Parul Khurana
Assessing Research Impact in Indian Conference Proceedings: Insights from Collaboration and Citations
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Conferences serve as a crucial avenue for scientific communication. However, the increase in conferences and the subsequent publication of proceedings have prompted inquiries regarding the research quality being showcased at such events. This investigation delves into the conference publications indexed by Springer's Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems Series. Among the 570 international conferences held worldwide in this series, 177 were exclusively hosted in India. These 177 conferences collectively published 11,066 papers as conference proceedings. All these publications, along with conference details, were sourced from the Scopus database. The study aims to evaluate the research impact of these conference proceedings and identify the primary contributors. The results reveal a downward trend in the average number of citations per year. The collective average citation for all publications is 1.01. Papers co-authored by Indian and international authors (5.6%) exhibit a higher average impact of 1.44, in contrast to those authored solely by Indian authors (84.9%), which have an average impact of 0.97. Notably, Indian-collaborated papers, among the largest contributors, predominantly originate from private colleges and universities. Only 19% of papers exhibit collaboration with institutes of different prestige, yet their impact is considerably higher as compared to collaboration with institutes of similar prestige. This study highlights the importance of improving research quality in academic forums.
Quantitative Analysis of IITs' Research Growth and SDG Contributions
Nov 23, 2024



Abstract:The Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) are vital to India's research ecosystem, advancing technology and engineering for industrial and societal benefits. This study reviews the research performance of top IITs-Bombay, Delhi, Madras, Kharagpur, and Kanpur based on Scopus-indexed publications (1952-2024). Research output has grown exponentially, supported by increased funding and collaborations. IIT-Kanpur excels in research impact, while IIT-Bombay and IIT-Madras are highly productive but show slightly lower per-paper impact. Internationally, IITs collaborate robustly with the USA, Germany, and the UK, alongside Asian nations like Japan and South Korea, with IIT-Madras leading inter-IIT partnerships. Research priorities align with SDG 3 (Health), SDG 7 (Clean Energy), and SDG 11 (Sustainable Cities). Despite strengths in fields like energy, fluid dynamics, and materials science, challenges persist, including limited collaboration with newer IITs and gaps in emerging fields. Strengthening specialization and partnerships is crucial for addressing global challenges and advancing sustainable development.
Emerging trends and collaboration patterns unveil the scientific production in blockchain technology: A bibliometric and network analysis from 2014-2020
Oct 05, 2021



Abstract:Significant attention in the financial industry has paved the way for blockchain technology to spread across other industries, resulting in a plethora of literature on the subject. This study approaches the subject through bibliometrics and network analysis of 6790 records extracted from the Web of Science from 2014-2020 based on blockchain. This study asserts (i) the impact of open access publication on the growth and visibility of literature, (ii) the collaboration patterns and impact of team size on collaboration, (iii) the ranking of countries based on their national and international collaboration, and (iv) the major themes in the literature through thematic analysis. Based on the significant momentum gained by the blockchain, the trend of open access publications has increased 1.5 times than no open access in 2020. This analysis articulates the numerous potentials of blockchain literature and its adoption by various countries and their authors. China and the USA are the top leaders in the field and applied blockchain more with smart contracts, supply chain, and internet of things. Also, results show that blockchain has attracted the attention of less than 1% of authors who have contributed to multiple works on the blockchain and authors also preferred to work in teams smaller in size.
Proof of Reference(PoR): A unified informetrics based consensus mechanism
Jul 01, 2021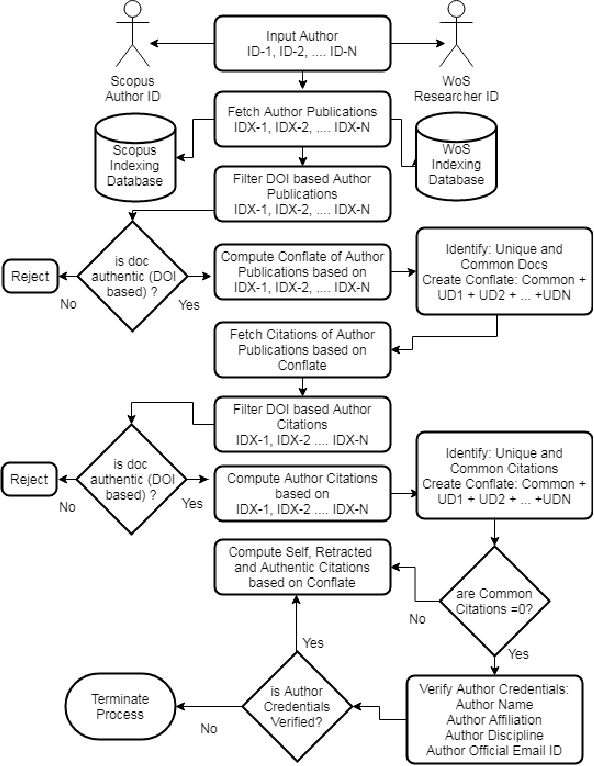
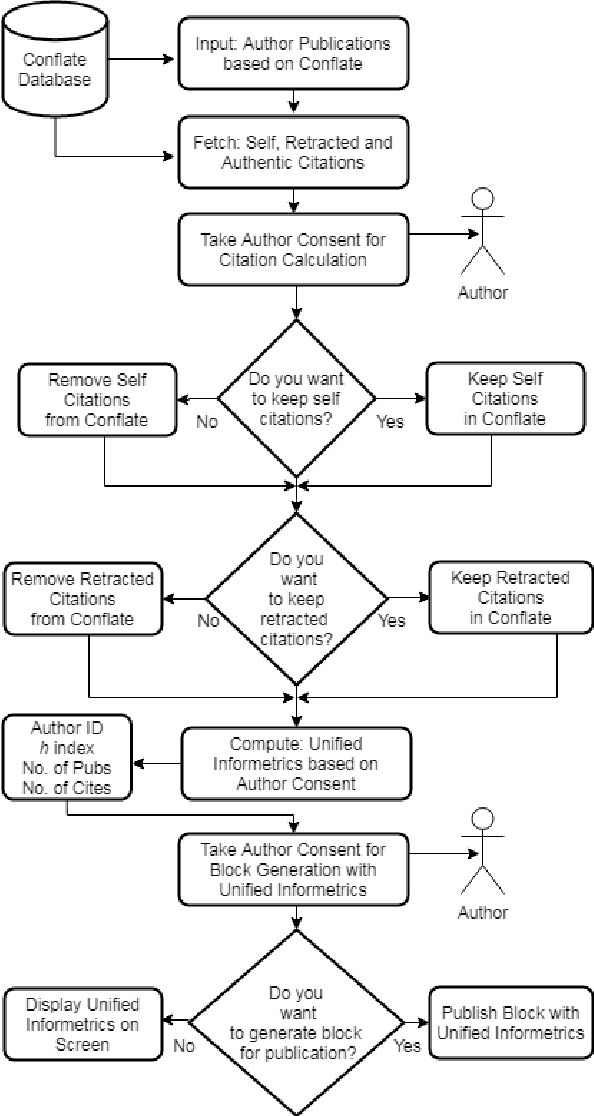

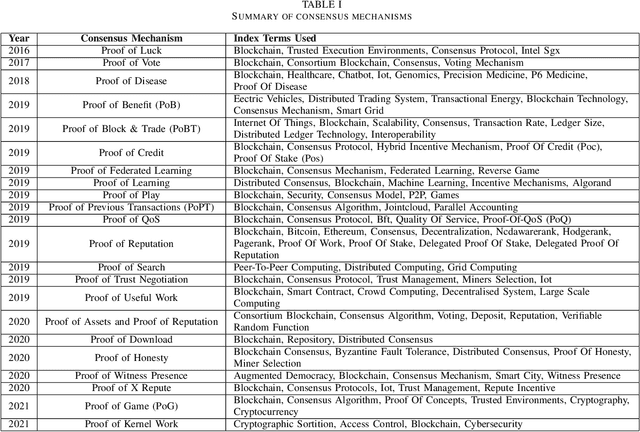
Abstract:Bibliometrics is useful to analyze the research impact for measuring the research quality. Different bibliographic databases like Scopus, Web of Science, Google Scholar etc. are accessed for evaluating the trend of publications and citations from time to time. Some of these databases are free and some are subscription based. Its always debatable that which bibliographic database is better and in what terms. To provide an optimal solution to availability of multiple bibliographic databases, we have implemented a single authentic database named as ``conflate'' which can be used for fetching publication and citation trend of an author. To further strengthen the generated database and to provide the transparent system to the stakeholders, a consensus mechanism ``proof of reference (PoR)'' is proposed. Due to three consent based checks implemented in PoR, we feel that it could be considered as a authentic and honest citation data source for the calculation of unified informetrics for an author.
A weighted unified informetrics based on Scopus and WoS
Jun 02, 2021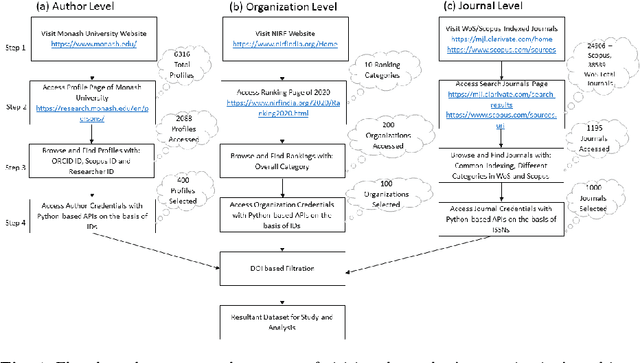
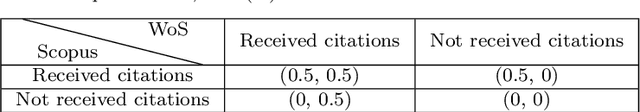
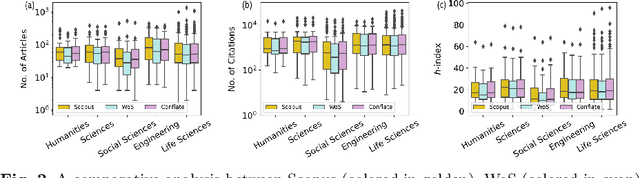
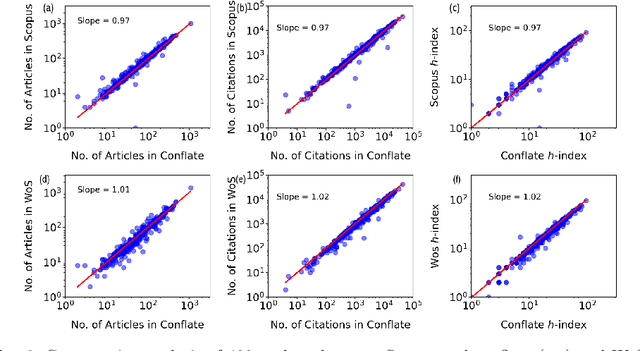
Abstract:Numerous indexing databases keep track of the number of publications, citations, etc. in order to maintain the progress of science and individual. However, the choice of journals and articles varies among these indexing databases, hence the number of citations and h-index varies. There is no common platform exists that can provide a single count for the number of publications, citations, h-index, etc. To overcome this limitation, we have proposed a weighted unified informetrics, named "conflate". The proposed system takes into account the input from multiple indexing databases and generates a single output. Here, we have used the data from Scopus and WoS to generate a conflate dataset. Further, a comparative analysis of conflate has been performed with Scopus and WoS at three levels: author, organization, and journal. Finally, a mapping is proposed between research publications and distributed ledger technology in order to provide a transparent and distributed view to its stakeholders.
Impact of $h$-index on authors ranking: An improvement to the h-index for lower-ranked author
May 18, 2021


Abstract:In academia, the research performance of a faculty is either evaluated by the number of publications or the number of citations. Most of the time h-index is widely used during the hiring process or the faculty performance evaluation. The calculation of the h-index is shown in various databases; however, there is no systematic evidence about the differences between them. Here we analyze the publication records of 385 authors from Monash University (Australia) to investigate (i) the impact of different databases like Scopus and WoS on the ranking of authors within a discipline, and (ii) to complement the $h$-index, named $h_c$, by adding the weight of the highest cited paper to the $h$-index of the authors. The results show the positive impact of $h_c$ on the lower-ranked authors in every discipline. Also, Scopus provides an overall better ranking than WoS; however, the ranking varies among Scopus and WoS for disciplines.
Impact of h-index on authors ranking: A comparative analysis of Scopus and WoS
Feb 13, 2021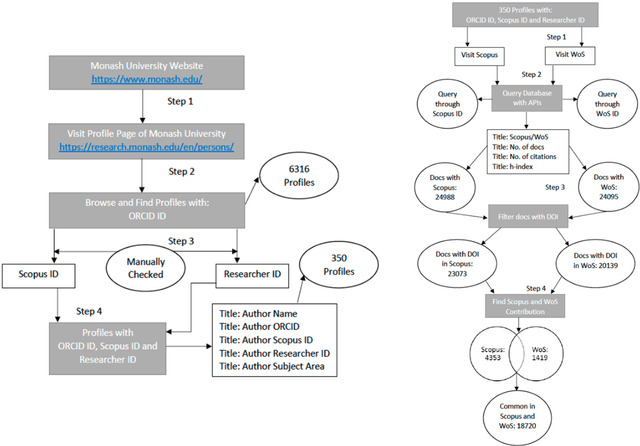
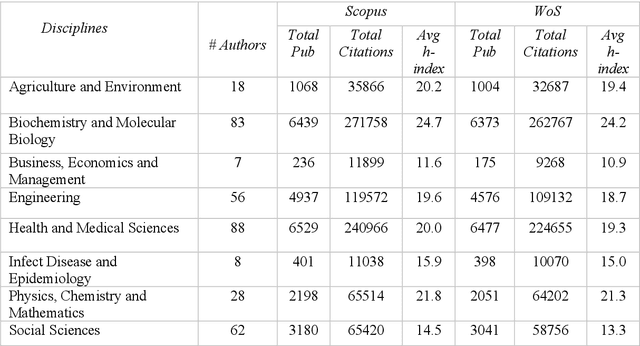

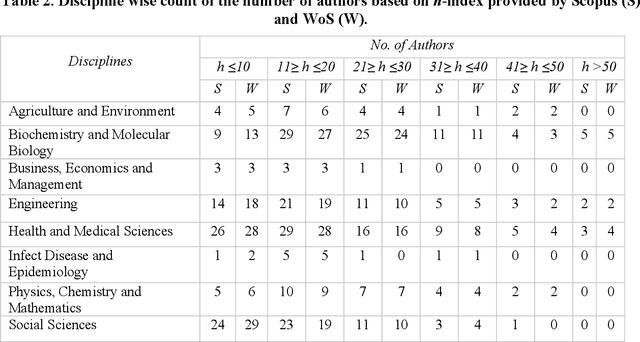
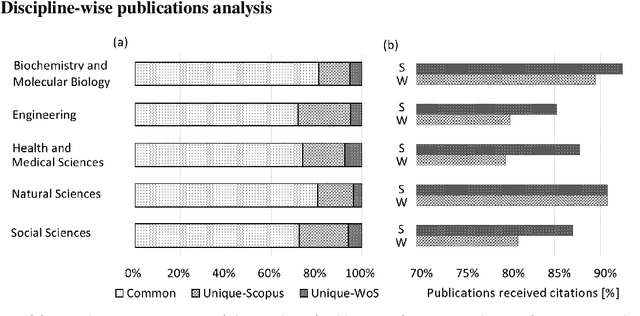
Abstract:In academia, the research performance of the faculty members is either evaluated by the number of publications or the number of citations. Most of the time h-index is widely used during the hiring process or the faculty performance evaluation. The calculation of the h-index is shown in various databases; however, there is no recent or systematic evidence about the differences between them. In this study, we compare the difference in the h-index compiled with Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) with the aim of analyzing the ranking of the authors within a university. We analyze the publication records of 350 authors from Monash University (Australia). We also investigate the discipline wise variation in the authors ranking. 31% of the author's profiles show no variation in the two datasets whereas 55% of the author's profiles show a higher count in Scopus and 9% in WoS. The maximum difference in h-index count among Scopus and WoS is 3. On average 12.4% of publications per author are unique in Scopus and 4.1% in WoS. 53.5% of publications are common in both Scopus and WoS. Despite larger unique publications in Scopus, there is no difference shown in the Spearman correlation coefficient between WoS and Scopus citation counts and h-index.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge