Pere Garcia
Combining Multiple-Valued Logics in Modular Expert Systems
Mar 20, 2013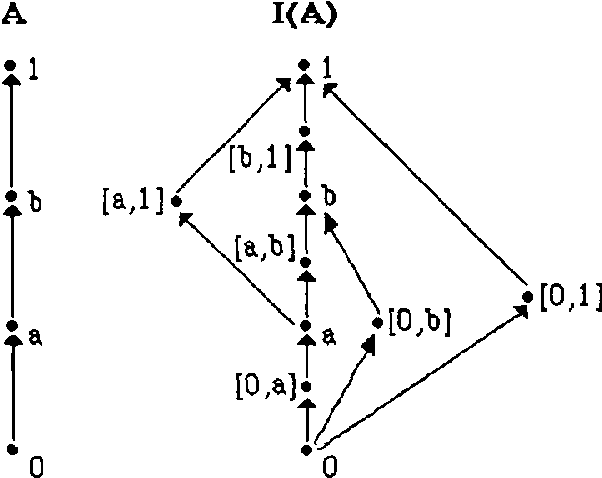
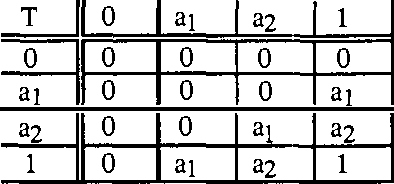
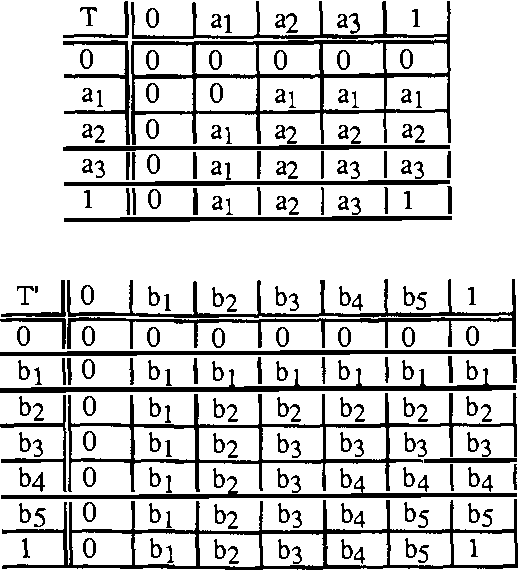
Abstract:The way experts manage uncertainty usually changes depending on the task they are performing. This fact has lead us to consider the problem of communicating modules (task implementations) in a large and structured knowledge based system when modules have different uncertainty calculi. In this paper, the analysis of the communication problem is made assuming that (i) each uncertainty calculus is an inference mechanism defining an entailment relation, and therefore the communication is considered to be inference-preserving, and (ii) we restrict ourselves to the case which the different uncertainty calculi are given by a class of truth functional Multiple-valued Logics.
On Modal Logics for Qualitative Possibility in a Fuzzy Setting
Feb 27, 2013Abstract:Within the possibilistic approach to uncertainty modeling, the paper presents a modal logical system to reason about qualitative (comparative) statements of the possibility (and necessity) of fuzzy propositions. We relate this qualitative modal logic to the many--valued analogues MVS5 and MVKD45 of the well known modal logics of knowledge and belief S5 and KD45 respectively. Completeness results are obtained for such logics and therefore, they extend previous existing results for qualitative possibilistic logics in the classical non-fuzzy setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge