Pham Van Quang
Severity Detection Tool for Patients with Infectious Disease
Dec 10, 2019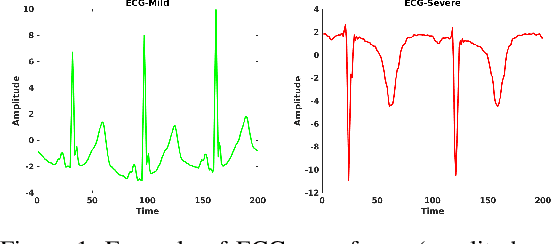
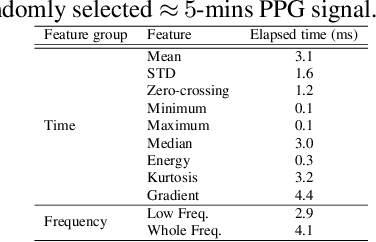
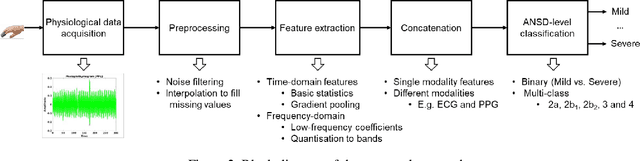
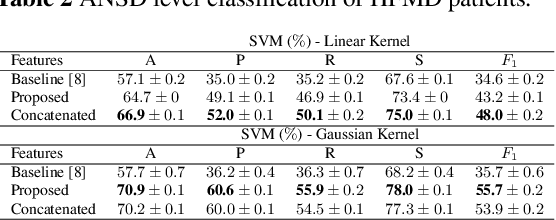
Abstract:Hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD) and tetanus are serious infectious diseases in low and middle income countries. Tetanus in particular has a high mortality rate and its treatment is resource-demanding. Furthermore, HFMD often affects a large number of infants and young children. As a result, its treatment consumes enormous healthcare resources, especially when outbreaks occur. Autonomic nervous system dysfunction (ANSD) is the main cause of death for both HFMD and tetanus patients. However, early detection of ANSD is a difficult and challenging problem. In this paper, we aim to provide a proof-of-principle to detect the ANSD level automatically by applying machine learning techniques to physiological patient data, such as electrocardiogram (ECG) and photoplethysmogram (PPG) waveforms, which can be collected using low-cost wearable sensors. Efficient features are extracted that encode variations in the waveforms in the time and frequency domains. A support vector machine is employed to classify the ANSD levels. The proposed approach is validated on multiple datasets of HFMD and tetanus patients in Vietnam. Results show that encouraging performance is achieved in classifying ANSD levels. Moreover, the proposed features are simple, more generalisable and outperformed the standard heart rate variability (HRV) analysis. The proposed approach would facilitate both the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases in low and middle income countries, and thereby improve overall patient care.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge