Pei-Yu Huang
Management and Digital Innovation, University of London, Singapore
Approach to Predicting News -- A Precise Multi-LSTM Network With BERT
Apr 26, 2022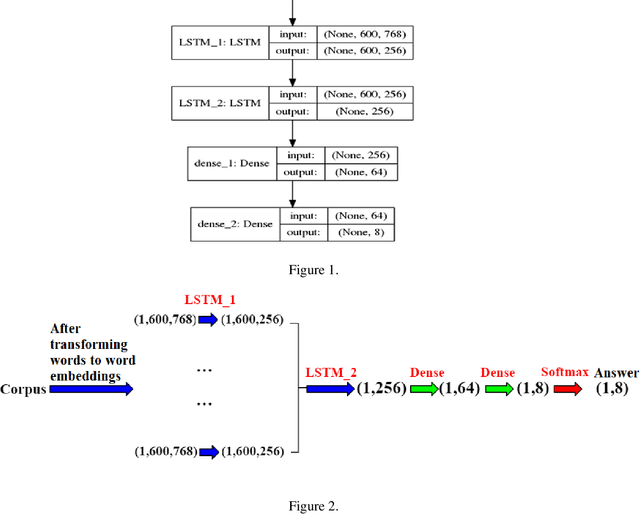
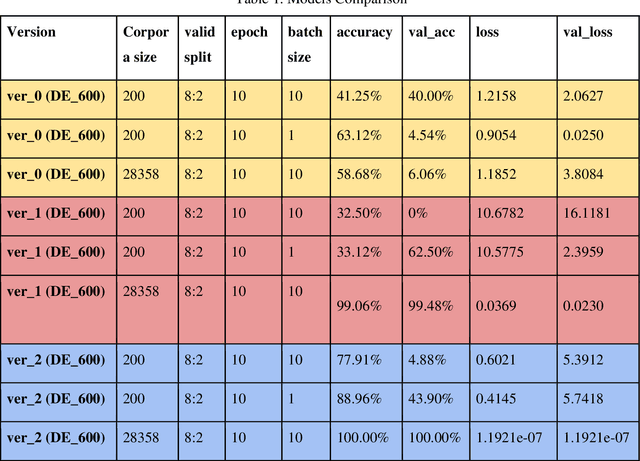
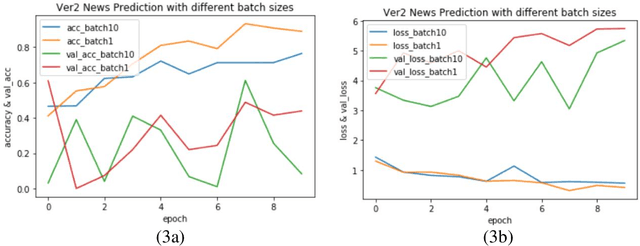
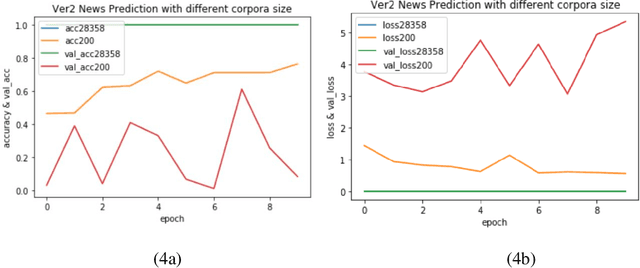
Abstract:Varieties of Democracy (V-Dem) is a new approach to conceptualizing and measuring democracy and politics. It has information for 200 countries and is one of the biggest databases for political science. According to the V-Dem annual democracy report 2019, Taiwan is one of the two countries that got disseminated false information from foreign governments the most. It also shows that the "made-up news" has caused a great deal of confusion in Taiwanese society and has serious impacts on global stability. Although there are several applications helping distinguish the false information, we found out that the pre-processing of categorizing the news is still done by human labor. However, human labor may cause mistakes and cannot work for a long time. The growing demands for automatic machines in the near decades show that while the machine can do as good as humans or even better, using machines can reduce humans' burden and cut down costs. Therefore, in this work, we build a predictive model to classify the category of news. The corpora we used contains 28358 news and 200 news scraped from the online newspaper Liberty Times Net (LTN) website and includes 8 categories: Technology, Entertainment, Fashion, Politics, Sports, International, Finance, and Health. At first, we use Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) for word embeddings which transform each Chinese character into a (1,768) vector. Then, we use a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) layer to transform word embeddings into sentence embeddings and add another LSTM layer to transform them into document embeddings. Each document embedding is an input for the final predicting model, which contains two Dense layers and one Activation layer. And each document embedding is transformed into 1 vector with 8 real numbers, then the highest one will correspond to the 8 news categories with up to 99% accuracy.
* Accepted by The 25th International Conference on Information Management & Practice (IMP) 2019
Headline Diagnosis: Manipulation of Content Farm Headlines
Apr 25, 2022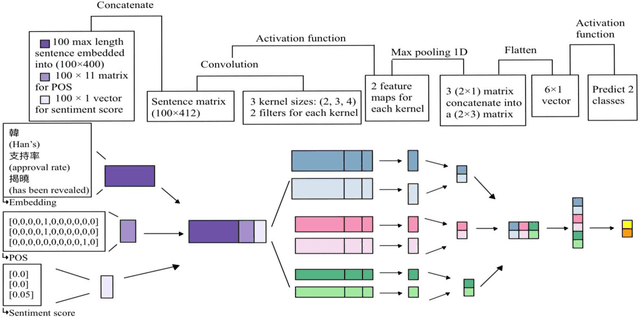
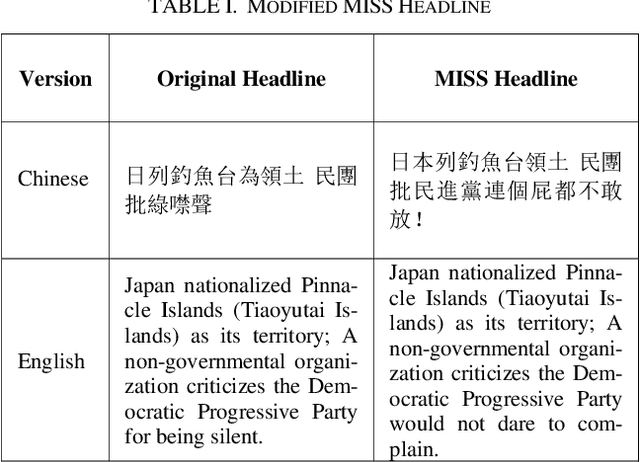
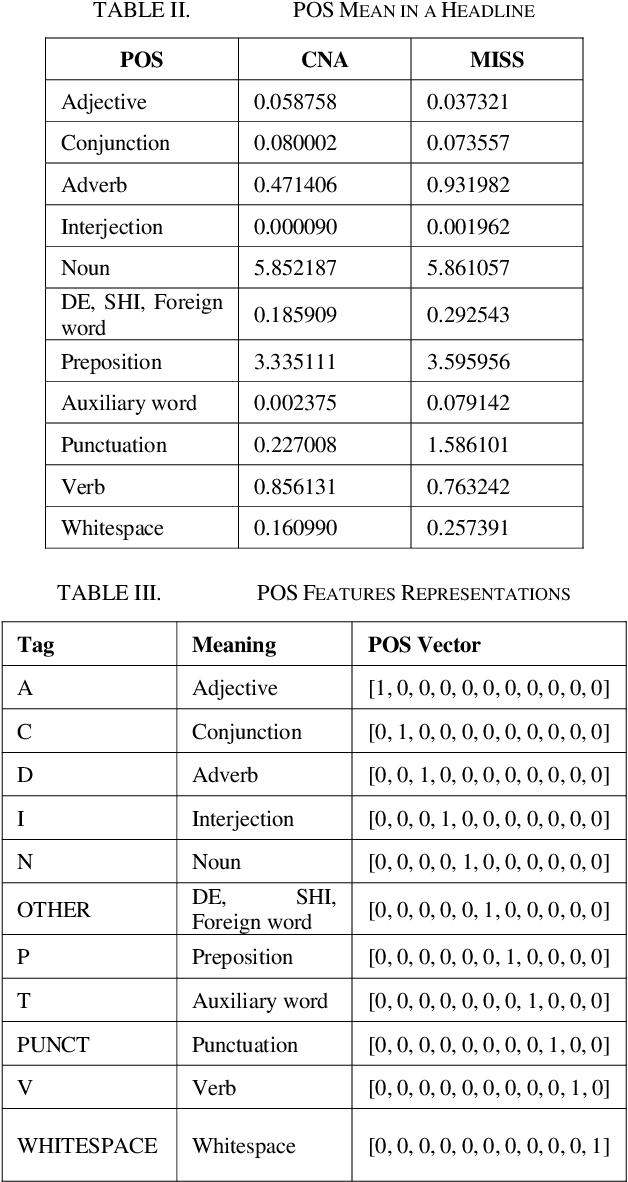
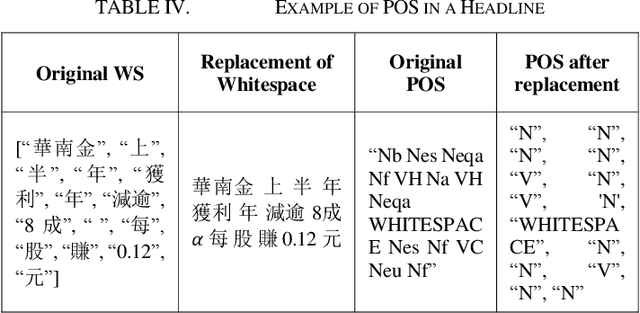
Abstract:As technology grows faster, the news spreads through social media. In order to attract more readers and acquire additional profit, some news agencies reproduce massive news in a more appealing manner. Therefore, it is essential to accurately predict whether a news article is from official news agencies. This work develops a headline classification based on Convoluted Neural Network to determine credibility of a news article. The model primarily focuses on investigating key factors from headlines. These factors include word segmentation, part-of-speech tags, and sentiment features. With integrating these features into the proposed classification model, the demonstrated evaluation achieves 93.99% for accuracy.
* Accepted by The 26th Taiwan Academic Network Conference (TANET) 2020
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge