 09, 2019


Abstract:Online propaganda is central to the recruitment strategies of extremist groups and in recent years these efforts have increasingly extended to women. To investigate ISIS' approach to targeting women in their online propaganda and uncover implications for counterterrorism, we rely on text mining and natural language processing (NLP). Specifically, we extract articles published in Dabiq and Rumiyah (ISIS's online English language publications) to identify prominent topics. To identify similarities or differences between these texts and those produced by non-violent religious groups, we extend the analysis to articles from a Catholic forum dedicated to women. We also perform an emotional analysis of both of these resources to better understand the emotional components of propaganda. We rely on Depechemood (a lexical-base emotion analysis method) to detect emotions most likely to be evoked in readers of these materials. The findings indicate that the emotional appeal of ISIS and Catholic materials are similar
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge