Parag Narkhede
Incremental learning of LSTM framework for sensor fusion in attitude estimation
Aug 04, 2021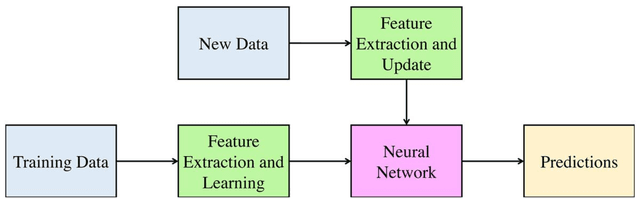
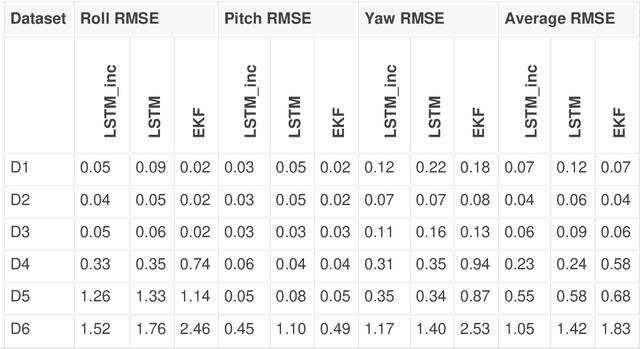
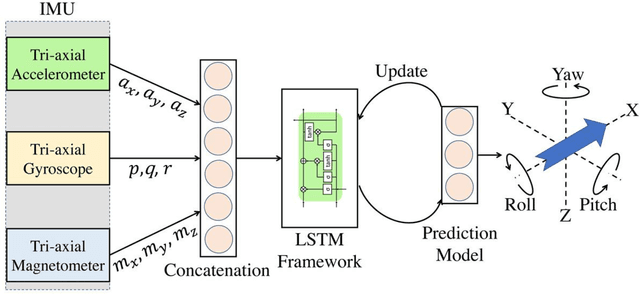
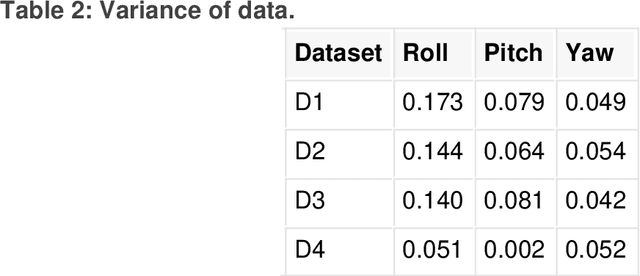
Abstract:This paper presents a novel method for attitude estimation of an object in 3D space by incremental learning of the Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) network. Gyroscope, accelerometer, and magnetometer are few widely used sensors in attitude estimation applications. Traditionally, multi-sensor fusion methods such as the Extended Kalman Filter and Complementary Filter are employed to fuse the measurements from these sensors. However, these methods exhibit limitations in accounting for the uncertainty, unpredictability, and dynamic nature of the motion in real-world situations. In this paper, the inertial sensors data are fed to the LSTM network which are then updated incrementally to incorporate the dynamic changes in motion occurring in the run time. The robustness and efficiency of the proposed framework is demonstrated on the dataset collected from a commercially available inertial measurement unit. The proposed framework offers a significant improvement in the results compared to the traditional method, even in the case of a highly dynamic environment. The LSTM framework-based attitude estimation approach can be deployed on a standard AI-supported processing module for real-time applications.
Gas Detection and Identification Using Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Based Sensor Fusion
Jun 11, 2021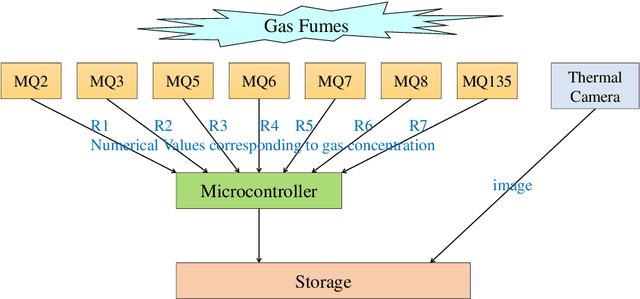
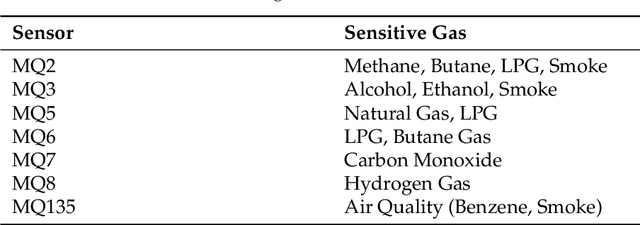
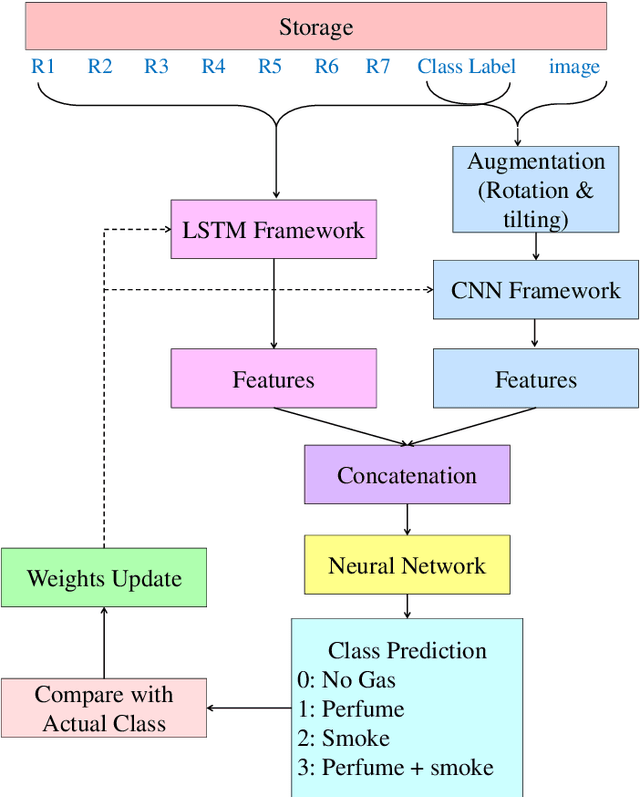
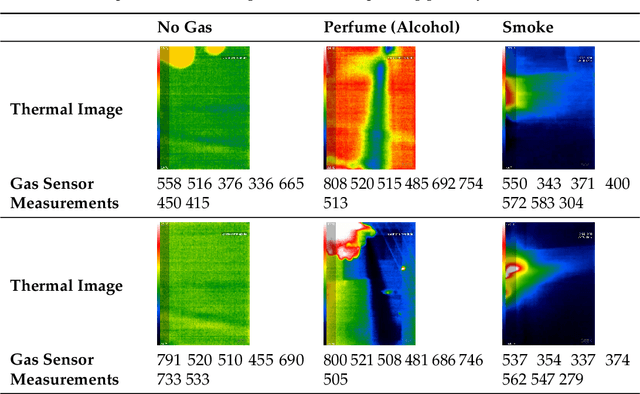
Abstract:With the rapid industrialization and technological advancements, innovative engineering technologies which are cost effective, faster and easier to implement are essential. One such area of concern is the rising number of accidents happening due to gas leaks at coal mines, chemical industries, home appliances etc. In this paper we propose a novel approach to detect and identify the gaseous emissions using the multimodal AI fusion techniques. Most of the gases and their fumes are colorless, odorless, and tasteless, thereby challenging our normal human senses. Sensing based on a single sensor may not be accurate, and sensor fusion is essential for robust and reliable detection in several real-world applications. We manually collected 6400 gas samples (1600 samples per class for four classes) using two specific sensors: the 7-semiconductor gas sensors array, and a thermal camera. The early fusion method of multimodal AI, is applied The network architecture consists of a feature extraction module for individual modality, which is then fused using a merged layer followed by a dense layer, which provides a single output for identifying the gas. We obtained the testing accuracy of 96% (for fused model) as opposed to individual model accuracies of 82% (based on Gas Sensor data using LSTM) and 93% (based on thermal images data using CNN model). Results demonstrate that the fusion of multiple sensors and modalities outperforms the outcome of a single sensor.
* 14 Pages, 9 Figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge