Panos Patros
Down the Rabbit Hole: Detecting Online Extremism, Radicalisation, and Politicised Hate Speech
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:Social media is a modern person's digital voice to project and engage with new ideas and mobilise communities $\unicode{x2013}$ a power shared with extremists. Given the societal risks of unvetted content-moderating algorithms for Extremism, Radicalisation, and Hate speech (ERH) detection, responsible software engineering must understand the who, what, when, where, and why such models are necessary to protect user safety and free expression. Hence, we propose and examine the unique research field of ERH context mining to unify disjoint studies. Specifically, we evaluate the start-to-finish design process from socio-technical definition-building and dataset collection strategies to technical algorithm design and performance. Our 2015-2021 51-study Systematic Literature Review (SLR) provides the first cross-examination of textual, network, and visual approaches to detecting extremist affiliation, hateful content, and radicalisation towards groups and movements. We identify consensus-driven ERH definitions and propose solutions to existing ideological and geographic biases, particularly due to the lack of research in Oceania/Australasia. Our hybridised investigation on Natural Language Processing, Community Detection, and visual-text models demonstrates the dominating performance of textual transformer-based algorithms. We conclude with vital recommendations for ERH context mining researchers and propose an uptake roadmap with guidelines for researchers, industries, and governments to enable a safer cyberspace.
Embedding Java Classes with code2vec: Improvements from Variable Obfuscation
Apr 06, 2020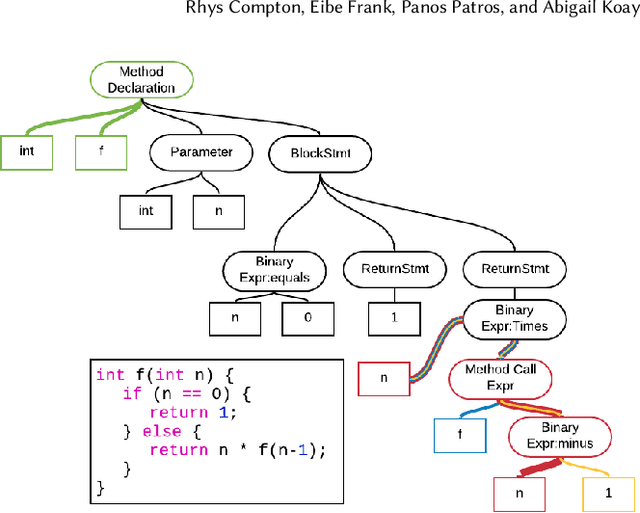

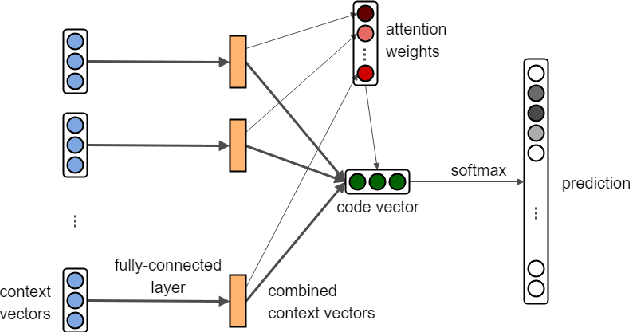
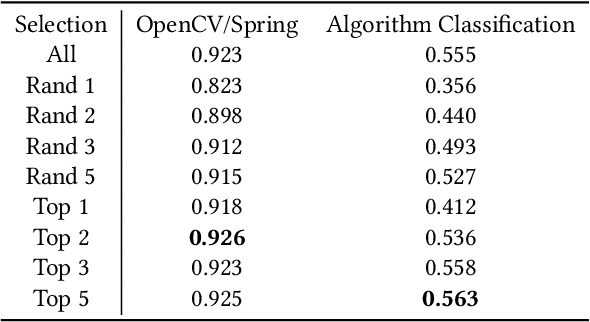
Abstract:Automatic source code analysis in key areas of software engineering, such as code security, can benefit from Machine Learning (ML). However, many standard ML approaches require a numeric representation of data and cannot be applied directly to source code. Thus, to enable ML, we need to embed source code into numeric feature vectors while maintaining the semantics of the code as much as possible. code2vec is a recently released embedding approach that uses the proxy task of method name prediction to map Java methods to feature vectors. However, experimentation with code2vec shows that it learns to rely on variable names for prediction, causing it to be easily fooled by typos or adversarial attacks. Moreover, it is only able to embed individual Java methods and cannot embed an entire collection of methods such as those present in a typical Java class, making it difficult to perform predictions at the class level (e.g., for the identification of malicious Java classes). Both shortcomings are addressed in the research presented in this paper. We investigate the effect of obfuscating variable names during the training of a code2vec model to force it to rely on the structure of the code rather than specific names and consider a simple approach to creating class-level embeddings by aggregating sets of method embeddings. Our results, obtained on a challenging new collection of source-code classification problems, indicate that obfuscating variable names produces an embedding model that is both impervious to variable naming and more accurately reflects code semantics. The datasets, models, and code are shared for further ML research on source code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge