Get our free extension to see links to code for papers anywhere online!Free add-on: code for papers everywhere!Free add-on: See code for papers anywhere!
Pankayraj Pathmanathan
Non-contact Infant Sleep Apnea Detection
Oct 10, 2019Authors:Gihan Jayatilaka, Harshana Weligampola, Suren Sritharan, Pankayraj Pathmanathan, Roshan Ragel, Isuru Nawinne
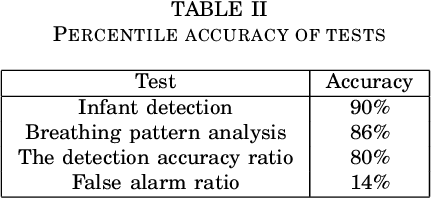
Figures and Tables: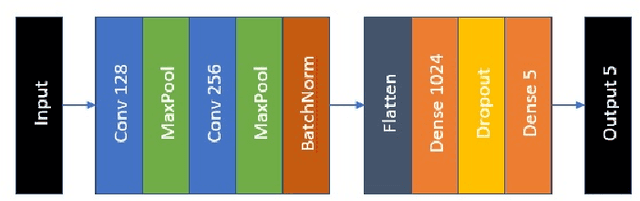



Abstract:Sleep apnea is a breathing disorder where a person repeatedly stops breathing in sleep. Early detection is crucial for infants because it might bring long term adversities. The existing accurate detection mechanism (pulse oximetry) is a skin contact measurement. The existing non-contact mechanisms (acoustics, video processing) are not accurate enough. This paper presents a novel algorithm for the detection of sleep apnea with video processing. The solution is non-contact, accurate and lightweight enough to run on a single board computer. The paper discusses the accuracy of the algorithm on real data, advantages of the new algorithm, its limitations and suggests future improvements.
* Gihan Jayatilaka, Harshana Weligampola and Suren Sritharan are
equally contributing authors
Via
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge