Peter Mandl
Digital Guardians: Can GPT-4, Perspective API, and Moderation API reliably detect hate speech in reader comments of German online newspapers?
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:In recent years, toxic content and hate speech have become widespread phenomena on the internet. Moderators of online newspapers and forums are now required, partly due to legal regulations, to carefully review and, if necessary, delete reader comments. This is a labor-intensive process. Some providers of large language models already offer solutions for automated hate speech detection or the identification of toxic content. These include GPT-4o from OpenAI, Jigsaw's (Google) Perspective API, and OpenAI's Moderation API. Based on the selected German test dataset HOCON34k, which was specifically created for developing tools to detect hate speech in reader comments of online newspapers, these solutions are compared with each other and against the HOCON34k baseline. The test dataset contains 1,592 annotated text samples. For GPT-4o, three different promptings are used, employing a Zero-Shot, One-Shot, and Few-Shot approach. The results of the experiments demonstrate that GPT-4o outperforms both the Perspective API and the Moderation API, and exceeds the HOCON34k baseline by approximately 5 percentage points, as measured by a combined metric of MCC and F2-score.
EnergyPlus Room Simulator
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:Research towards energy optimization in buildings heavily relies on building-related data such as measured indoor climate factors. While data collection is a labor- and cost-intensive task, simulations are a cheap alternative to generate datasets of arbitrary sizes, particularly useful for data-intensive deep learning methods. In this paper, we present the tool EnergyPlus Room Simulator, which enables the simulation of indoor climate in a specific room of a building using the simulation software EnergyPlus. It allows to alter room models and simulate various factors such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 concentration. In contrast to manually working with EnergyPlus, this tool enhances the simulation process by offering a convenient interface, including a user-friendly graphical user interface (GUI) as well as a REST API. The tool is intended to support scientific, building-related tasks such as occupancy detection on a room level by facilitating fast access to simulation data that may, for instance, be used for pre-training machine learning models.
Innovations in Cover Song Detection: A Lyrics-Based Approach
Jun 06, 2024



Abstract:Cover songs are alternate versions of a song by a different artist. Long being a vital part of the music industry, cover songs significantly influence music culture and are commonly heard in public venues. The rise of online music platforms has further increased their prevalence, often as background music or video soundtracks. While current automatic identification methods serve adequately for original songs, they are less effective with cover songs, primarily because cover versions often significantly deviate from the original compositions. In this paper, we propose a novel method for cover song detection that utilizes the lyrics of a song. We introduce a new dataset for cover songs and their corresponding originals. The dataset contains 5078 cover songs and 2828 original songs. In contrast to other cover song datasets, it contains the annotated lyrics for the original song and the cover song. We evaluate our method on this dataset and compare it with multiple baseline approaches. Our results show that our method outperforms the baseline approaches.
Towards the Detection of Building Occupancy with Synthetic Environmental Data
Oct 08, 2020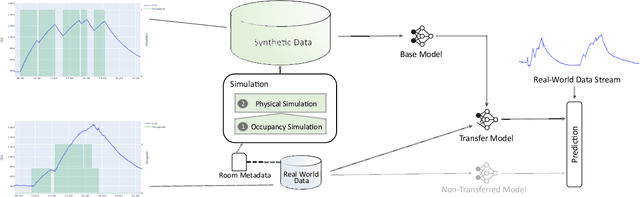
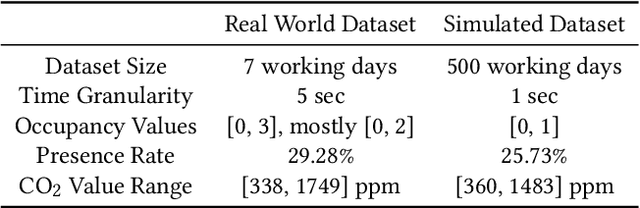
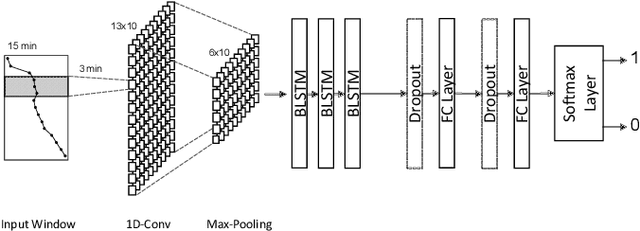
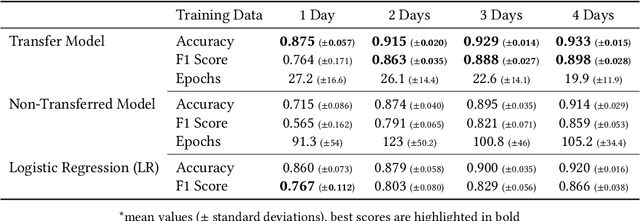
Abstract:Information about room-level occupancy is crucial to many building-related tasks, such as building automation or energy performance simulation. Current occupancy detection literature focuses on data-driven methods, but is mostly based on small case studies with few rooms. The necessity to collect room-specific data for each room of interest impedes applicability of machine learning, especially data-intensive deep learning approaches, in practice. To derive accurate predictions from less data, we suggest knowledge transfer from synthetic data. In this paper, we conduct an experiment with data from a CO$_2$ sensor in an office room, and additional synthetic data obtained from a simulation. Our contribution includes (a) a simulation method for CO$_2$ dynamics under randomized occupant behavior, (b) a proof of concept for knowledge transfer from simulated CO$_2$ data, and (c) an outline of future research implications. From our results, we can conclude that the transfer approach can effectively reduce the required amount of data for model training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge