Patricia Roze
Are word boundaries useful for unsupervised language learning?
Oct 06, 2022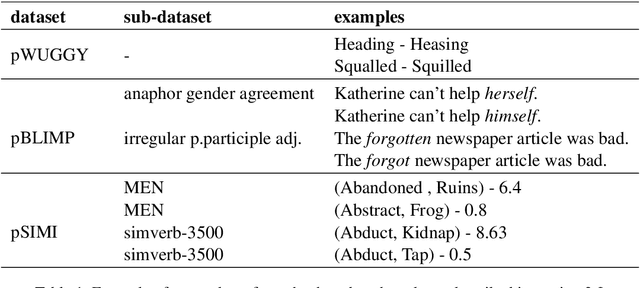

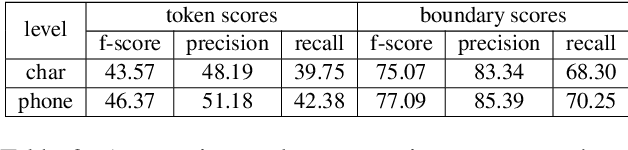
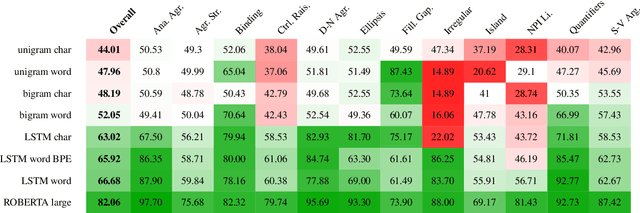
Abstract:Word or word-fragment based Language Models (LM) are typically preferred over character-based ones in many downstream applications. This may not be surprising as words seem more linguistically relevant units than characters. Words provide at least two kinds of relevant information: boundary information and meaningful units. However, word boundary information may be absent or unreliable in the case of speech input (word boundaries are not marked explicitly in the speech stream). Here, we systematically compare LSTMs as a function of the input unit (character, phoneme, word, word part), with or without gold boundary information. We probe linguistic knowledge in the networks at the lexical, syntactic and semantic levels using three speech-adapted black box NLP psycholinguistically-inpired benchmarks (pWUGGY, pBLIMP, pSIMI). We find that the absence of boundaries costs between 2\% and 28\% in relative performance depending on the task. We show that gold boundaries can be replaced by automatically found ones obtained with an unsupervised segmentation algorithm, and that even modest segmentation performance gives a gain in performance on two of the three tasks compared to basic character/phone based models without boundary information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge