Paul Marty
Experimental Pragmatics with Machines: Testing LLM Predictions for the Inferences of Plain and Embedded Disjunctions
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Human communication is based on a variety of inferences that we draw from sentences, often going beyond what is literally said. While there is wide agreement on the basic distinction between entailment, implicature, and presupposition, the status of many inferences remains controversial. In this paper, we focus on three inferences of plain and embedded disjunctions, and compare them with regular scalar implicatures. We investigate this comparison from the novel perspective of the predictions of state-of-the-art large language models, using the same experimental paradigms as recent studies investigating the same inferences with humans. The results of our best performing models mostly align with those of humans, both in the large differences we find between those inferences and implicatures, as well as in fine-grained distinctions among different aspects of those inferences.
Knowledge, Justification, and Reason-Based Belief
May 20, 2015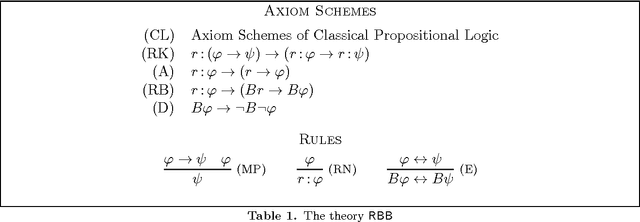
Abstract:Is knowledge definable as justified true belief ("JTB")? We argue that one can legitimately answer positively or negatively, depending on how the notion of justification is understood. To facilitate our argument, we introduce a simple propositional logic of reason-based belief. We show that this logic is sufficiently flexible to accommodate various useful features, including quantification over reasons. We use our framework to contrast two notions of JTB: one internalist, the other externalist. We argue that Gettier cases essentially challenge the internalist notion but not the externalist one. In particular, we may equate knowledge and JTB if the latter is grounded in what we call "adequate" reasons.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge