Patricia Molina-Costa
A Machine Learning Approach for the Efficient Estimation of Ground-Level Air Temperature in Urban Areas
Nov 05, 2024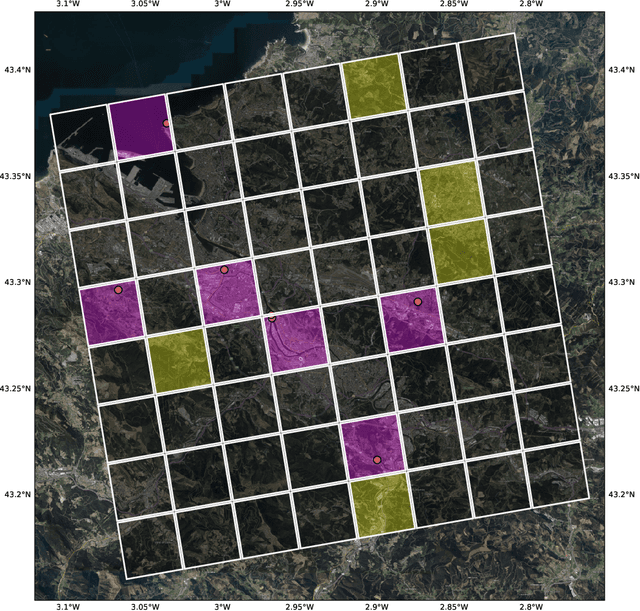

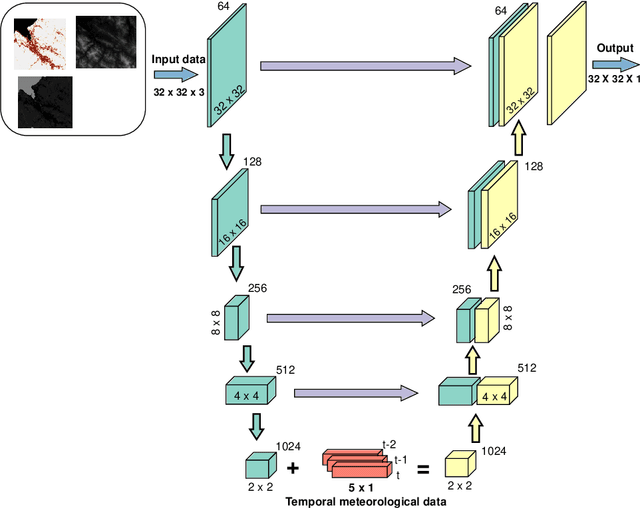

Abstract:The increasingly populated cities of the 21st Century face the challenge of being sustainable and resilient spaces for their inhabitants. However, climate change, among other problems, makes these objectives difficult to achieve. The Urban Heat Island (UHI) phenomenon that occurs in cities, increasing their thermal stress, is one of the stumbling blocks to achieve a more sustainable city. The ability to estimate temperatures with a high degree of accuracy allows for the identification of the highest priority areas in cities where urban improvements need to be made to reduce thermal discomfort. In this work we explore the usefulness of image-to-image deep neural networks (DNNs) for correlating spatial and meteorological variables of a urban area with street-level air temperature. The air temperature at street-level is estimated both spatially and temporally for a specific use case, and compared with existing, well-established numerical models. Based on the obtained results, deep neural networks are confirmed to be faster and less computationally expensive alternative for ground-level air temperature compared to numerical models.
Age-Friendly Route Planner: Calculating Comfortable Routes for Senior Citizens
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:The application of routing algorithms to real-world situations is a widely studied research topic. Despite this, routing algorithms and applications are usually developed for a general purpose, meaning that certain groups, such as ageing people, are often marginalized due to the broad approach of the designed algorithms. This situation may pose a problem in cities which are suffering a slow but progressive ageing of their populations. With this motivation in mind, this paper focuses on describing our implemented Age-Friendly Route Planner, whose goal is to improve the experience in the city for senior citizens. In order to measure the age-friendliness of a route, several variables have been deemed, such as the number of amenities along the route, the amount of comfortable elements found, or the avoidance of sloppy sections. In this paper, we describe one of the main features of the Age-Friendly Route Planner: the preference-based routes, and we also demonstrate how it can contribute to the creation of adapted friendly routes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge