Peter Wurman
The Trajectory Alignment Coefficient in Two Acts: From Reward Tuning to Reward Learning
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The success of reinforcement learning (RL) is fundamentally tied to having a reward function that accurately reflects the task objective. Yet, designing reward functions is notoriously time-consuming and prone to misspecification. To address this issue, our first goal is to understand how to support RL practitioners in specifying appropriate weights for a reward function. We leverage the Trajectory Alignment Coefficient (TAC), a metric that evaluates how closely a reward function's induced preferences match those of a domain expert. To evaluate whether TAC provides effective support in practice, we conducted a human-subject study in which RL practitioners tuned reward weights for Lunar Lander. We found that providing TAC during reward tuning led participants to produce more performant reward functions and report lower cognitive workload relative to standard tuning without TAC. However, the study also underscored that manual reward design, even with TAC, remains labor-intensive. This limitation motivated our second goal: to learn a reward model that maximizes TAC directly. Specifically, we propose Soft-TAC, a differentiable approximation of TAC that can be used as a loss function to train reward models from human preference data. Validated in the racing simulator Gran Turismo 7, reward models trained using Soft-TAC successfully captured preference-specific objectives, resulting in policies with qualitatively more distinct behaviors than models trained with standard Cross-Entropy loss. This work demonstrates that TAC can serve as both a practical tool for guiding reward tuning and a reward learning objective in complex domains.
Event Tables for Efficient Experience Replay
Nov 01, 2022Abstract:Experience replay (ER) is a crucial component of many deep reinforcement learning (RL) systems. However, uniform sampling from an ER buffer can lead to slow convergence and unstable asymptotic behaviors. This paper introduces Stratified Sampling from Event Tables (SSET), which partitions an ER buffer into Event Tables, each capturing important subsequences of optimal behavior. We prove a theoretical advantage over the traditional monolithic buffer approach and combine SSET with an existing prioritized sampling strategy to further improve learning speed and stability. Empirical results in challenging MiniGrid domains, benchmark RL environments, and a high-fidelity car racing simulator demonstrate the advantages and versatility of SSET over existing ER buffer sampling approaches.
Reinforcement Learning for Optimization of COVID-19 Mitigation policies
Oct 20, 2020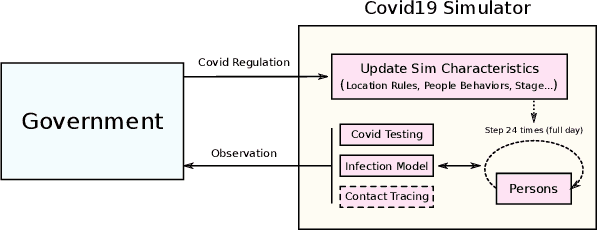
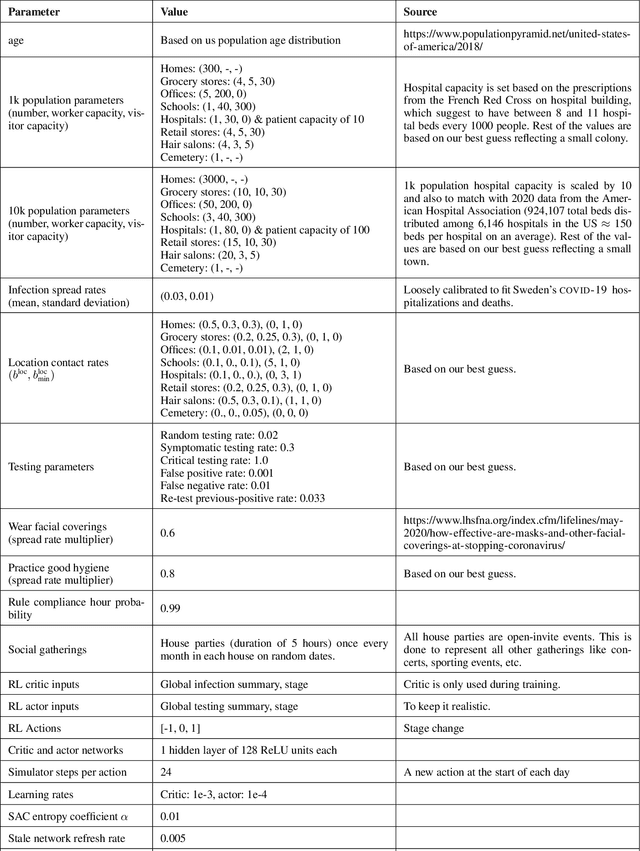
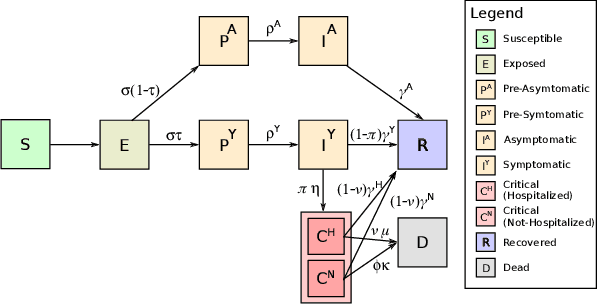
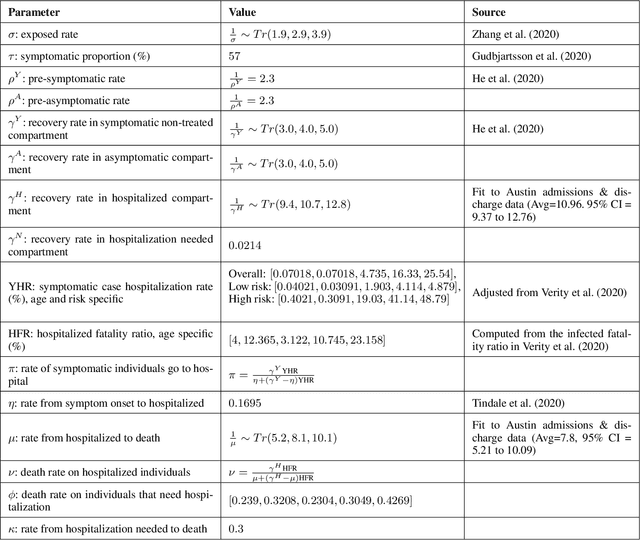
Abstract:The year 2020 has seen the COVID-19 virus lead to one of the worst global pandemics in history. As a result, governments around the world are faced with the challenge of protecting public health, while keeping the economy running to the greatest extent possible. Epidemiological models provide insight into the spread of these types of diseases and predict the effects of possible intervention policies. However, to date,the even the most data-driven intervention policies rely on heuristics. In this paper, we study how reinforcement learning (RL) can be used to optimize mitigation policies that minimize the economic impact without overwhelming the hospital capacity. Our main contributions are (1) a novel agent-based pandemic simulator which, unlike traditional models, is able to model fine-grained interactions among people at specific locations in a community; and (2) an RL-based methodology for optimizing fine-grained mitigation policies within this simulator. Our results validate both the overall simulator behavior and the learned policies under realistic conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge