Panagiotis Stalidis
Examining Deep Learning Architectures for Crime Classification and Prediction
Dec 03, 2018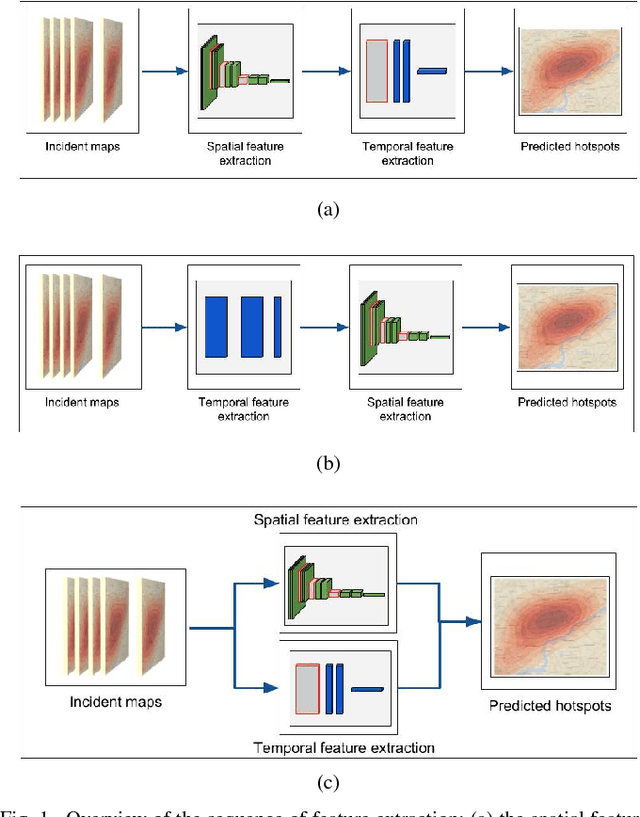
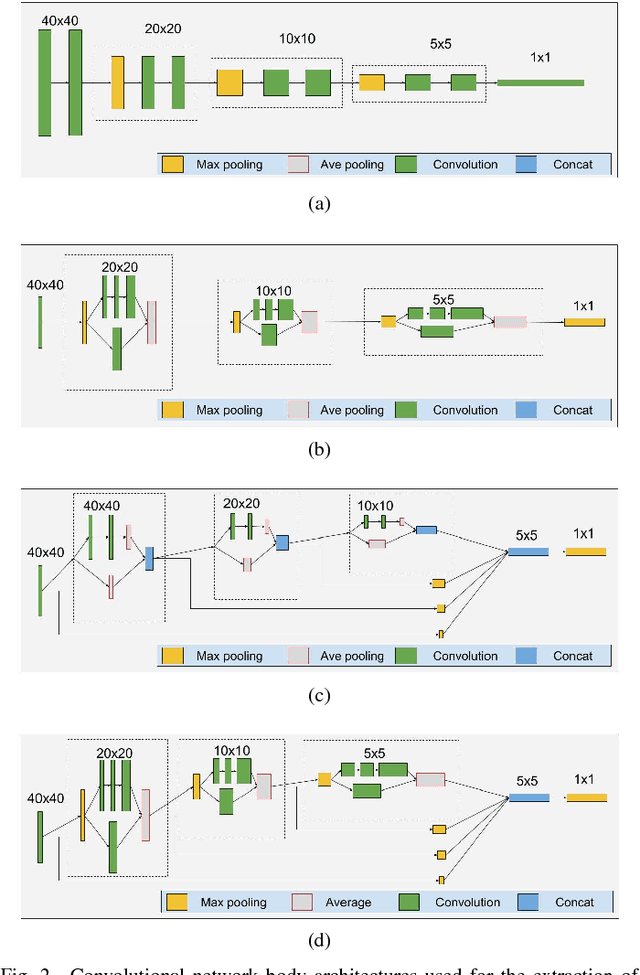
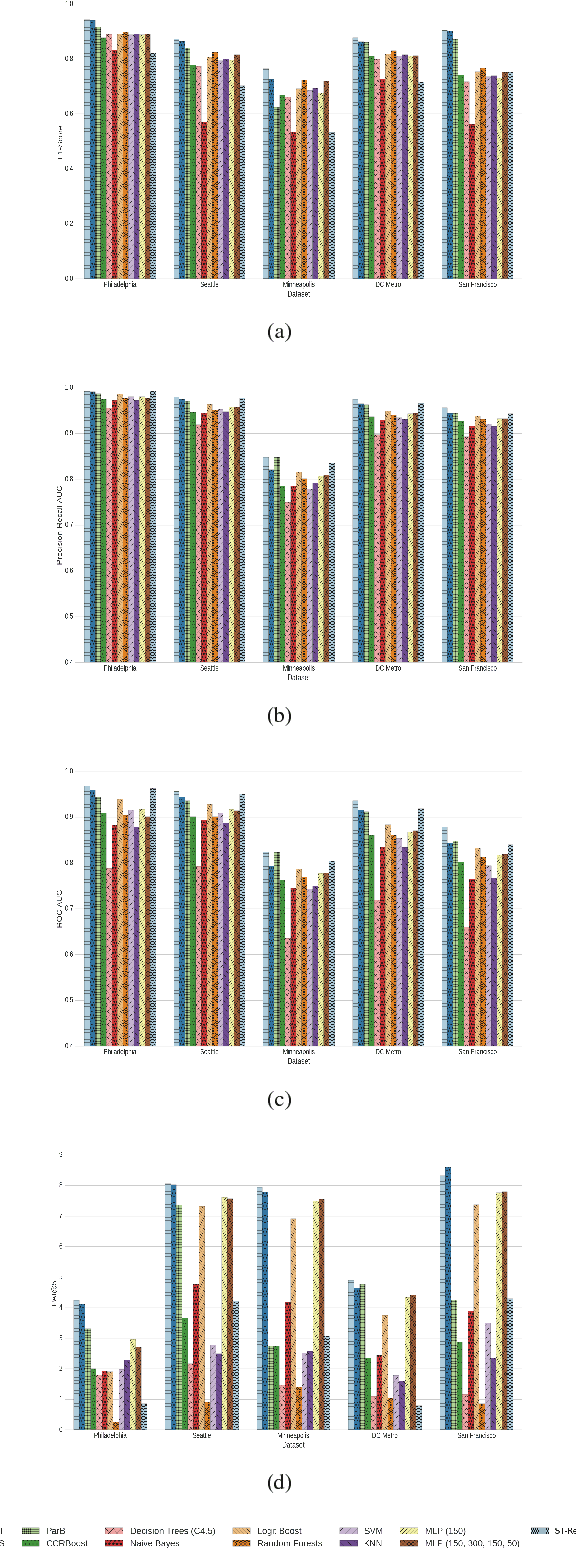
Abstract:In this paper, a detailed study on crime classification and prediction using deep learning architectures is presented. We examine the effectiveness of deep learning algorithms on this domain and provide recommendations for designing and training deep learning systems for predicting crime areas, using open data from police reports. Having as training data time-series of crime types per location, a comparative study of 10 state-of-the-art methods against 3 different deep learning configurations is conducted. In our experiments with five publicly available datasets, we demonstrate that the deep learning-based methods consistently outperform the existing best-performing methods. Moreover, we evaluate the effectiveness of different parameters in the deep learning architectures and give insights for configuring them in order to achieve improved performance in crime classification and finally crime prediction.
Machine Learning Sentiment Prediction based on Hybrid Document Representation
Nov 29, 2015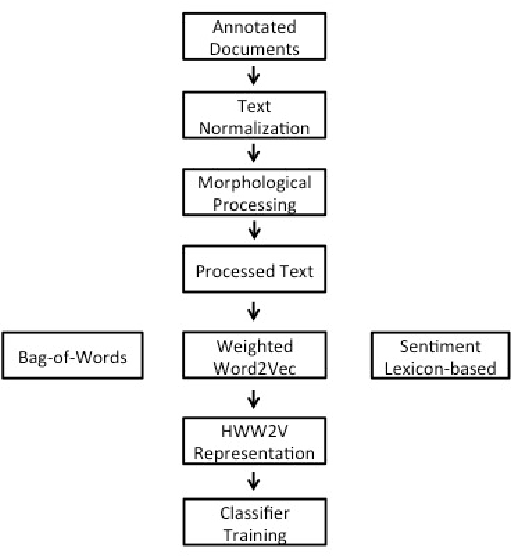
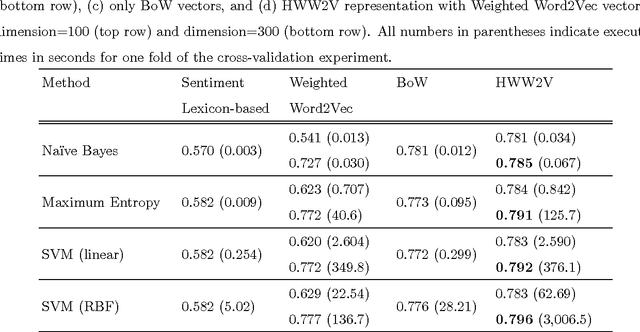
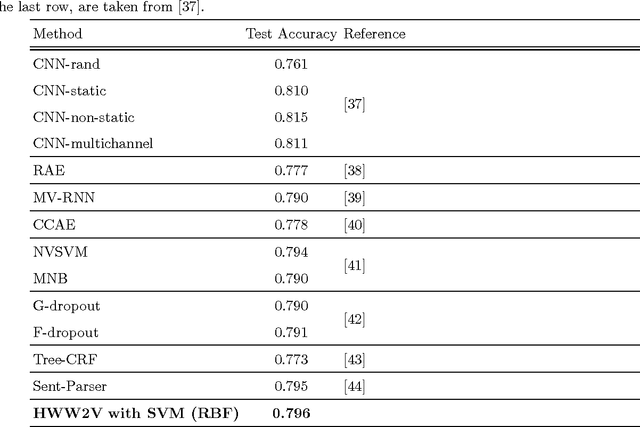
Abstract:Automated sentiment analysis and opinion mining is a complex process concerning the extraction of useful subjective information from text. The explosion of user generated content on the Web, especially the fact that millions of users, on a daily basis, express their opinions on products and services to blogs, wikis, social networks, message boards, etc., render the reliable, automated export of sentiments and opinions from unstructured text crucial for several commercial applications. In this paper, we present a novel hybrid vectorization approach for textual resources that combines a weighted variant of the popular Word2Vec representation (based on Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency) representation and with a Bag- of-Words representation and a vector of lexicon-based sentiment values. The proposed text representation approach is assessed through the application of several machine learning classification algorithms on a dataset that is used extensively in literature for sentiment detection. The classification accuracy derived through the proposed hybrid vectorization approach is higher than when its individual components are used for text represenation, and comparable with state-of-the-art sentiment detection methodologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge