Pankaj Yadav
Kolmogorov Arnold Networks (KANs) for Imbalanced Data -- An Empirical Perspective
Jul 18, 2025Abstract:Kolmogorov Arnold Networks (KANs) are recent architectural advancement in neural computation that offer a mathematically grounded alternative to standard neural networks. This study presents an empirical evaluation of KANs in context of class imbalanced classification, using ten benchmark datasets. We observe that KANs can inherently perform well on raw imbalanced data more effectively than Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLPs) without any resampling strategy. However, conventional imbalance strategies fundamentally conflict with KANs mathematical structure as resampling and focal loss implementations significantly degrade KANs performance, while marginally benefiting MLPs. Crucially, KANs suffer from prohibitive computational costs without proportional performance gains. Statistical validation confirms that MLPs with imbalance techniques achieve equivalence with KANs (|d| < 0.08 across metrics) at minimal resource costs. These findings reveal that KANs represent a specialized solution for raw imbalanced data where resources permit. But their severe performance-resource tradeoffs and incompatibility with standard resampling techniques currently limits practical deployment. We identify critical research priorities as developing KAN specific architectural modifications for imbalance learning, optimizing computational efficiency, and theoretical reconciling their conflict with data augmentation. This work establishes foundational insights for next generation KAN architectures in imbalanced classification scenarios.
Rebalancing the Scales: A Systematic Mapping Study of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in Addressing Data Imbalance
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Machine learning algorithms are used in diverse domains, many of which face significant challenges due to data imbalance. Studies have explored various approaches to address the issue, like data preprocessing, cost-sensitive learning, and ensemble methods. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) showed immense potential as a data preprocessing technique that generates good quality synthetic data. This study employs a systematic mapping methodology to analyze 3041 papers on GAN-based sampling techniques for imbalanced data sourced from four digital libraries. A filtering process identified 100 key studies spanning domains such as healthcare, finance, and cybersecurity. Through comprehensive quantitative analysis, this research introduces three categorization mappings as application domains, GAN techniques, and GAN variants used to handle the imbalanced nature of the data. GAN-based over-sampling emerges as an effective preprocessing method. Advanced architectures and tailored frameworks helped GANs to improve further in the case of data imbalance. GAN variants like vanilla GAN, CTGAN, and CGAN show great adaptability in structured imbalanced data cases. Interest in GANs for imbalanced data has grown tremendously, touching a peak in recent years, with journals and conferences playing crucial roles in transmitting foundational theories and practical applications. While with these advances, none of the reviewed studies explicitly explore hybridized GAN frameworks with diffusion models or reinforcement learning techniques. This gap leads to a future research idea develop innovative approaches for effectively handling data imbalance.
Enhancing Synthetic Oversampling for Imbalanced Datasets Using Proxima-Orion Neighbors and q-Gaussian Weighting Technique
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:In this article, we propose a novel oversampling algorithm to increase the number of instances of minority class in an imbalanced dataset. We select two instances, Proxima and Orion, from the set of all minority class instances, based on a combination of relative distance weights and density estimation of majority class instances. Furthermore, the q-Gaussian distribution is used as a weighting mechanism to produce new synthetic instances to improve the representation and diversity. We conduct a comprehensive experiment on 42 datasets extracted from KEEL software and eight datasets from the UCI ML repository to evaluate the usefulness of the proposed (PO-QG) algorithm. Wilcoxon signed-rank test is used to compare the proposed algorithm with five other existing algorithms. The test results show that the proposed technique improves the overall classification performance. We also demonstrate the PO-QG algorithm to a dataset of Indian patients with sarcopenia.
Action-based Early Autism Diagnosis Using Contrastive Feature Learning
Sep 12, 2022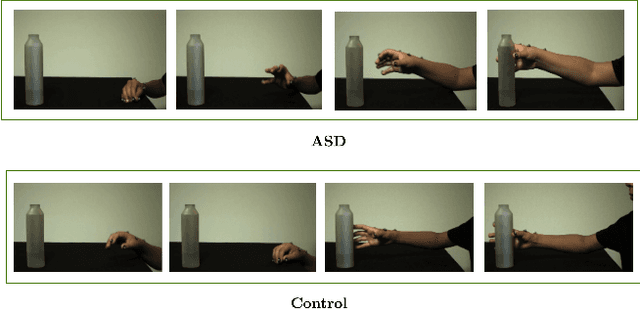
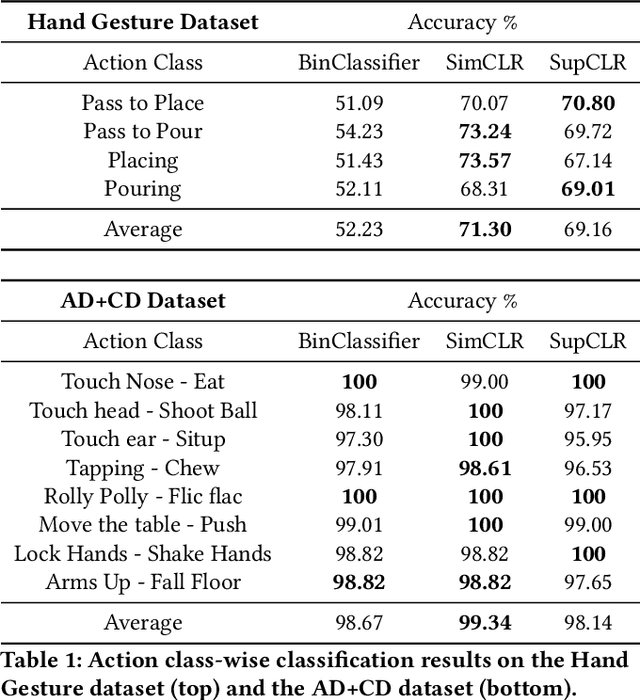

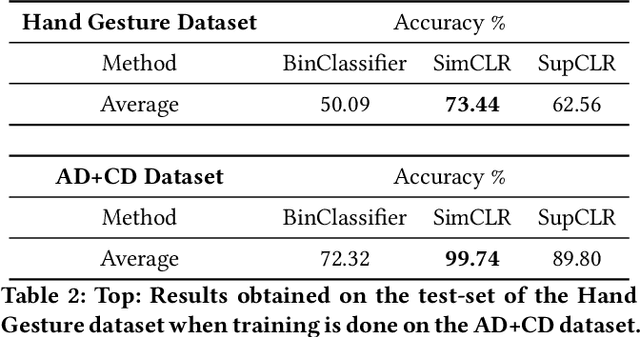
Abstract:Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (or ASD), is a neurological disorder. Its main symptoms include difficulty in (verbal and/or non-verbal) communication, and rigid/repetitive behavior. These symptoms are often indistinguishable from a normal (control) individual, due to which this disorder remains undiagnosed in early childhood leading to delayed treatment. Since the learning curve is steep during the initial age, an early diagnosis of autism could allow to take adequate interventions at the right time, which might positively affect the growth of an autistic child. Further, the traditional methods of autism diagnosis require multiple visits to a specialized psychiatrist, however this process can be time-consuming. In this paper, we present a learning based approach to automate autism diagnosis using simple and small action video clips of subjects. This task is particularly challenging because the amount of annotated data available is small, and the variations among samples from the two categories (ASD and control) are generally indistinguishable. This is also evident from poor performance of a binary classifier learned using the cross-entropy loss on top of a baseline encoder. To address this, we adopt contrastive feature learning in both self supervised and supervised learning frameworks, and show that these can lead to a significant increase in the prediction accuracy of a binary classifier on this task. We further validate this by conducting thorough experimental analyses under different set-ups on two publicly available datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge